Nikrosebeijingalumninov2010
... most important area of DNA diagnostics will be the identification of genes that predispose individuals to disease. However, many such diseases – cardiovascular, neurological, autoimmune – are polygenic; they are the result of the action of two or more genes. Human genetic mapping will permit the ide ...
... most important area of DNA diagnostics will be the identification of genes that predispose individuals to disease. However, many such diseases – cardiovascular, neurological, autoimmune – are polygenic; they are the result of the action of two or more genes. Human genetic mapping will permit the ide ...
Aequatus User Guide
... cross-references these sequences to Ensembl Core databases for each species to gather genomic feature information via stable_ids. Aequatus then processes the comparative and feature data to provide a visual representation of the phylogenetic and structural relationships among the set of chosen speci ...
... cross-references these sequences to Ensembl Core databases for each species to gather genomic feature information via stable_ids. Aequatus then processes the comparative and feature data to provide a visual representation of the phylogenetic and structural relationships among the set of chosen speci ...
BIO 344- Quiz12
... 1.What is A. tumefaciens and what special feature does it have that has allowed it to become useful for genetic engineering? It is a bacteria that infects plants (tobacco). It has an extrachromosomal element that leaves the bacteria and enter the plant cell during infection. One can engineer genes o ...
... 1.What is A. tumefaciens and what special feature does it have that has allowed it to become useful for genetic engineering? It is a bacteria that infects plants (tobacco). It has an extrachromosomal element that leaves the bacteria and enter the plant cell during infection. One can engineer genes o ...
CSI” Plant Style: From Laboratory to your Lunch Tray
... Molecular Markers—DNA segments that can be used as flags to track genes Linkage—occurs when particular genes are inherited jointly Linked Markers—markers which are closely associated with a gene ...
... Molecular Markers—DNA segments that can be used as flags to track genes Linkage—occurs when particular genes are inherited jointly Linked Markers—markers which are closely associated with a gene ...
NAME
... homozygous dominant ( BB Bb bb ) _______________________ homozygous recessive ( BB Bb bb ) __________________ heterozygous ( BB Bb bb ) _________________________ 5. Fill in the blanks below using these choices: dominant, genes, genetics, heterozygous, homozygous, recessive, chromosomes, Punnett Squa ...
... homozygous dominant ( BB Bb bb ) _______________________ homozygous recessive ( BB Bb bb ) __________________ heterozygous ( BB Bb bb ) _________________________ 5. Fill in the blanks below using these choices: dominant, genes, genetics, heterozygous, homozygous, recessive, chromosomes, Punnett Squa ...
overview
... supplemented with 3 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, thus allowing growth only of cells that express the HIS3 two-hybrid reporter gene. Three other components of factor IA, Rna14, Rna15 and Clp1, were identified as Pcf11 interactors. Positives that do not appear in Table 2 were either not reproducible or ...
... supplemented with 3 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, thus allowing growth only of cells that express the HIS3 two-hybrid reporter gene. Three other components of factor IA, Rna14, Rna15 and Clp1, were identified as Pcf11 interactors. Positives that do not appear in Table 2 were either not reproducible or ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... mostly of DNA that appear banded because they consist of sections of DNA (genes) that code for the production of proteins and therefore determine a trait. Each of these consists of millions of bases. ...
... mostly of DNA that appear banded because they consist of sections of DNA (genes) that code for the production of proteins and therefore determine a trait. Each of these consists of millions of bases. ...
A aa - Albinizms
... have disorder and 2 copies of the “bad” gene Half Green/Half White= because this is a dominant disorder (rules of dominance), the person has the disease and only has one copy of the “bad” gene and one copy of the “healthy” gene. ...
... have disorder and 2 copies of the “bad” gene Half Green/Half White= because this is a dominant disorder (rules of dominance), the person has the disease and only has one copy of the “bad” gene and one copy of the “healthy” gene. ...
What is Genetic Modification?
... a new gene altogether.A gene is a code that governs how we appear and what characteristics we have.Like animals, plants have genes too. Genes decide the colour of flowers, and how tall a plant can grow. Like people, the characteristics of a plant will be transferred to its childrenthe plant seeds, w ...
... a new gene altogether.A gene is a code that governs how we appear and what characteristics we have.Like animals, plants have genes too. Genes decide the colour of flowers, and how tall a plant can grow. Like people, the characteristics of a plant will be transferred to its childrenthe plant seeds, w ...
