Client Informed Consent for Genetic Screening
... all variants identified in this screening reflects the current state of scientific understanding at the time the report is issued. In some instances, the classification and interpretation of variants may change as scientific information becomes available. LIMITATIONS OF THIS SCREENING I understand t ...
... all variants identified in this screening reflects the current state of scientific understanding at the time the report is issued. In some instances, the classification and interpretation of variants may change as scientific information becomes available. LIMITATIONS OF THIS SCREENING I understand t ...
Biology 321 Spring 2013 Assignment Set 7 Reading Assignments in
... Ì Problem 5 Males exhibiting FMPP (familial precocious puberty) generally show signs of puberty by age 4. The gene that is mutated in this syndrome codes for the LH (lutenizing hormone) receptor protein. The wild-type receptor protein, when bound to lutenizing hormone, transmits a signal to the ce ...
... Ì Problem 5 Males exhibiting FMPP (familial precocious puberty) generally show signs of puberty by age 4. The gene that is mutated in this syndrome codes for the LH (lutenizing hormone) receptor protein. The wild-type receptor protein, when bound to lutenizing hormone, transmits a signal to the ce ...
The Role of Genetic Diversity in Restoration Success for
... • How extensive are clones within locations? • How many different individuals are there at individual locations? • Is there any evidence for local adaptation within the Bay? – Are occurrences of Vallisneria genetically isolated or are levels of gene flow high enough to prevent differentiation? – Do ...
... • How extensive are clones within locations? • How many different individuals are there at individual locations? • Is there any evidence for local adaptation within the Bay? – Are occurrences of Vallisneria genetically isolated or are levels of gene flow high enough to prevent differentiation? – Do ...
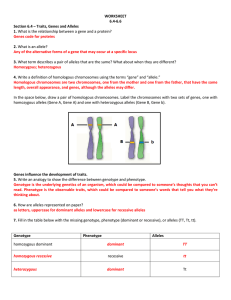
probability & genetics
... 1. Parents pass on characteristics, sexually, through genes to their offspring 2. When there are multiple alleles (appearances) for one gene, some are dominant & some are recessive 3. During formation of parental gametes, alleles are segregated into separate gametes. Each parent is then able to pass ...
... 1. Parents pass on characteristics, sexually, through genes to their offspring 2. When there are multiple alleles (appearances) for one gene, some are dominant & some are recessive 3. During formation of parental gametes, alleles are segregated into separate gametes. Each parent is then able to pass ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... yellow Labrador retrievers instead of the three that would have been predicted by Mendel’s work. ...
... yellow Labrador retrievers instead of the three that would have been predicted by Mendel’s work. ...
Natural Selection - This area is password protected
... likely to survive and reproduce, meaning that their genes are less likely to be passed to the next generation S Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve… ...
... likely to survive and reproduce, meaning that their genes are less likely to be passed to the next generation S Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve… ...
unit 8: mendelian and human genetics
... A) Explain what is meant by a “recessive” and a “dominant” trait. B) Explain the “Law of Segregation” and “Law of Independent Assortment” . C) Explain what effect independent assortment has on the species’ offspring. 3) From chapter 9 pages 178 titled "Support for Mendel’s Conclusions" be able to; A ...
... A) Explain what is meant by a “recessive” and a “dominant” trait. B) Explain the “Law of Segregation” and “Law of Independent Assortment” . C) Explain what effect independent assortment has on the species’ offspring. 3) From chapter 9 pages 178 titled "Support for Mendel’s Conclusions" be able to; A ...
Lecture 3
... Pick up a couple of solutions (at random) and compare their fitness, the better individual is in the mating pool It can work also with groups of individuals picking up a subset of them It does not require a sorting or a knowledge of the fitness distribution over the individuals of the population Lec ...
... Pick up a couple of solutions (at random) and compare their fitness, the better individual is in the mating pool It can work also with groups of individuals picking up a subset of them It does not require a sorting or a knowledge of the fitness distribution over the individuals of the population Lec ...
