Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... 11) What is RNA splicing? Why is this done? RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” bu ...
... 11) What is RNA splicing? Why is this done? RNA splicing takes out sections of mRNA that are not coding for a section of the protein; introns are spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” bu ...
INTERVENING SEQUENCES IN EUKARYOTES
... 2. The most interesting speculation about possible function of introns is exon shuffling. (a) Most, proteins have several domains. These domains include substrate recognition, cofactor recognition, catalytic regions, allosteric functions, et cetera. Examples previously discussed include the DNA poly ...
... 2. The most interesting speculation about possible function of introns is exon shuffling. (a) Most, proteins have several domains. These domains include substrate recognition, cofactor recognition, catalytic regions, allosteric functions, et cetera. Examples previously discussed include the DNA poly ...
Genetics I
... 9. Section of a chromosome __gene___________________________________ 10. Gene that keeps other genes from showing trait ___dominant_____________ 11. Recessive gene __genes that do not show traits in presence of dominant gene 12. Heterozygous _has a dominant and recessive gene for a trait_____ 13. Me ...
... 9. Section of a chromosome __gene___________________________________ 10. Gene that keeps other genes from showing trait ___dominant_____________ 11. Recessive gene __genes that do not show traits in presence of dominant gene 12. Heterozygous _has a dominant and recessive gene for a trait_____ 13. Me ...
Nucliec acids and dna review
... The three bases on the tRNA molecule that are complementary to one of the mRNA codons are called the ___________________. A. message matches B. anticodon C. promoter D. exon E. intron DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, ___________________________________________ A. each with two new stran ...
... The three bases on the tRNA molecule that are complementary to one of the mRNA codons are called the ___________________. A. message matches B. anticodon C. promoter D. exon E. intron DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, ___________________________________________ A. each with two new stran ...
Study Guide – Unit 6 Test: Genetics and DNA Name: Per: 1 2 3 4 5 6
... Define multiple alleles. Give an example of a phenotype that is determined by multiple allele. ...
... Define multiple alleles. Give an example of a phenotype that is determined by multiple allele. ...
How Genes Are Regulated
... While all somatic cells within an organism contain the same DNA, not all cells within that organism express the same proteins. Prokaryotic organisms express the entire DNA they encode in every cell, but not necessarily all at the same time. Proteins are expressed only when they are needed. Eukaryoti ...
... While all somatic cells within an organism contain the same DNA, not all cells within that organism express the same proteins. Prokaryotic organisms express the entire DNA they encode in every cell, but not necessarily all at the same time. Proteins are expressed only when they are needed. Eukaryoti ...
Exons and Introns
... We are interested in the evolution of the intron/exon structure of genes. Are the introns ancient structures, used to assemble the first genes four billion years ago? Or are they more recent acquisitions, used for exon shuffling in recently evolved proteins? Our work ranges from theoretical estimate ...
... We are interested in the evolution of the intron/exon structure of genes. Are the introns ancient structures, used to assemble the first genes four billion years ago? Or are they more recent acquisitions, used for exon shuffling in recently evolved proteins? Our work ranges from theoretical estimate ...
NCBI - Alumni Medical Library
... • Gives sequence, expression, information about protein structure and function. • Doesn't list all known and predicted genes • Focuses on completely sequenced genomes or ones where research communities are actively contributing genetic information. • Information from RefSeq and collaborating model o ...
... • Gives sequence, expression, information about protein structure and function. • Doesn't list all known and predicted genes • Focuses on completely sequenced genomes or ones where research communities are actively contributing genetic information. • Information from RefSeq and collaborating model o ...
Powerpoint - Wishart Research Group
... • Most gene finders don’t handle overlapping or nested genes • Most can’t find non-protein genes (tRNAs) ...
... • Most gene finders don’t handle overlapping or nested genes • Most can’t find non-protein genes (tRNAs) ...
`Genes` Like That, Who Needs an Environment?
... 3.2. RNA Editing. Another gene regulatory mechanism that can significantly diversify the proteome is RNA editing. Whereas most other forms of posttranscriptional modifications of mRNA (capping, polyadenylation, and cis-splicing) retain the correspondence of the primary structure of exon and gene pro ...
... 3.2. RNA Editing. Another gene regulatory mechanism that can significantly diversify the proteome is RNA editing. Whereas most other forms of posttranscriptional modifications of mRNA (capping, polyadenylation, and cis-splicing) retain the correspondence of the primary structure of exon and gene pro ...
reading guide
... There seem to be two categories of genes involved in cancer: oncogenes, which code for proteins to regulate cell growth, and should not be stuck “on,” much like the accelerator in a car; and tumor-suppressor genes, which work like the brakes on a car and must function! Let’s begin with a look at the ...
... There seem to be two categories of genes involved in cancer: oncogenes, which code for proteins to regulate cell growth, and should not be stuck “on,” much like the accelerator in a car; and tumor-suppressor genes, which work like the brakes on a car and must function! Let’s begin with a look at the ...
