Document
... – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
... – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
ch14_sec1
... – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
... – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
Crusades
... – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
... – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
As Word (text only) - Discover Islamic Art
... Foundation of the kingdom of al-Mu‘izz ibn Badis, which splits from the Fatimid Caliphate of Cairo. ...
... Foundation of the kingdom of al-Mu‘izz ibn Badis, which splits from the Fatimid Caliphate of Cairo. ...
The Crusades! - John Bowne High School
... • Please follow along and fill in your class notes for the day. ...
... • Please follow along and fill in your class notes for the day. ...
Offensive Against Islam
... Retook Antioch, unsuccessful siege to Jerusalem ‐ Treaty with Saladin ...
... Retook Antioch, unsuccessful siege to Jerusalem ‐ Treaty with Saladin ...
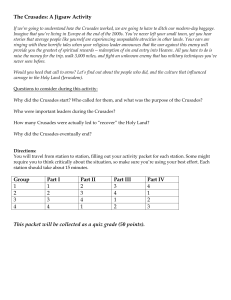
The Crusades: A Jigsaw Activity
... The Children’s Crusade The Children's Crusade is one of the more unusual events, and took place after the Fourth Crusade (1202 to 1204). The Fourth Crusade had been a disaster for the Christians as many crusaders had not even got to the Holy Land, let alone fight for Jerusalem. Many Christians had ...
... The Children’s Crusade The Children's Crusade is one of the more unusual events, and took place after the Fourth Crusade (1202 to 1204). The Fourth Crusade had been a disaster for the Christians as many crusaders had not even got to the Holy Land, let alone fight for Jerusalem. Many Christians had ...
The Childrens Crusade (1160)
... the places appointed for rendezvous. Nothing could restrain them or thwart their purpose. "Even bolts and bars," says an old chronicler, "could not hold them." The movement excited the most diverse views. Some declared that it was inspired by the Holy Spirit, and quoted such Scriptural texts as thes ...
... the places appointed for rendezvous. Nothing could restrain them or thwart their purpose. "Even bolts and bars," says an old chronicler, "could not hold them." The movement excited the most diverse views. Some declared that it was inspired by the Holy Spirit, and quoted such Scriptural texts as thes ...
The Crusades
... The Invaders • In 1093, Byzantine Emperor named Alexius Comnenus ask for help against invaders – THE INVADERS: The Muslim Turks aka Ottoman Turks ...
... The Invaders • In 1093, Byzantine Emperor named Alexius Comnenus ask for help against invaders – THE INVADERS: The Muslim Turks aka Ottoman Turks ...
The Crusades
... The Invaders • In 1093, Byzantine Emperor named Alexius Comnenus ask for help against invaders – THE INVADERS: The Muslim Turks aka Ottoman Turks ...
... The Invaders • In 1093, Byzantine Emperor named Alexius Comnenus ask for help against invaders – THE INVADERS: The Muslim Turks aka Ottoman Turks ...
Editable - Patrick Minges
... Saladin was 26 years old when he first fought beside his uncle against the Crusaders. The Christians held the city of Cairo, and the Muslims wanted them out. Each time Saladin’s army faced the Crusaders they were beaten, until finally, in their fifth battle, the Muslims achieved victory. Saladin’s u ...
... Saladin was 26 years old when he first fought beside his uncle against the Crusaders. The Christians held the city of Cairo, and the Muslims wanted them out. Each time Saladin’s army faced the Crusaders they were beaten, until finally, in their fifth battle, the Muslims achieved victory. Saladin’s u ...
Chapter 10 - Packet (2017)
... Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades Directions: Read Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades (first part only) on page 119 in your textbook. 1. Why did the emperor of the Byzantine Empire appeal to Pope Urban for help in 1095 C.E.? ...
... Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades Directions: Read Section 10.3 – The Story of the Crusades (first part only) on page 119 in your textbook. 1. Why did the emperor of the Byzantine Empire appeal to Pope Urban for help in 1095 C.E.? ...
The Crusades - TeacherV.net
... With thorns, Thine only crown; O sacred Head, what glory, What bliss till now was Thine! Yet, though despised and gory, I joy to call thee mine. ...
... With thorns, Thine only crown; O sacred Head, what glory, What bliss till now was Thine! Yet, though despised and gory, I joy to call thee mine. ...
No Slide Title
... Pillaged on route Wiped out as soon as they entered Asia Minor (Near Nicea in 1096). ...
... Pillaged on route Wiped out as soon as they entered Asia Minor (Near Nicea in 1096). ...
Socratic Seminar: The Crusades Background: Beginning in 1096
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
File
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
THE CRUSADES
... Godfrey of Bouillon, the first king of Jerusalem; Richard the Lionhearted, king of England; Barbarossa, king of Germany; and Philip, king of France. Alexis, emperor of Byzantium, who feared the crusades as much as he needed them. Pope Innocent III who condemned the 4 th crusade. ...
