16-1 Genes and Variation - Lincoln Park High School
... Fig. 1: Imagine that you go to the mountaintop this year, sample these beetles, and determine that 80% of the genes in the population are for green coloration and 20% of them are for brown coloration.You go back the next year, repeat the procedure, and find a new ratio: 60% green genes to 40% brown ...
... Fig. 1: Imagine that you go to the mountaintop this year, sample these beetles, and determine that 80% of the genes in the population are for green coloration and 20% of them are for brown coloration.You go back the next year, repeat the procedure, and find a new ratio: 60% green genes to 40% brown ...
Ch. 23 The Evolution of Populations. Rauch 2007-2008
... that have suffered bottleneck incidents have lost at least some alleles from the gene pool. This reduces individual variation and adaptability. For example, the genetic variation in the three small surviving wild populations of cheetahs is very low when compared to other mammals. Their genetic ...
... that have suffered bottleneck incidents have lost at least some alleles from the gene pool. This reduces individual variation and adaptability. For example, the genetic variation in the three small surviving wild populations of cheetahs is very low when compared to other mammals. Their genetic ...
Explain how humans impact variation in other species
... List seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa—kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species—using an example from two different kingdoms for each level. Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using simple external recognition features: bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and ...
... List seven levels in the hierarchy of taxa—kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species—using an example from two different kingdoms for each level. Distinguish between the following phyla of plants, using simple external recognition features: bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and ...
AP Biology - ReicheltScience.com
... Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or groups of species Systematics – system used to classifying diversity and determining the evolutionary relationships of living and extinct organisms Taxonomy - determines how organisms are classified and named. ...
... Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or groups of species Systematics – system used to classifying diversity and determining the evolutionary relationships of living and extinct organisms Taxonomy - determines how organisms are classified and named. ...
Document
... areas and are not able to interbreed. Ecological isolation results from two species who occur in the same area but utilize different portions of the environment and are unlikely to hybridize. Temporal isolation results from two species having different reproductive periods, or breeding seasons, that ...
... areas and are not able to interbreed. Ecological isolation results from two species who occur in the same area but utilize different portions of the environment and are unlikely to hybridize. Temporal isolation results from two species having different reproductive periods, or breeding seasons, that ...
Population
... -Imagine that green beetles are easier for birds to spot (and hence, eat). Brown beetles are a little more likely to survive to produce offspring The brown beetles pass their genes for brown coloration on to their offspring Next generation: brown beetles are more common than in the previous ge ...
... -Imagine that green beetles are easier for birds to spot (and hence, eat). Brown beetles are a little more likely to survive to produce offspring The brown beetles pass their genes for brown coloration on to their offspring Next generation: brown beetles are more common than in the previous ge ...
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations
... How does gene duplication occur? How might it play a role in evolution? Gene duplication can occur due to errors in meiosis, slippage during DNA replication, or the activities of transposable elements. Duplications that do not have severe effects can persist over generations, allowing mutations to a ...
... How does gene duplication occur? How might it play a role in evolution? Gene duplication can occur due to errors in meiosis, slippage during DNA replication, or the activities of transposable elements. Duplications that do not have severe effects can persist over generations, allowing mutations to a ...
Lecture 5 Notes
... (a) Directional Selection: As shown above, individuals at the left-most end of the phenotype distribution have lower fitness &/or lower probability of surviving. As generations continue to reproduce with the same selective pressure, the curve is pushed to the right of the original because those phen ...
... (a) Directional Selection: As shown above, individuals at the left-most end of the phenotype distribution have lower fitness &/or lower probability of surviving. As generations continue to reproduce with the same selective pressure, the curve is pushed to the right of the original because those phen ...
File - Honors Biology 16-17
... Result = the variance increases as the population is divided into two distinct groups. Disruptive selection plays an important role in speciation. Stabilizing Selection occurs when selection favors the intermediate trait value over the extreme values. Result= a decrease in the amount of genetic va ...
... Result = the variance increases as the population is divided into two distinct groups. Disruptive selection plays an important role in speciation. Stabilizing Selection occurs when selection favors the intermediate trait value over the extreme values. Result= a decrease in the amount of genetic va ...
Shown below is a pedigree chart for the inheritance of achondroplasia
... 1. Using D to represent the dominant allele and d to represent the recessive allele, determine the genotypes of the indicated (numbered) individuals. Record your answers next to the circle/rectangle below. Hint: Start by indicating the genotypes of 2, 3, and 7. Next, determine the genotypes of 1 and ...