Genetic Disorders - Michigan Department of Education Technology
... protein molecules and that this is virtually the same mechanism for all life forms. B4.2h Recognize that genetic engineering techniques provide great potential and responsibilities. B4.r2i Explain how recombinant DNA technology allows scientists to analyze the structure and function of genes. (recom ...
... protein molecules and that this is virtually the same mechanism for all life forms. B4.2h Recognize that genetic engineering techniques provide great potential and responsibilities. B4.r2i Explain how recombinant DNA technology allows scientists to analyze the structure and function of genes. (recom ...
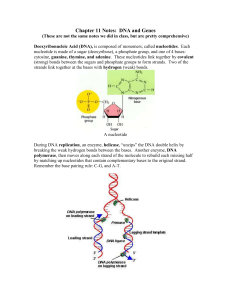
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... The proteins produced are in the 1˚ level of protein structure, which the genes determine Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? W ...
... The proteins produced are in the 1˚ level of protein structure, which the genes determine Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? W ...
Transcription
... molecules to the 3’ end of mRNA to form what is called as poly(A) tail. • This process is important for the transport of RNA from nucleus to cytoplasm and translation. ...
... molecules to the 3’ end of mRNA to form what is called as poly(A) tail. • This process is important for the transport of RNA from nucleus to cytoplasm and translation. ...
Teachers Introductory notes for Genetic Modification (GM)
... genes of another. GM can also mean deleting a gene or genes from an organism. Every cell of the new organism then carries those new genes or deletions, and they will pass them on to to any offspring they have. For example, the genes for human insulin have been inserted into a type of bacteria, this ...
... genes of another. GM can also mean deleting a gene or genes from an organism. Every cell of the new organism then carries those new genes or deletions, and they will pass them on to to any offspring they have. For example, the genes for human insulin have been inserted into a type of bacteria, this ...
Chapter 21 The Genetic Control of Animal Development
... The Drosophila homeotic genes form two large clusters on one of the autosomes. All of the homeotic genes encode helix-turn-helix transcription factors with a conserved homeodomain region involved in DNA binding. These genes control a regulatory cascade of target genes that control segment identi ...
... The Drosophila homeotic genes form two large clusters on one of the autosomes. All of the homeotic genes encode helix-turn-helix transcription factors with a conserved homeodomain region involved in DNA binding. These genes control a regulatory cascade of target genes that control segment identi ...
Tasmanian Devil gene annotation methods
... The gene set was screened for potential pseudogenes. Before public release the transcripts and translations were given external references cross references to external databases), while translations were searched for domains/signatures of interest and labeled where appropriate. Stable Identifiers we ...
... The gene set was screened for potential pseudogenes. Before public release the transcripts and translations were given external references cross references to external databases), while translations were searched for domains/signatures of interest and labeled where appropriate. Stable Identifiers we ...
Notes
... assembled contig sequences. Contig sequences are assemblies of several clones. These clones were direct sequenced. We can inspect the sequences of these clones. The next gray histogram depicts the amount of ESTs aligned to a region A UniGene entry is a set of transcript sequences that appear to come ...
... assembled contig sequences. Contig sequences are assemblies of several clones. These clones were direct sequenced. We can inspect the sequences of these clones. The next gray histogram depicts the amount of ESTs aligned to a region A UniGene entry is a set of transcript sequences that appear to come ...
Essential software for all your sequence analysis needs
... your sequences — either one at a time or as a large batch — using a carefully curated database of features. Simply select your sequences and SeqBuilder will provide you with a list of matched features for your consideration, making it easy to identify missing annotations and replace inaccurate annot ...
... your sequences — either one at a time or as a large batch — using a carefully curated database of features. Simply select your sequences and SeqBuilder will provide you with a list of matched features for your consideration, making it easy to identify missing annotations and replace inaccurate annot ...
Human genome study reveals certain genes are less essential than
... “We can now let clinicians know that there are certain genes that really should not be used to try to explain diseases in this way,” Dr Eichler said. The 1,000 Genomes Project investigated the smallest mutational differences between genomes, the so-called single nucleotide polymorphisms where just o ...
... “We can now let clinicians know that there are certain genes that really should not be used to try to explain diseases in this way,” Dr Eichler said. The 1,000 Genomes Project investigated the smallest mutational differences between genomes, the so-called single nucleotide polymorphisms where just o ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... breaking the hydrogen bonds between paired bases ■ An enzyme bonds RNA nucleotides to one DNA strand ■ C bonds to G and A (on DNA) bonds to U (on RNA) ...
... breaking the hydrogen bonds between paired bases ■ An enzyme bonds RNA nucleotides to one DNA strand ■ C bonds to G and A (on DNA) bonds to U (on RNA) ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 4 of 14
... no others. The idea of redundancy refers to the fact that more than one codon can code for the same amino acid since there are only 20 and many combinations of codons. ...
... no others. The idea of redundancy refers to the fact that more than one codon can code for the same amino acid since there are only 20 and many combinations of codons. ...
RNA-Seq

RNA-seq (RNA sequencing), also called whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing (WTSS), is a technology that uses the capabilities of next-generation sequencing to reveal a snapshot of RNA presence and quantity from a genome at a given moment in time.