Full Text - Molecular Biology and Evolution
... *Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, Harvard University Adaptation is often regarded as the sequential fixation of individually, intrinsically beneficial mutations. Contrary to this expectation, we find a surprisingly large number of evolutionary trajectories on which natural selectio ...
... *Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, Harvard University Adaptation is often regarded as the sequential fixation of individually, intrinsically beneficial mutations. Contrary to this expectation, we find a surprisingly large number of evolutionary trajectories on which natural selectio ...
Evolution and Diversity - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... was an “RNA world” some 4 billion years ago. Another hypothesis is termed the protein-first hypothesis. Sidney Fox has shown that amino acids polymerize abiotically (without life) when exposed to dry heat. He suggests that amino acids collected in shallow puddles along the rocky shore, and the heat ...
... was an “RNA world” some 4 billion years ago. Another hypothesis is termed the protein-first hypothesis. Sidney Fox has shown that amino acids polymerize abiotically (without life) when exposed to dry heat. He suggests that amino acids collected in shallow puddles along the rocky shore, and the heat ...
Unit 12 Test Review
... 3. When Mendel crossed a homozygous tall plant with a homozygous short plant the F1 plants inherited a ____________allele from the ________ parent and a_______________ allele from the ___________ parent. 4. Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study the inheritance of _____________. 5. When Mendel cross ...
... 3. When Mendel crossed a homozygous tall plant with a homozygous short plant the F1 plants inherited a ____________allele from the ________ parent and a_______________ allele from the ___________ parent. 4. Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study the inheritance of _____________. 5. When Mendel cross ...
Genetics
... Incomplete Dominance – One allele is not completely dominant over the other. White flower crosses with a red = pink ...
... Incomplete Dominance – One allele is not completely dominant over the other. White flower crosses with a red = pink ...
Inherited Disease and Genetic Testing
... The mutated allele that results in Huntington disease (HD) is dominant over the normal allele. This means that a person with only one mutated allele is not just a carrier, but will also develop the disease associated with the mutation. However, unlike persons with sickle cell disease or CF, those wi ...
... The mutated allele that results in Huntington disease (HD) is dominant over the normal allele. This means that a person with only one mutated allele is not just a carrier, but will also develop the disease associated with the mutation. However, unlike persons with sickle cell disease or CF, those wi ...
what can zebrafish tell us about human skin
... the A allele, while it is extremely rare among West Africans. This is very similar to the MC1R variation seen (or not seen!) among individuals in these populations, which was caused by selection. 6. Sample answer: Not really; although people who are homozygous for the G allele have the highest ...
... the A allele, while it is extremely rare among West Africans. This is very similar to the MC1R variation seen (or not seen!) among individuals in these populations, which was caused by selection. 6. Sample answer: Not really; although people who are homozygous for the G allele have the highest ...
Human evolutionary genomics: ethical and
... other alleles (its haplotype). If an allele spreads rapidly (as under selection), not enough time may have passed for these associations to be broken down. Accordingly, regions with long haplotypes (longer than would be expected for their age) are indicative of selection. Population differences Rela ...
... other alleles (its haplotype). If an allele spreads rapidly (as under selection), not enough time may have passed for these associations to be broken down. Accordingly, regions with long haplotypes (longer than would be expected for their age) are indicative of selection. Population differences Rela ...
Chapter 14 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... dehydration. Deoxygenated HgSS molecules can chemically link to each other, creating chains of molecules - a polymer. In turn, these abnormal elongated hemoglobin polymer structures distort the shape of the whole red blood cell. The abnormal RBC's can damage the vessels around them and the tissues t ...
... dehydration. Deoxygenated HgSS molecules can chemically link to each other, creating chains of molecules - a polymer. In turn, these abnormal elongated hemoglobin polymer structures distort the shape of the whole red blood cell. The abnormal RBC's can damage the vessels around them and the tissues t ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.