The crusaders - Happy Kids Cooking Healthy
... • In the middle ages there were people from the Catholic church trying to get possession of Jerusalem. They were called the Crusaders. • Muslims occupied Jerusalem and had certain rules for people to follow if they lived there. • In total there were nine crusades, called Holy Wars, here is a graph ...
... • In the middle ages there were people from the Catholic church trying to get possession of Jerusalem. They were called the Crusaders. • Muslims occupied Jerusalem and had certain rules for people to follow if they lived there. • In total there were nine crusades, called Holy Wars, here is a graph ...
Crusade Notes Part 1 and 2
... Crusader primary accounts of cannibalism. Men, women, children, Muslim, Christian, Jews 1099 Siege of Jerusalem six weeks using two 50 foot siege towers the Crusaders scale the wall and again kill all inside. Later Crusades: Under Saladin the first Sultan of Egypt and Syria, the Muslims will recaptu ...
... Crusader primary accounts of cannibalism. Men, women, children, Muslim, Christian, Jews 1099 Siege of Jerusalem six weeks using two 50 foot siege towers the Crusaders scale the wall and again kill all inside. Later Crusades: Under Saladin the first Sultan of Egypt and Syria, the Muslims will recaptu ...
The Crusades
... The Crusades were not an example of Christian aggression. They were a series of just wars in response to Muslim conquest. Crusaders weren't in it to get rich, or for a bit of sport, killing, robbing and pillaging in a faraway ...
... The Crusades were not an example of Christian aggression. They were a series of just wars in response to Muslim conquest. Crusaders weren't in it to get rich, or for a bit of sport, killing, robbing and pillaging in a faraway ...
1. MUSLIMS had conquered portions of Europe and most of the
... SECOND CRUSADE was defeated by SALADIN, SALADIN who led the Muslim forces in recapturing the Crusader States and Jerusalem ...
... SECOND CRUSADE was defeated by SALADIN, SALADIN who led the Muslim forces in recapturing the Crusader States and Jerusalem ...
TCI CH10 Interactive Notebook Answer Key
... As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in Anatolia and Damascus. Third Crusade: Richard I of England led the Third Crusade to retake the Holy L ...
... As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in Anatolia and Damascus. Third Crusade: Richard I of England led the Third Crusade to retake the Holy L ...
TCI CH10 Interactive Notebook Answer Key
... As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in Anatolia and Damascus. Third Crusade: Richard I of England led the Third Crusade to retake the Holy L ...
... As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in Anatolia and Damascus. Third Crusade: Richard I of England led the Third Crusade to retake the Holy L ...
The Second Crusade
... This was the situation in the summer of 1148 when the armies of the Second Crusade began arriving in Jerusalem. Nuradin was in the north, but could come south if needed. Unur of Damascus was trying to be the ally both of Nuradin and of Jerusalem. One faction of the Palestinian barons wished to keep ...
... This was the situation in the summer of 1148 when the armies of the Second Crusade began arriving in Jerusalem. Nuradin was in the north, but could come south if needed. Unur of Damascus was trying to be the ally both of Nuradin and of Jerusalem. One faction of the Palestinian barons wished to keep ...
GLOBAL HISTORY I The Crusades
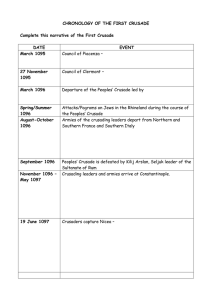
... Christians because it is where Jesus was crucified and where he went to heaven. The Third Crusade was the bloodiest of them all. More than 300,000 Christians and Muslims died. I was glad to go on the Crusade because I was doing God’s work. The First Crusade was called for by Pope Urban II in the yea ...
... Christians because it is where Jesus was crucified and where he went to heaven. The Third Crusade was the bloodiest of them all. More than 300,000 Christians and Muslims died. I was glad to go on the Crusade because I was doing God’s work. The First Crusade was called for by Pope Urban II in the yea ...
Threats and Defence of Crusader Kingdoms4mb
... The premature deaths of the leper king Baldwin IV in 1183 and his nephew Baldwin V in 1186 led to the coronation of his sister Sybilla as Queen of Jerusalem. Her husband and consort Guy de Lusignan was given command of the field army of Jerusalem. After a relatively competent three years in command, ...
... The premature deaths of the leper king Baldwin IV in 1183 and his nephew Baldwin V in 1186 led to the coronation of his sister Sybilla as Queen of Jerusalem. Her husband and consort Guy de Lusignan was given command of the field army of Jerusalem. After a relatively competent three years in command, ...
The crusader States
... Once the crusaders had defeated the Saracens they decided to divide the conquered lands between them. This included Jerusalem, Antioch, Edessa and Tripoli. These four areas became known as the crusader states. Jerusalem soon became a kingdom and claimed to have overlordship of the three other states ...
... Once the crusaders had defeated the Saracens they decided to divide the conquered lands between them. This included Jerusalem, Antioch, Edessa and Tripoli. These four areas became known as the crusader states. Jerusalem soon became a kingdom and claimed to have overlordship of the three other states ...
The Crusades
... Series of military campaigns sanctioned by the Roman Catholic Church during the Middle Ages Intended to stop Muslim expansion in the 10th century Muslim Turks attacked Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire, in 1093 ...
