Genetics
... Explain the random process of chromosome segregation and distribution of alleles in gametes. Predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. ...
... Explain the random process of chromosome segregation and distribution of alleles in gametes. Predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. ...
Natural Selection
... 3) Differential Successful Reproduction (fitness): What effect does the deer's behavior have on the survival and reproduction of these two types of cactus? ...
... 3) Differential Successful Reproduction (fitness): What effect does the deer's behavior have on the survival and reproduction of these two types of cactus? ...
Biology 101 – Quiz 13 – Exercise 14 – Useful Applications of Genetics
... Billy Bob is NOT a hemophiliac (hemophilia is a X-linked recessive disorder). Billy Bob has a daughter, Edna, with Noreen, a carrier of the hemophilia trait. What are the chances that Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Sin ...
... Billy Bob is NOT a hemophiliac (hemophilia is a X-linked recessive disorder). Billy Bob has a daughter, Edna, with Noreen, a carrier of the hemophilia trait. What are the chances that Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Sin ...
nonmendel
... 4. Another characteristic of polygenic traits is that if you cross two individuals with intermediate characteristics, the offspring will have a range of characteristics, with a few individuals and the extremes C. The number of different phenotypes for additive alleles is the number of alleles an ind ...
... 4. Another characteristic of polygenic traits is that if you cross two individuals with intermediate characteristics, the offspring will have a range of characteristics, with a few individuals and the extremes C. The number of different phenotypes for additive alleles is the number of alleles an ind ...
ch 11 pre-test
... c. the genes are probably located far apart from each other. d. the genes are probably located close to each other. ...
... c. the genes are probably located far apart from each other. d. the genes are probably located close to each other. ...
EEB 122b FIRST MIDTERM
... mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Such individuals suffer from severe lung damage over time. For people of European ancestry, the frequency of CF-causing alleles in the population is .02. In some populations, up to 4% of individuals are heterozygous car ...
... mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Such individuals suffer from severe lung damage over time. For people of European ancestry, the frequency of CF-causing alleles in the population is .02. In some populations, up to 4% of individuals are heterozygous car ...
Quiz 7A
... gene controls the color of the petals, but there may be several different versions (or alleles) of the gene. One version might result in red petals, while another might result in white petals. The resulting color of an individual flower will depend on which two alleles it possesses for the gene and ...
... gene controls the color of the petals, but there may be several different versions (or alleles) of the gene. One version might result in red petals, while another might result in white petals. The resulting color of an individual flower will depend on which two alleles it possesses for the gene and ...
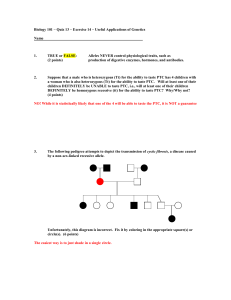
Pedigree analysis
... The pedigree chart below shows inheritance of the gene that causes albinism. A and B represent a couple who had five children, including C and E. Only one of the children, E, was albino. E and her husband had five children, including G. In the pedigree below write the genotypes of the individuals w ...
... The pedigree chart below shows inheritance of the gene that causes albinism. A and B represent a couple who had five children, including C and E. Only one of the children, E, was albino. E and her husband had five children, including G. In the pedigree below write the genotypes of the individuals w ...
PP - Cloudfront.net
... Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles of different traits will separate and assort themselves independently of each other. The alleles are put into the gametes in all possible combinations as long as a gamete has one allele for each gene. All of “mom’s” alleles don’t have to segregate together. In ...
... Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles of different traits will separate and assort themselves independently of each other. The alleles are put into the gametes in all possible combinations as long as a gamete has one allele for each gene. All of “mom’s” alleles don’t have to segregate together. In ...
Review Quizzes
... a. stabilizing selection b. directional selection c. sympatric selection d. allopatric selection e. disruptive selection 9. mortality in an annual plant is highest among the extreme variants A 10. favors selection of both larger and smaller snails relative to intermediate variants E 11. favors sele ...
... a. stabilizing selection b. directional selection c. sympatric selection d. allopatric selection e. disruptive selection 9. mortality in an annual plant is highest among the extreme variants A 10. favors selection of both larger and smaller snails relative to intermediate variants E 11. favors sele ...
File - Mrs. Harlin`s Website
... Sometimes genes are damaged or copied incorrectly, resulting in faulty proteins. These mutations can cause disorders that may or may not be lethal. ...
... Sometimes genes are damaged or copied incorrectly, resulting in faulty proteins. These mutations can cause disorders that may or may not be lethal. ...
File
... not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele 3. Natural selection can only act on rare homozygous individuals who do not follow dietary restrictions 4. The population is large 5. Migration has no effect as many other populations have similar allele frequencies © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele 3. Natural selection can only act on rare homozygous individuals who do not follow dietary restrictions 4. The population is large 5. Migration has no effect as many other populations have similar allele frequencies © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Origin and Nature of Genetic Variation
... 1. EVOLUTION – Mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation that is required for evolutionary change. (Each zygote has approximately 100 new base pair combinations not present in the genome of either parent.) ...
... 1. EVOLUTION – Mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation that is required for evolutionary change. (Each zygote has approximately 100 new base pair combinations not present in the genome of either parent.) ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Lee Lab - University of Wisconsin
... Acquired characters (phenotypic plasticity) are not inherited Traits are inherited via genes, and they do not “blend” with other genes (Darwin was wrong about this one) Genes mutate, resulting in different alleles Evolution occurs at the population level, due to a change in proportions of individual ...
... Acquired characters (phenotypic plasticity) are not inherited Traits are inherited via genes, and they do not “blend” with other genes (Darwin was wrong about this one) Genes mutate, resulting in different alleles Evolution occurs at the population level, due to a change in proportions of individual ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... In paternity lawsuits, blood typing often is used to provide genetic evidence that the alleged father could not be related to the child. For the following mother-child combinations, indicate which blood types could NOT have been the father’s: (1) Mother with O and child with B; (2) Mother with B and ...
... In paternity lawsuits, blood typing often is used to provide genetic evidence that the alleged father could not be related to the child. For the following mother-child combinations, indicate which blood types could NOT have been the father’s: (1) Mother with O and child with B; (2) Mother with B and ...
Honors Biology
... 3. In sexual reproduction, each parent contributes only one allele to the offspring. 4. This is why meiosis takes diploid cells and makes them haploid. The process of meiosis separates the homologous pairs, separating the alleles from each other. Each gamete (sperm and egg) when fused will result wi ...
... 3. In sexual reproduction, each parent contributes only one allele to the offspring. 4. This is why meiosis takes diploid cells and makes them haploid. The process of meiosis separates the homologous pairs, separating the alleles from each other. Each gamete (sperm and egg) when fused will result wi ...
Lecture 3 - Population genetics.key
... P(offspring genotype = Go|parents genotypes = Gm,Gf). Suppose we do not know parents, but we do know P(allele) = p. How to compute: P(person’s genoty ...
... P(offspring genotype = Go|parents genotypes = Gm,Gf). Suppose we do not know parents, but we do know P(allele) = p. How to compute: P(person’s genoty ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.