No Slide Title
... Reductions in population size can lead to losses of genetic polymorphism Two special cases of reductions in population size are: 1. A few individuals move to a new area and start a new population that is isolated from other populations – founder effect 2. We can also experience a population bottlene ...
... Reductions in population size can lead to losses of genetic polymorphism Two special cases of reductions in population size are: 1. A few individuals move to a new area and start a new population that is isolated from other populations – founder effect 2. We can also experience a population bottlene ...
Hardy Weinberg - EDHSGreenSea.net
... illustrate how phenotypes can change from generation to generation. • RR = red; rr = white; Rr = pink • The phenotypic frequency is equal to the number of individuals with a particular phenotype divided by the total number of individuals in the population. ...
... illustrate how phenotypes can change from generation to generation. • RR = red; rr = white; Rr = pink • The phenotypic frequency is equal to the number of individuals with a particular phenotype divided by the total number of individuals in the population. ...
Population Genetics
... probability in which purely chance events determine which alleles (variants of a gene) within a reproductive population will be carried forward while others disappear. Especially in the case of small populations, the statistical effect of sampling error during random sampling of certain alleles from ...
... probability in which purely chance events determine which alleles (variants of a gene) within a reproductive population will be carried forward while others disappear. Especially in the case of small populations, the statistical effect of sampling error during random sampling of certain alleles from ...
Chapter 16 summary
... near the middle or other end of the curve. Directional selection causes a shift in the curve toward the higher fitness end. • Stabilizing selection occurs when individuals near the middle of the curve have higher fitness than those at either end. Stabilizing selection leads to a narrowing of the cur ...
... near the middle or other end of the curve. Directional selection causes a shift in the curve toward the higher fitness end. • Stabilizing selection occurs when individuals near the middle of the curve have higher fitness than those at either end. Stabilizing selection leads to a narrowing of the cur ...
TPS on Evolution - Aurora City Schools
... • Explain why genetic variation is a prerequisite for evolution. List three factors that can result in more variation in the population. • Why do only a very small fraction of mutations become widespread in a population? • A fruit fly population has a gene with two possible allele variations. It is ...
... • Explain why genetic variation is a prerequisite for evolution. List three factors that can result in more variation in the population. • Why do only a very small fraction of mutations become widespread in a population? • A fruit fly population has a gene with two possible allele variations. It is ...
File
... 6. Speciation: the emergence of new species after the process of evolution; when a species has evolutionized to the point that its new characteristics are different enough for it to be considered a different species. Allopatric Speciation: when a new species develops due to geographical separatio ...
... 6. Speciation: the emergence of new species after the process of evolution; when a species has evolutionized to the point that its new characteristics are different enough for it to be considered a different species. Allopatric Speciation: when a new species develops due to geographical separatio ...
Natural Selection
... applications of the same insecticide will be less effective, and the frequency of resistant insects in the population will grow ...
... applications of the same insecticide will be less effective, and the frequency of resistant insects in the population will grow ...
05 Evolution 2010
... population because of differential survival and reproduction of individuals with those traits. • Individuals with the most offspring are selected and the proportion of their genes increases over time. • Fitness: the genetic contribution by an individual to future generations. • Relative fitness: Max ...
... population because of differential survival and reproduction of individuals with those traits. • Individuals with the most offspring are selected and the proportion of their genes increases over time. • Fitness: the genetic contribution by an individual to future generations. • Relative fitness: Max ...
HARDY-WEINBERG and GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
... very short and a few are very long, most are of average length ...
... very short and a few are very long, most are of average length ...
The Evolution of Populations
... independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis, random combination of gametes in fertilization ...
... independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis, random combination of gametes in fertilization ...
Chapter 17 Review ppt
... In a certain population of 100 individuals, one fourth of the individuals have the genotype BB, half have the genotype Bb, and one fourth have the genotype aa. One day, 10 individuals with the genotype bb leave the area and cross a river into a new habitat. Which of these processes has changed the ...
