N E W S A N D ...
... for understanding basic biology and human genetics. Epistasis is an old idea The idea that the effects of a given gene on a trait can be dependent on one or more other genes has been around for at least 100 years. William Bateson4 used the term ‘epistasis’ to describe distortions of mendelian segreg ...
... for understanding basic biology and human genetics. Epistasis is an old idea The idea that the effects of a given gene on a trait can be dependent on one or more other genes has been around for at least 100 years. William Bateson4 used the term ‘epistasis’ to describe distortions of mendelian segreg ...
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of exon 2 of the
... genetic variation, demonstrated in the Lowland line for all marker systems, is caused by a severe population bottleneck with only five (initially seven) founders of this line and an extremely large genetic impact of only two founders in the present population, which is estimated to range from 60 to ...
... genetic variation, demonstrated in the Lowland line for all marker systems, is caused by a severe population bottleneck with only five (initially seven) founders of this line and an extremely large genetic impact of only two founders in the present population, which is estimated to range from 60 to ...
Genetic evaluation in the honey bee considering queen and worker
... method currently available for evaluating breeding values in other animals, the Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (BLUP)-Animal Model, has been adapted to the peculiarities of honey bee genetics and reproduction. This method considers maternal (queen) effects using all available records of relatives an ...
... method currently available for evaluating breeding values in other animals, the Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (BLUP)-Animal Model, has been adapted to the peculiarities of honey bee genetics and reproduction. This method considers maternal (queen) effects using all available records of relatives an ...
Genetic mapping of Theobroma cacao (Malvaceae - Funpec-RP
... the construction of linkage maps for most plant species, even perennials, such as forest and fruit trees (Carneiro and Vieira, 2002). In the case of T. cacao, genetic mapping has been done with molecular markers, comparing segregating populations (Pugh et al., 2004; Faleiro et al., 2006). Compatibil ...
... the construction of linkage maps for most plant species, even perennials, such as forest and fruit trees (Carneiro and Vieira, 2002). In the case of T. cacao, genetic mapping has been done with molecular markers, comparing segregating populations (Pugh et al., 2004; Faleiro et al., 2006). Compatibil ...
LAB 9 – Principles of Genetic Inheritance
... chromosomes (X and Y) as illustrated in the human male karyotype shown below (notice the X and Y sex chromosomes): Notice one more thing about this human karyotype: there are two of each autosome as well as two sex chromosomes. This is because human beings are diploid, which means having two of each ...
... chromosomes (X and Y) as illustrated in the human male karyotype shown below (notice the X and Y sex chromosomes): Notice one more thing about this human karyotype: there are two of each autosome as well as two sex chromosomes. This is because human beings are diploid, which means having two of each ...
Classical Genetics
... b. WT (wild-type) allele – not just only normal version, just most common (most common sequence at certain position in allele of gene) c. Mutant - anything that differs from WT (usually mutant refers to deleterious change) d. Read slide e. This is the basis for linkage analysis – determine if certai ...
... b. WT (wild-type) allele – not just only normal version, just most common (most common sequence at certain position in allele of gene) c. Mutant - anything that differs from WT (usually mutant refers to deleterious change) d. Read slide e. This is the basis for linkage analysis – determine if certai ...
6.1-BIO-GEN-gentics.punnetsquares
... Let’s look at the trait of rolling your tongue: 1. First assign the trait a letter: Let’s choose “r”. 2. Then assign alleles: • Tongue rollers = R (dominant) • Non-tongue rollers = r (recessive) If your genes are RR or Rr you can roll your tongue If your genes are rr you cannot roll your tongue. ...
... Let’s look at the trait of rolling your tongue: 1. First assign the trait a letter: Let’s choose “r”. 2. Then assign alleles: • Tongue rollers = R (dominant) • Non-tongue rollers = r (recessive) If your genes are RR or Rr you can roll your tongue If your genes are rr you cannot roll your tongue. ...
The Binary Genetic Algorithm
... leads to the example problem of finding the highest point in Rocky Mountain National Park. A three-dimensional plot of a portion of the park (our search space) is shown in Figure 2.3, and a crude topographical map (128 ¥ 128 points) with some of the highlights is shown in Figure 2.4. Locating the to ...
