04BIO201 Exam 1 key
... be formally possible, give me an answer other than “the albino male was not the biological father of the children”!). The best answer is that this is an example of two genes controlling skin color and duplicative recessive epistasis. Gene A is for the tyrosinase and Gene B is for another gene requir ...
... be formally possible, give me an answer other than “the albino male was not the biological father of the children”!). The best answer is that this is an example of two genes controlling skin color and duplicative recessive epistasis. Gene A is for the tyrosinase and Gene B is for another gene requir ...
Why Sex? — Monte Carlo Simulations of Survival After Catastrophes
... second string of the baby. The sex of the baby is then randomly chosen. When only deleterious mutations are considered, and this is our case, whenever a 1 bit is randomly chosen in the parent genome, it remains equal to 1 in the offspring genome (no mutation occurs). However, if the randomly chosen ...
... second string of the baby. The sex of the baby is then randomly chosen. When only deleterious mutations are considered, and this is our case, whenever a 1 bit is randomly chosen in the parent genome, it remains equal to 1 in the offspring genome (no mutation occurs). However, if the randomly chosen ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Counting Babies or Studying
... Wilson on Natural Selection and the Human Mind • Camus said that the only serious philosophical question is suicide. That is wrong even in the strict sense intended. The biologist, who is concerned with questions of physiology and evolutionary history, realizes that self-knowledge is constrained an ...
... Wilson on Natural Selection and the Human Mind • Camus said that the only serious philosophical question is suicide. That is wrong even in the strict sense intended. The biologist, who is concerned with questions of physiology and evolutionary history, realizes that self-knowledge is constrained an ...
Genome-wide scan with SNPs
... with evidence of linkage found over p-value threshold and by relaxing the stringency (t>4) it generated 984 expression phenotypes, which is 7 times more prone to false positive generation. Considering the regions that are liked to the expression levels to be regulatory regions, they categorised 142 ...
... with evidence of linkage found over p-value threshold and by relaxing the stringency (t>4) it generated 984 expression phenotypes, which is 7 times more prone to false positive generation. Considering the regions that are liked to the expression levels to be regulatory regions, they categorised 142 ...
Genetic Algorithms: A Tutorial
... Always an answer; answer gets better with time Inherently parallel; easily distributed ...
... Always an answer; answer gets better with time Inherently parallel; easily distributed ...
Notes
... o Extra segments of DNA added The Genetic Code & Mutations Mutations can cause a cell to produce an ______________________________protein. This causes the organism’s trait, or _____________________________, to be different from what it normally would have been. Mutations that occur in a ______ ...
... o Extra segments of DNA added The Genetic Code & Mutations Mutations can cause a cell to produce an ______________________________protein. This causes the organism’s trait, or _____________________________, to be different from what it normally would have been. Mutations that occur in a ______ ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 3. In an attempt to breed winter barley that is resistant to barley mild mosaic virus, agricultural researchers cross a susceptible domesticated strain with a resistant wild strain. The F1 plants are all susceptible, but when the F1 plants are crossed with each other, some of the F2 individuals are ...
... 3. In an attempt to breed winter barley that is resistant to barley mild mosaic virus, agricultural researchers cross a susceptible domesticated strain with a resistant wild strain. The F1 plants are all susceptible, but when the F1 plants are crossed with each other, some of the F2 individuals are ...
The Simple Genetic Algorithm Evolutionary Computation BLG602E
... Cmult: expected no. of copies of best individual in population (Note: Typically for populations of size 50 to 100, Cmult=1.2 to 2 is ...
... Cmult: expected no. of copies of best individual in population (Note: Typically for populations of size 50 to 100, Cmult=1.2 to 2 is ...
Genetic Algorithms: A Tutorial
... about problem domain is gained Easy to exploit previous or alternate solutions Flexible building blocks for hybrid applications Substantial history and range of use ...
... about problem domain is gained Easy to exploit previous or alternate solutions Flexible building blocks for hybrid applications Substantial history and range of use ...
References
... Lost alleles are not re-introduced (there is no mutation in the simulation), and there is a finite probability that an allele in any given position will be lost in each generation. When all alleles ...
... Lost alleles are not re-introduced (there is no mutation in the simulation), and there is a finite probability that an allele in any given position will be lost in each generation. When all alleles ...
HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE NSPIRED - Education TI
... Students will perform a simulation and change the environment partway through. This is a nice way to demonstrate how populations can adapt to their environment. Have them set up the following simulation: At the equator, white fur is the dominant mutation, and introducing the mutation after three gen ...
... Students will perform a simulation and change the environment partway through. This is a nice way to demonstrate how populations can adapt to their environment. Have them set up the following simulation: At the equator, white fur is the dominant mutation, and introducing the mutation after three gen ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics
... Certain alleles (forms of a trait) can hide/mask other alleles. These alleles are called dominant alleles and are represented by a capital letter (A). The alleles that may be hidden are called recessive alleles and are represented by the lower case of the same letter (a). Thus, homozygous dominant i ...