... In a certain population of 100 individuals, one fourth of the individuals have the genotype BB, half have the genotype Bb, and one fourth have the genotype aa. One day, 10 individuals with the genotype bb leave the area and cross a river into a new habitat. Which of these processes has changed the ...
Genetics
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
Genetics - Dave Brodbeck
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
Microevolution - Phillips Scientific Methods
... - a = square root of 0.09 which is 0.3 - A = (1 – 0.3) which is 0.7 - AA = (0.7) 2 which is 0.49 ...
... - a = square root of 0.09 which is 0.3 - A = (1 – 0.3) which is 0.7 - AA = (0.7) 2 which is 0.49 ...
Document
... The probability of autozygosity expressed by the coefficeint of inbreeding will have a different value when, from one generation to the next, allele frequencies change because of gene flow among populations. ...
... The probability of autozygosity expressed by the coefficeint of inbreeding will have a different value when, from one generation to the next, allele frequencies change because of gene flow among populations. ...
genetic equilibrium
... • Can also occur by accident or chance and not by natural selection • Evolution by random chance is called genetic drift • Usually happens in smaller populations, because larger ones can recover from these accidents. ...
... • Can also occur by accident or chance and not by natural selection • Evolution by random chance is called genetic drift • Usually happens in smaller populations, because larger ones can recover from these accidents. ...
disruptive selection
... Newly founded populations have allele frequencies different from original population. Not the cause of natural selection, but chance. ...
... Newly founded populations have allele frequencies different from original population. Not the cause of natural selection, but chance. ...
Chapter 9 Maintenance of Genetic Diversity
... Maintenance of Genetic Diversity Levels of genetic diversity result from the joint impacts of: Mutation & migration adding variation Chance & directional selection removing variation Balancing selection impeding its loss The balance between these factors depends strongly on population size and diffe ...
... Maintenance of Genetic Diversity Levels of genetic diversity result from the joint impacts of: Mutation & migration adding variation Chance & directional selection removing variation Balancing selection impeding its loss The balance between these factors depends strongly on population size and diffe ...
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
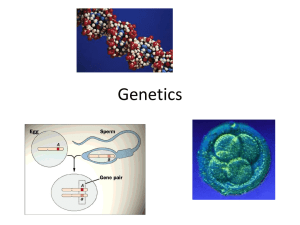
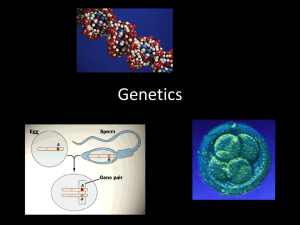
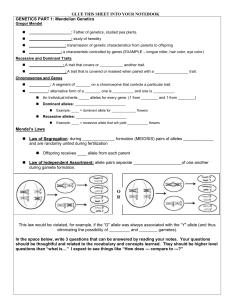
... GENETICS PART 1: Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel ...
... GENETICS PART 1: Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel ...
Population Genetics and Speciation Notes
... (Natural selection describes the tendency of beneficial alleles to become more common over time (and detrimental ones less common), genetic drift refers to the tendency of any allele to vary randomly in frequency over time due to statistical variation alone.) ...
... (Natural selection describes the tendency of beneficial alleles to become more common over time (and detrimental ones less common), genetic drift refers to the tendency of any allele to vary randomly in frequency over time due to statistical variation alone.) ...
GLYPHOSATE RESISTANCE Background / Problem
... Some “unfit” alleles do become fixed What happens without drift? No populations are fixed for A1 after 20 generations How long until these become fixed? ...
... Some “unfit” alleles do become fixed What happens without drift? No populations are fixed for A1 after 20 generations How long until these become fixed? ...
15.2 Mechanisms of Evolution
... All of the alleles of a population’s genes together make up a gene pool. Allelic frequency - % of any specific allele in the gene pool. Genetic equilibrium – a population in which the frequency of alleles remains the same over generations. ...
... All of the alleles of a population’s genes together make up a gene pool. Allelic frequency - % of any specific allele in the gene pool. Genetic equilibrium – a population in which the frequency of alleles remains the same over generations. ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.