... 1. Using D to represent the dominant allele and d to represent the recessive allele, determine the genotypes of the indicated (numbered) individuals. Record your answers next to the circle/rectangle below. Hint: Start by indicating the genotypes of 2, 3, and 7. Next, determine the genotypes of 1 and ...
Biology Chapter 15-17 Study Guide Name Period ______ Date
... How does natural selection result in change in a population over time? What is artificial selection? How did this concept affect Darwin’s thinking about change over time? What is an adaptation? How can an adaptation help an organism survive? Define the term vestigial structure? How might vestigial s ...
... How does natural selection result in change in a population over time? What is artificial selection? How did this concept affect Darwin’s thinking about change over time? What is an adaptation? How can an adaptation help an organism survive? Define the term vestigial structure? How might vestigial s ...
Chapter 8
... Allele frequencies involve percentages of dominant and recessive traits within a population. • The Hardy-Weinberg formula: – Is a mathematical representation of a gene pool. – p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 – Adds up all of the genotypes in a population. ...
... Allele frequencies involve percentages of dominant and recessive traits within a population. • The Hardy-Weinberg formula: – Is a mathematical representation of a gene pool. – p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 – Adds up all of the genotypes in a population. ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... – Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes. ...
... – Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes. ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... – Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes. ...
... – Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes. ...
The Evolutionary Synthesis
... • Punnett felt unhappy with his attempt to explain why recessive phenotypes still exist, and asked his cricket partner and Cambridge mathematician Godfrey Harold Hardy (1877-1947) • Question: what happens to a Mendelian mutation? • Hardy’s approach: Assumed a 2-allele case: A and a, with starting ƒ ...
... • Punnett felt unhappy with his attempt to explain why recessive phenotypes still exist, and asked his cricket partner and Cambridge mathematician Godfrey Harold Hardy (1877-1947) • Question: what happens to a Mendelian mutation? • Hardy’s approach: Assumed a 2-allele case: A and a, with starting ƒ ...
7.1 Solutions File
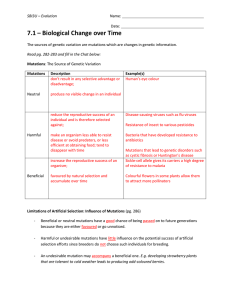
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
AP biology-Exam Review Unit 1 Evolution
... biologists hypothesize that the increase in storm frequency and severity has an effect on the frequency of long and short-winged birds, since medium-sized wings allow the birds to survive these storms better. The biologists collect phenotype frequency data about the wing length trait in the sparrow ...
... biologists hypothesize that the increase in storm frequency and severity has an effect on the frequency of long and short-winged birds, since medium-sized wings allow the birds to survive these storms better. The biologists collect phenotype frequency data about the wing length trait in the sparrow ...
Evolution - Hannah E. Styron
... During the industrial revolution, factories in England polluted the air with tons of soot which coated the trees. This caused dark colored moths to increase in population and the light colored moths to decline because dark colored moths were more suited for survival. ...
... During the industrial revolution, factories in England polluted the air with tons of soot which coated the trees. This caused dark colored moths to increase in population and the light colored moths to decline because dark colored moths were more suited for survival. ...
Evolution of Populations
... cactus plants with the fewest spines As a result, at flowering time there are more cacti with higher spine numbers; thus, there are more of their alleles going into pollen, eggs, and seeds for the next generation. ...
... cactus plants with the fewest spines As a result, at flowering time there are more cacti with higher spine numbers; thus, there are more of their alleles going into pollen, eggs, and seeds for the next generation. ...
Multifactorial Traits - An-Najah National University
... Individuals with certain genotypes sometimes mate with one another more commonly than would be expected on a random basis, a phenomenon known as nonrandom mating. Inbreeding (mating with relatives) is a type of nonrandom mating that causes the frequencies of particular genotypes to differ greatl ...
... Individuals with certain genotypes sometimes mate with one another more commonly than would be expected on a random basis, a phenomenon known as nonrandom mating. Inbreeding (mating with relatives) is a type of nonrandom mating that causes the frequencies of particular genotypes to differ greatl ...
BioA414 Handout IX-2017
... – Transformation of an entire species into a descendant species – Accumulation of changes gradualism – New species enough genetic alteration from original – No increase in biodiversity ...
... – Transformation of an entire species into a descendant species – Accumulation of changes gradualism – New species enough genetic alteration from original – No increase in biodiversity ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.