... leads to the example problem of finding the highest point in Rocky Mountain National Park. A three-dimensional plot of a portion of the park (our search space) is shown in Figure 2.3, and a crude topographical map (128 ¥ 128 points) with some of the highlights is shown in Figure 2.4. Locating the to ...
Implications of Genetic Discrimination: Who Should Know What?
... individualized, effective and efficient medical treatment. A patient’s genetic information provides his doctor a more complete background of his condition. With this knowledge, the doctor is able to prescribe more appropriate, more effective treatment, including medications. With further progress in ...
... individualized, effective and efficient medical treatment. A patient’s genetic information provides his doctor a more complete background of his condition. With this knowledge, the doctor is able to prescribe more appropriate, more effective treatment, including medications. With further progress in ...
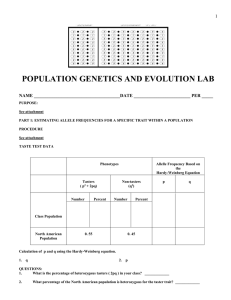
POPULATION GENETICS AND EVOLUTION LAB
... In certain African countries, 4 percent of the newborn babies have sickle-cell anemia, which is a recessive trait. Out of a random population of 1000 newborn babiew, how many would you expect for each of the three possible genotypes? ...
... In certain African countries, 4 percent of the newborn babies have sickle-cell anemia, which is a recessive trait. Out of a random population of 1000 newborn babiew, how many would you expect for each of the three possible genotypes? ...
CHAPTER 14 MENDEL AND THE GENE IDEA
... Mendel developed a hypothesis to explain these results that consisted of four related ideas. We will explain each idea with the modern understanding of genes and chromosomes. 1. Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters. ° The gene for flower color in pea plants ex ...
... Mendel developed a hypothesis to explain these results that consisted of four related ideas. We will explain each idea with the modern understanding of genes and chromosomes. 1. Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters. ° The gene for flower color in pea plants ex ...
Three-letter Symbols - Online Open Genetics
... Three alleles in a series for the w gene. The first is wild type; the second two are different mutant alleles. ...
... Three alleles in a series for the w gene. The first is wild type; the second two are different mutant alleles. ...
10.3
... AABBCC would be a tall individual AXBBCC would be a little shorter AXBYCC would be even shorter, and so on . . . until XXYYZZ would be the shortest individual The potential combinations of alleles (and phenotypes) for a character increases with the # of genes that affect that character --> huge rang ...
... AABBCC would be a tall individual AXBBCC would be a little shorter AXBYCC would be even shorter, and so on . . . until XXYYZZ would be the shortest individual The potential combinations of alleles (and phenotypes) for a character increases with the # of genes that affect that character --> huge rang ...
Ch. 9 Presentation - Faculty Website Listing
... 9.12 Many genes have more than two alleles in the population Although an individual can at most carry two different alleles for a particular gene, more than two alleles often exist in the wider population. Human ABO blood group phenotypes involve three alleles for a single gene. The four huma ...
... 9.12 Many genes have more than two alleles in the population Although an individual can at most carry two different alleles for a particular gene, more than two alleles often exist in the wider population. Human ABO blood group phenotypes involve three alleles for a single gene. The four huma ...
Laboratory #4: Segregation of Traits According to Mendel
... homozygous for all their important qualitative genes and are known as a pure line. Mendel crossfertilized different homozygous pea lines to see what would happen. As a result of his work with peas, Mendel concluded that physical traits are passed from one generation to the next as discrete units, wh ...
... homozygous for all their important qualitative genes and are known as a pure line. Mendel crossfertilized different homozygous pea lines to see what would happen. As a result of his work with peas, Mendel concluded that physical traits are passed from one generation to the next as discrete units, wh ...
Evolution of Phenotypic Robustness
... one might think of a high-level feedback mechanism or special “canalizing genes” (such as, perhaps, certain heat-shock proteins), in theoretical modeling this corresponds to approaches where variability is regulated by independent modifier loci. The other endpoint of the scale is the cooperative sce ...
... one might think of a high-level feedback mechanism or special “canalizing genes” (such as, perhaps, certain heat-shock proteins), in theoretical modeling this corresponds to approaches where variability is regulated by independent modifier loci. The other endpoint of the scale is the cooperative sce ...