... Series of military campaigns sanctioned by the Roman Catholic Church during the Middle Ages Intended to stop Muslim expansion in the 10th century Muslim Turks attacked Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire, in 1093 ...
File - Mr. Butts World History
... departed. To govern the conquered territory, those who remained established (13) _______________ large western settlements, or Crusader states, in Jerusalem, Edessa, Antioch and Tripoli. Guarded by formidable castles, the Crusader states retained the upper hand in the region until around 1130, when ...
... departed. To govern the conquered territory, those who remained established (13) _______________ large western settlements, or Crusader states, in Jerusalem, Edessa, Antioch and Tripoli. Guarded by formidable castles, the Crusader states retained the upper hand in the region until around 1130, when ...
The Crusades - Beechen Cliff School Humanities Faculty
... thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When this did not hap ...
... thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When this did not hap ...
The Crusades
... Fighting the Seljuk Turks could be profitable – could reclaim land from them Pope Urban II claimed that God spoke to him and told him to go to battle and to kill for control of the “holy land” – “Dues Vult” became the battle cry (means “God wills it” ...
... Fighting the Seljuk Turks could be profitable – could reclaim land from them Pope Urban II claimed that God spoke to him and told him to go to battle and to kill for control of the “holy land” – “Dues Vult” became the battle cry (means “God wills it” ...
The Crusades Teacher Notes
... French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When this did not happen, those wh ...
... French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When this did not happen, those wh ...
Crusades ppt File
... nobles to act to free the Holy Land from the Muslims. -Pope Urban II hoped to increase his power in Europe and put an end to the feud of the “Great Schism” that separated the Roman and Byzantine churches in 1054. ...
... nobles to act to free the Holy Land from the Muslims. -Pope Urban II hoped to increase his power in Europe and put an end to the feud of the “Great Schism” that separated the Roman and Byzantine churches in 1054. ...
Plantagenets, part 2 and Crusades, part 2
... Germans met main Moslem army at Dorylaum (Asia Minor), lost 90% of force French received false news of German victory, marched recklessly, decimated by starvation and raids At Attalia, Louis and nobles took ships to Antioch and left army in Attalia, later decimated Louis and Conrad reached Jerusalem ...
... Germans met main Moslem army at Dorylaum (Asia Minor), lost 90% of force French received false news of German victory, marched recklessly, decimated by starvation and raids At Attalia, Louis and nobles took ships to Antioch and left army in Attalia, later decimated Louis and Conrad reached Jerusalem ...
The Crusades Notes
... the manors and move to cities • Europeans become more interested in travel • People learn about new ...
... the manors and move to cities • Europeans become more interested in travel • People learn about new ...
The Crusades
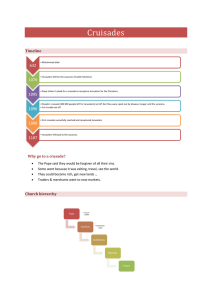
... Causes of the Crusades 1. Muslim invasions of and attacks on Christian lands, especially Jerusalem 2. Desire to spread and unite Christianity 3. Desire to open up trade routes to the East 4. Individuals hoped to gain land and riches 5. Protection of Christian pilgrims headed to Jerusalem ...
... Causes of the Crusades 1. Muslim invasions of and attacks on Christian lands, especially Jerusalem 2. Desire to spread and unite Christianity 3. Desire to open up trade routes to the East 4. Individuals hoped to gain land and riches 5. Protection of Christian pilgrims headed to Jerusalem ...
Church Reform
... 1085: recaptured city of Toledo 1300: Christians controlled almost of all Spain Muslim influence remained ...
... 1085: recaptured city of Toledo 1300: Christians controlled almost of all Spain Muslim influence remained ...
Three major religious groups all claimed Jerusalem in the land of
... attacked Constantinople. They stole statues, money, paintings and jewelry. They burned libraries. They destroyed churches. Their ridiculous excuse was that they needed money to defend Constantinople from the same fate as Jerusalem, as well as to fund the rescue of Jerusalem. The people of Constantin ...
... attacked Constantinople. They stole statues, money, paintings and jewelry. They burned libraries. They destroyed churches. Their ridiculous excuse was that they needed money to defend Constantinople from the same fate as Jerusalem, as well as to fund the rescue of Jerusalem. The people of Constantin ...
The Third Crusade
... rest of the German army defeat Saladin at the Battle of Acre. Phillip and Leopold leave b/c Richard is being difficult slaughters 3,000 Muslims when Saladin is slow to pay. ...
... rest of the German army defeat Saladin at the Battle of Acre. Phillip and Leopold leave b/c Richard is being difficult slaughters 3,000 Muslims when Saladin is slow to pay. ...
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem was a crusader state established in the Southern Levant in 1099 after the First Crusade. The kingdom lasted nearly two hundred years, from 1099 until 1291 when the last remaining possession, Acre, was destroyed by the Mamluks, but its history is divided into two distinct periods. The sometimes so-called First Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted from 1099 to 1187, when it was almost entirely overrun by Saladin. After the subsequent Third Crusade, the kingdom was re-established in Acre in 1192, and lasted until that city's destruction in 1291. This second kingdom is sometimes called the Second Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Kingdom of Acre, after its new capital.