... Certain alleles (forms of a trait) can hide/mask other alleles. These alleles are called dominant alleles and are represented by a capital letter (A). The alleles that may be hidden are called recessive alleles and are represented by the lower case of the same letter (a). Thus, homozygous dominant i ...
Study Questions for Chapter 12 –
... Answer: The only untrue statement is (d). Since daughters receive an X chromosome from each of their parents, they can inherit an X-linked dominant disease from either their mother or father. Women who were known to be carriers of the X-linked recessive hemophilia gene were studied to determine the ...
... Answer: The only untrue statement is (d). Since daughters receive an X chromosome from each of their parents, they can inherit an X-linked dominant disease from either their mother or father. Women who were known to be carriers of the X-linked recessive hemophilia gene were studied to determine the ...
Chapter 5: Mendelian Traits and Behavior
... the heterozygote takes on a value somewhere between the two homozygotes, then allele action is said to be partially dominant, incompletely dominant, additive, or codominant, depending on exact value of the heterozygote. Because the genotype AB gives a different phenotype from both genotypes AA and B ...
... the heterozygote takes on a value somewhere between the two homozygotes, then allele action is said to be partially dominant, incompletely dominant, additive, or codominant, depending on exact value of the heterozygote. Because the genotype AB gives a different phenotype from both genotypes AA and B ...
Reconstructing Indian population history
... provide strong evidence for two ancient populations, genetically divergent, that are ancestral to most Indians today. One, the ‘Ancestral North Indians’ (ANI), is genetically close to Middle Easterners, Central Asians, and Europeans, whereas the other, the ‘Ancestral South Indians’ (ASI), is as dist ...
... provide strong evidence for two ancient populations, genetically divergent, that are ancestral to most Indians today. One, the ‘Ancestral North Indians’ (ANI), is genetically close to Middle Easterners, Central Asians, and Europeans, whereas the other, the ‘Ancestral South Indians’ (ASI), is as dist ...
Genetic Algorithms and Evolutionary Strategies 1
... integer in which case we can use a stochastic sampling method, e.g. if reproductive trials for individuals i and j are 1.8 and 1.2 then each will have one copy in the mating pool and the third will be either i or j with remainder probabilities Selection probabilities may not add up to 1.0 in which c ...
... integer in which case we can use a stochastic sampling method, e.g. if reproductive trials for individuals i and j are 1.8 and 1.2 then each will have one copy in the mating pool and the third will be either i or j with remainder probabilities Selection probabilities may not add up to 1.0 in which c ...
SNPs - Biology, Genetics and Bioinformatics Unit
... Decrease failed drug trials, Decrease the time for drug approved by government, Decrease the time and the number of medication on patients ...
... Decrease failed drug trials, Decrease the time for drug approved by government, Decrease the time and the number of medication on patients ...
Concepts and Misconceptions about the Polygenic Additive Model
... values’ in the quantitative genetics literature in the absence of non-additive variation, but initially called ‘essential genotypes’ by Fisher [12]). The model is sometimes called the infinitesimal model, but one does not need an infinite number of variants to approach normality (actually only a sma ...
... values’ in the quantitative genetics literature in the absence of non-additive variation, but initially called ‘essential genotypes’ by Fisher [12]). The model is sometimes called the infinitesimal model, but one does not need an infinite number of variants to approach normality (actually only a sma ...
Diagram 1. For use in Activity 2 Draw the chromosomes, with
... This not only indicates that the trait is recessive, but that it is autosomal recessive. Fathers give their only X to their daughters. That the daughter shows a recessive trait would demand (if it were sex-linked) that she receive an X carrying the recessive allele from each parent. But then the fat ...
... This not only indicates that the trait is recessive, but that it is autosomal recessive. Fathers give their only X to their daughters. That the daughter shows a recessive trait would demand (if it were sex-linked) that she receive an X carrying the recessive allele from each parent. But then the fat ...
t - nslc.wustl.edu
... THE JUKES-CANTOR GENETIC DISTANCE Consider a single nucleotide site that has a probability of mutating per unit time (only neutral mutations are allowed). This model assumes that when a nucleotide site mutates it is equally likely to mutate to any of the three other nucleotide states. Suppose furt ...
... THE JUKES-CANTOR GENETIC DISTANCE Consider a single nucleotide site that has a probability of mutating per unit time (only neutral mutations are allowed). This model assumes that when a nucleotide site mutates it is equally likely to mutate to any of the three other nucleotide states. Suppose furt ...
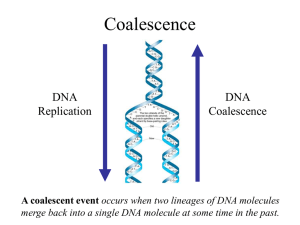
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.