LAB 1: Scientific Method/Tools of Scientific Inquiry
... male karyotype shown below (notice the X and Y sex chromosomes): Notice one more thing about this human karyotype: there are two of each autosome as well as two sex chromosomes. This is because human beings are diploid, which means having two of each chromosome type. Most plants and animals are in f ...
... male karyotype shown below (notice the X and Y sex chromosomes): Notice one more thing about this human karyotype: there are two of each autosome as well as two sex chromosomes. This is because human beings are diploid, which means having two of each chromosome type. Most plants and animals are in f ...
Ch 9 PPT
... • Describe how Mendel was able to control how his pea plants were pollinated. • Describe the steps in Mendel’s experiments on true-breeding garden peas. • Distinguish between dominant and recessive traits. • State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. • Describe how Mendel’s r ...
... • Describe how Mendel was able to control how his pea plants were pollinated. • Describe the steps in Mendel’s experiments on true-breeding garden peas. • Distinguish between dominant and recessive traits. • State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. • Describe how Mendel’s r ...
Sexual selection can constrain sympatric speciation
... (rij ⬍ 1/3 for the plant model, rij ⬍ 1/6 for the animal model when pi = p j = 1/2 and bi = b j ) suffices to reverse that trend, however, so that stronger assortment actually decreases the overall variance. Thus tighter linkage inhibits the potential for sympatric speciation. If it occurs, the full ...
... (rij ⬍ 1/3 for the plant model, rij ⬍ 1/6 for the animal model when pi = p j = 1/2 and bi = b j ) suffices to reverse that trend, however, so that stronger assortment actually decreases the overall variance. Thus tighter linkage inhibits the potential for sympatric speciation. If it occurs, the full ...
Marker-assisted backcross breeding
... * Marker locus is fixed for recurrent parent (i.e. homozygous) so does not need to be selected for in BC2 ...
... * Marker locus is fixed for recurrent parent (i.e. homozygous) so does not need to be selected for in BC2 ...
Molluscan Studies - Oxford Academic
... Many of these P. lignaria subspecies are distributed along the Mokihinui River valley and associated catchments, which were recently proposed for dam development. Although this proposal was cancelled in 2012, the habitat of P. lignaria is clearly of interest. In the absence of a taxonomic revision, ...
... Many of these P. lignaria subspecies are distributed along the Mokihinui River valley and associated catchments, which were recently proposed for dam development. Although this proposal was cancelled in 2012, the habitat of P. lignaria is clearly of interest. In the absence of a taxonomic revision, ...
Lab 7. Mendelian Genetics
... example, there is an allele for blond hair, another for black hair, etc. Only two alleles, one from each parent, are inherited for any one trait. Geneticists depict an individual's genetic make–up in a variety of different ways depending on the particular set of alleles they are working with. This m ...
... example, there is an allele for blond hair, another for black hair, etc. Only two alleles, one from each parent, are inherited for any one trait. Geneticists depict an individual's genetic make–up in a variety of different ways depending on the particular set of alleles they are working with. This m ...
15_Lecture_Stock
... • In humans and other mammals, there are two varieties of sex chromosomes: a larger X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome • Only the ends of the Y chromosome have regions that are homologous with corresponding regions of the X chromosome • The SRY gene on the Y chromosome codes for a protein that ...
... • In humans and other mammals, there are two varieties of sex chromosomes: a larger X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome • Only the ends of the Y chromosome have regions that are homologous with corresponding regions of the X chromosome • The SRY gene on the Y chromosome codes for a protein that ...
Mikael Puurtinen Evolution of Hermaphroditic Mating Systems in
... why most animals are gonochoric. A reason for this bias may be due to the fact that as humans we perceive having separate sexes as ‘normal’, whereas hermaphroditism seems ‘odd’. The most influential theories for hermaphroditism relate to situations where availability of mating partners is low. Imagi ...
... why most animals are gonochoric. A reason for this bias may be due to the fact that as humans we perceive having separate sexes as ‘normal’, whereas hermaphroditism seems ‘odd’. The most influential theories for hermaphroditism relate to situations where availability of mating partners is low. Imagi ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.