... Godfrey of Bouillon, the first king of Jerusalem; Richard the Lionhearted, king of England; Barbarossa, king of Germany; and Philip, king of France. Alexis, emperor of Byzantium, who feared the crusades as much as he needed them. Pope Innocent III who condemned the 4 th crusade. ...
The First Crusade: The Forgotten Realities - PDXScholar
... Crusade as an aimless expedition in the Middle East that landless younger sons could exploit for their own financial gain. Scholars essentially blame the victory on the division of the Islamic state. Through close examination, however, it is apparent there was a method to the madness. The First Crus ...
... Crusade as an aimless expedition in the Middle East that landless younger sons could exploit for their own financial gain. Scholars essentially blame the victory on the division of the Islamic state. Through close examination, however, it is apparent there was a method to the madness. The First Crus ...
Crusades - Historiasiglo20.org
... England. The Children's Crusade took place after the Fourth Crusade. By the end of the Fourth Crusade (1202 to 1204), it was clear that the Christian crusaders had gained no long term success. In fact, the Fourth Crusade had been a disaster for the Christians as many crusaders had not even got to th ...
... England. The Children's Crusade took place after the Fourth Crusade. By the end of the Fourth Crusade (1202 to 1204), it was clear that the Christian crusaders had gained no long term success. In fact, the Fourth Crusade had been a disaster for the Christians as many crusaders had not even got to th ...
The Crusades - Muslim Population
... In 1144 CE, the Muslims recaptured Edessa. This city was vital for the safety of the Frankish holdings as it guarded their back door. News of the fall of Edessa spread throughout Europe and a second crusade was called by Pope Eugenius III. The Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad III and the French king, Loui ...
... In 1144 CE, the Muslims recaptured Edessa. This city was vital for the safety of the Frankish holdings as it guarded their back door. News of the fall of Edessa spread throughout Europe and a second crusade was called by Pope Eugenius III. The Holy Roman Emperor, Conrad III and the French king, Loui ...
Discipline History Course Title Bachelor of Arts (Omnibus
... Seminar: discussion of primary sources & secondary titles read in advance This seminar examines the so-called ‘First Crusade’ in its 11th- & early 12th-century context through close analysis of contemporary documents & narrative accounts of events (in translation), including several written by crusa ...
... Seminar: discussion of primary sources & secondary titles read in advance This seminar examines the so-called ‘First Crusade’ in its 11th- & early 12th-century context through close analysis of contemporary documents & narrative accounts of events (in translation), including several written by crusa ...
If YOU were there `~
... Crusades Change Europe Although the Crusades failed, they changed Europe forever. Trade between Europe and Asia grew. Europeans who went to the Holy Land learned about products such as apricots, rice, and cotton cloth. Crusaders also brought ideas of Muslim thinkers to Europe. Politics in Europe al ...
... Crusades Change Europe Although the Crusades failed, they changed Europe forever. Trade between Europe and Asia grew. Europeans who went to the Holy Land learned about products such as apricots, rice, and cotton cloth. Crusaders also brought ideas of Muslim thinkers to Europe. Politics in Europe al ...
The impact of the crusades
... Second, crusading played a major role in European territorial expansion. The First Crusade resulted in the formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and easter ...
... Second, crusading played a major role in European territorial expansion. The First Crusade resulted in the formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and easter ...
the impact of the crusades
... Second, crusading played a major role in European territorial expansion. The First Crusade resulted in the formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and easter ...
... Second, crusading played a major role in European territorial expansion. The First Crusade resulted in the formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and easter ...
File
... Clermont in France Crusader armies marched to Jerusalem sacked several cities on their way. In 1099, they took Jerusalem back from the Muslims and massacred the population of ______________________ and __________________________ there. 2nd Crusade The __________________________ easily defeated ...
... Clermont in France Crusader armies marched to Jerusalem sacked several cities on their way. In 1099, they took Jerusalem back from the Muslims and massacred the population of ______________________ and __________________________ there. 2nd Crusade The __________________________ easily defeated ...
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem was a crusader state established in the Southern Levant in 1099 after the First Crusade. The kingdom lasted nearly two hundred years, from 1099 until 1291 when the last remaining possession, Acre, was destroyed by the Mamluks, but its history is divided into two distinct periods. The sometimes so-called First Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted from 1099 to 1187, when it was almost entirely overrun by Saladin. After the subsequent Third Crusade, the kingdom was re-established in Acre in 1192, and lasted until that city's destruction in 1291. This second kingdom is sometimes called the Second Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Kingdom of Acre, after its new capital.