Genomes and their evolution
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
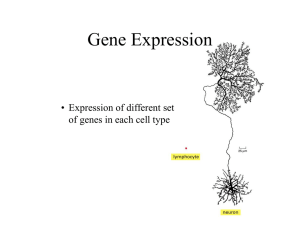
differential gene expression
... Prokaryotic regulation is different from eukaryotic regulation. 1. Eukaryotic cells have many more genes (23,700 in human cells) in their genomes than prokaryotic cells (average 3000). 2. Physically there are more obstacles as eukaryotic chromatin is wrapped around histone proteins. ...
... Prokaryotic regulation is different from eukaryotic regulation. 1. Eukaryotic cells have many more genes (23,700 in human cells) in their genomes than prokaryotic cells (average 3000). 2. Physically there are more obstacles as eukaryotic chromatin is wrapped around histone proteins. ...
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary
... To Use a Matching Activity: 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
... To Use a Matching Activity: 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
Document
... – …SmZF1 binds both ds and ss DNA oligonucleotides,… (TN) – Coexpression of Ss and Tgo in Drosophila SL2 cells… (TP) – The origin of germline-limited chromosomes (Ks) as descendants of somatic chromosomes (Ss) and their… (FP) ...
... – …SmZF1 binds both ds and ss DNA oligonucleotides,… (TN) – Coexpression of Ss and Tgo in Drosophila SL2 cells… (TP) – The origin of germline-limited chromosomes (Ks) as descendants of somatic chromosomes (Ss) and their… (FP) ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
Advances in Genetics
... • Genetically Modified Organism(GMO): An organism that has recombinant DNA. ...
... • Genetically Modified Organism(GMO): An organism that has recombinant DNA. ...
Bioinformatics and Personal Health/Intro computer lab
... transcription factors, inactivating them. When GA is present the DELLA domain binds the protein GID1. This binding causes the DELLA protein to be tagged for degradation (using ubiquitination). With DELLA proteins degraded the transcription factors are able to bind promoters and turn on gene expressi ...
... transcription factors, inactivating them. When GA is present the DELLA domain binds the protein GID1. This binding causes the DELLA protein to be tagged for degradation (using ubiquitination). With DELLA proteins degraded the transcription factors are able to bind promoters and turn on gene expressi ...
Slide 1
... carriers of the defective gene (two carriers have to mate to produce an affected individual). Why is the prevalence of this defect so high? ...
... carriers of the defective gene (two carriers have to mate to produce an affected individual). Why is the prevalence of this defect so high? ...
Chapter 9b
... • Gene therapy to replace defective or missing genes • Human Genome Project – Nucleotides have been sequenced – Human Proteome Project may provide diagnostics and treatments ...
... • Gene therapy to replace defective or missing genes • Human Genome Project – Nucleotides have been sequenced – Human Proteome Project may provide diagnostics and treatments ...
Gene Section BCL7B (B-cell CLL/lymphoma 7B) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... BCL7B is located in a chromosomal region commonly deleted in Williams syndrome. The role of BCL7B loss in this syndrome is yet to be established. Furthermore, in rare cases, malignancies have presented in patients with Williams syndrome including non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a 29-year-old woman and an 8 ...
... BCL7B is located in a chromosomal region commonly deleted in Williams syndrome. The role of BCL7B loss in this syndrome is yet to be established. Furthermore, in rare cases, malignancies have presented in patients with Williams syndrome including non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a 29-year-old woman and an 8 ...
Set 2 - The Science Spot
... 1. What term refers to the physical appearance of a trait? Example: Yellow body color 2. What term refers to the gene that is expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If your grandparents are the parental generation, what term would refer to your parents? 4. What ...
... 1. What term refers to the physical appearance of a trait? Example: Yellow body color 2. What term refers to the gene that is expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If your grandparents are the parental generation, what term would refer to your parents? 4. What ...
name averill park hs
... Evolution (change over time) is how modern organisms have descended from ancient ancestors over long periods of time. It is responsible for the remarkable similarities we see across all life and the amazing diversity of that life. Evolution is often described as "descent with modification." (passing ...
... Evolution (change over time) is how modern organisms have descended from ancient ancestors over long periods of time. It is responsible for the remarkable similarities we see across all life and the amazing diversity of that life. Evolution is often described as "descent with modification." (passing ...