Notes Chapter 16 - Spring Branch ISD
... D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes may form new combinations during meiosis Example: crossing ...
... D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes may form new combinations during meiosis Example: crossing ...
Population Genetics and Speciation
... either extreme variation of a trait have a greater fitness than individual with the average form of the trait. ...
... either extreme variation of a trait have a greater fitness than individual with the average form of the trait. ...
Evolution exam 1 File
... A The theory of natural selection was proposed by Watson and Crick in 1959. B Alfred Russel Wallace was a strong opponent of natural selection. C Natural selection acts on phenotypic variation that is genetically inherited. D Can occur through the effects of genetic drift. E Occurs through the inher ...
... A The theory of natural selection was proposed by Watson and Crick in 1959. B Alfred Russel Wallace was a strong opponent of natural selection. C Natural selection acts on phenotypic variation that is genetically inherited. D Can occur through the effects of genetic drift. E Occurs through the inher ...
Explain how humans impact variation in other species
... Explain two examples of evolution in response to environmental change; one must be antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Note: Other examples could include: the changes in size and shape of the beaks of Galapagos finches; pesticide resistance, peppered moths, industrial melanism or heavymetal tolerance ...
... Explain two examples of evolution in response to environmental change; one must be antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Note: Other examples could include: the changes in size and shape of the beaks of Galapagos finches; pesticide resistance, peppered moths, industrial melanism or heavymetal tolerance ...
Name: OBJ 3.05 Mechanisms and Features of Evolution Changes in
... 6. During the past decade, doctors have noted the appearance of several super bugs, which are bacteria that show multiple resistances to hand sanitizer. The development of these super bugs has been linked to the overuse of hand sanitizer. Explain how these super bugs could have appeared. ...
... 6. During the past decade, doctors have noted the appearance of several super bugs, which are bacteria that show multiple resistances to hand sanitizer. The development of these super bugs has been linked to the overuse of hand sanitizer. Explain how these super bugs could have appeared. ...
Evolution - Home - Mr. Wright's Class Website
... • Natural selection determines what individuals survive and reproduces – an organism either passes on ALL genes, or none at all. ...
... • Natural selection determines what individuals survive and reproduces – an organism either passes on ALL genes, or none at all. ...
Changes Over Time - Effingham County Schools
... be less effective, and the frequency of resistant insects in the population ...
... be less effective, and the frequency of resistant insects in the population ...
Evolution
... Allopatric - Part of a population is separated from the original population and geographically isolated from it leading to reproductive isolation. Variations occur due to genetic drift and mutations with each population Synpatric – Groups within a population become reproductively isolation from each ...
... Allopatric - Part of a population is separated from the original population and geographically isolated from it leading to reproductive isolation. Variations occur due to genetic drift and mutations with each population Synpatric – Groups within a population become reproductively isolation from each ...
evolution, heredity, and behavior
... nucleotide specifies and particular amino acid that has instructions for synthesization,causing trait to appear
... nucleotide specifies and particular amino acid that has instructions for synthesization,causing trait to appear
Name: Date - Dorsey High School
... 1. What is our definition of “evolution”? __________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Natural selection tells us that organisms with the most favorable ___________________ will survive, rep ...
... 1. What is our definition of “evolution”? __________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Natural selection tells us that organisms with the most favorable ___________________ will survive, rep ...
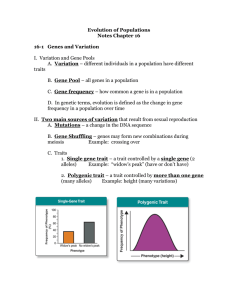
Genes and Variation
... • Because members of the population interbreed, they share a common group of genes called a gene pool. • A gene pool consists of all the genes, including all the different alleles, that are present in a population. ...
... • Because members of the population interbreed, they share a common group of genes called a gene pool. • A gene pool consists of all the genes, including all the different alleles, that are present in a population. ...
Population Genetics, Speciation, and Classification
... trait have the highest fitness. • Disruptive- Those with either extreme variation of a trait have greater fitness. • Directional- Those that display one extreme form of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with an average form of the trait. ...
... trait have the highest fitness. • Disruptive- Those with either extreme variation of a trait have greater fitness. • Directional- Those that display one extreme form of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with an average form of the trait. ...
Natural selection - Mercer Island School District
... Limitations to Adaptation • Adaptations can only occur if favorable traits exist in the gene pool. • Because organisms must do many things, adaptations are usually compromises. • A population’s ability to adapt is limited by its reproductive capacity. (Species with faster reproductive rate may be a ...
... Limitations to Adaptation • Adaptations can only occur if favorable traits exist in the gene pool. • Because organisms must do many things, adaptations are usually compromises. • A population’s ability to adapt is limited by its reproductive capacity. (Species with faster reproductive rate may be a ...
chapter 16 - Cloudfront.net
... The Gene Pool Gene Pool: the total genetic information available ...
... The Gene Pool Gene Pool: the total genetic information available ...
Mutation Migration
... (a) Directional Selection: As shown above, individuals at the left-most end of the graph have lower fitness/lower probability of surviving. As generations continue to reproduce in a stable environment, the curve is pushed to the right of the original because those phenotypes are more advantageous. ( ...
... (a) Directional Selection: As shown above, individuals at the left-most end of the graph have lower fitness/lower probability of surviving. As generations continue to reproduce in a stable environment, the curve is pushed to the right of the original because those phenotypes are more advantageous. ( ...
“The Mechanisms of Evolution” Section 11.1 “Darwin Meets DNA”
... May carry different alleles than original population. Genetically different species are produced. ...
... May carry different alleles than original population. Genetically different species are produced. ...
bionotes124
... Heterozygotes - two different alleles Homozygotes - same alleles Homologous Chromosomes Same length Same centromere position Possess traits genes for same trait at corresponding location The offspring will get one homologue from mom and the other from dad Genotype - sum of all genetic material ...
... Heterozygotes - two different alleles Homozygotes - same alleles Homologous Chromosomes Same length Same centromere position Possess traits genes for same trait at corresponding location The offspring will get one homologue from mom and the other from dad Genotype - sum of all genetic material ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... favours individuals with variations at opposite extremes of a trait over individuals with intermediate variations environment may favour more than one phenotype this is a significant evolutionary mechanism for the formation of distinctive forms within a populations ...
... favours individuals with variations at opposite extremes of a trait over individuals with intermediate variations environment may favour more than one phenotype this is a significant evolutionary mechanism for the formation of distinctive forms within a populations ...
Chapter 23 (OLD)
... for any feature, there can be many phenotypes phenotypes are determined by alleles must examine change in allele frequency of a population over time ...
... for any feature, there can be many phenotypes phenotypes are determined by alleles must examine change in allele frequency of a population over time ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.























