VOCABAULARY LIST CHAPTER 8
... 19. Meiosis – a process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number by two division of the nucleus, which results in the production of sex cells 20. Metaphase – one of the stages of mitosis and meiosis, during which all of the chromosomes move to th ...
... 19. Meiosis – a process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number by two division of the nucleus, which results in the production of sex cells 20. Metaphase – one of the stages of mitosis and meiosis, during which all of the chromosomes move to th ...
Conservation of a rare alpine plant (Prenanthes boottii) in the face of
... These data indicate that the Vermont and Maine populations may have increased vulnerability due to low reproductive rates. P. boottii primarily reproduces clonally, but sexual reproduction is important for longer distance dispersal and maintenance of genetic diversity within populations. The New Yor ...
... These data indicate that the Vermont and Maine populations may have increased vulnerability due to low reproductive rates. P. boottii primarily reproduces clonally, but sexual reproduction is important for longer distance dispersal and maintenance of genetic diversity within populations. The New Yor ...
Homologous Chromosomes
... for those located on the same chromosome; this allows alleles to assort independently; genes linked together on same chromosome are inherited together, therefore they are called ______________ _________ Telophase I- cell membrane pinches in; each new cell will have ____ chromosomes; however due to _ ...
... for those located on the same chromosome; this allows alleles to assort independently; genes linked together on same chromosome are inherited together, therefore they are called ______________ _________ Telophase I- cell membrane pinches in; each new cell will have ____ chromosomes; however due to _ ...
5-1 outline answers genetics Mendel and his peas
... 1. Mendel’s crosses between true-breeding plants with purple flowers produced plants ...
... 1. Mendel’s crosses between true-breeding plants with purple flowers produced plants ...
Linnaeus as Biologist. The Importance and
... gave 1,870,000 hits. Ice bear, a wrong translation of the name to English gave 163,000 hits. For the Latin name, I found four versions: Ursus maritimus (260,000 hits), Ursus arcticus (47 hits), Thalarctos maritimus (24,300 hits) and Thalarctus maritimus (37 hits). Two of these names are clearly mist ...
... gave 1,870,000 hits. Ice bear, a wrong translation of the name to English gave 163,000 hits. For the Latin name, I found four versions: Ursus maritimus (260,000 hits), Ursus arcticus (47 hits), Thalarctos maritimus (24,300 hits) and Thalarctus maritimus (37 hits). Two of these names are clearly mist ...
1. Explain why organisms only reproduce their own
... which results from the transmission of genes from parents to offspring Because they share similar genes, offspring more closely resemble their parents or close relatives than others ...
... which results from the transmission of genes from parents to offspring Because they share similar genes, offspring more closely resemble their parents or close relatives than others ...
1 - life.illinois.edu
... 35. Mendel based his explanations/hypotheses/theories of genetic inheritance on a. the patterns of inheritance of chromosomes during mitosis. b. the patterns of inheritance of chromosomes during meiosis. c. mathematical models of the number of factors required to explain his crossing results. d. a d ...
... 35. Mendel based his explanations/hypotheses/theories of genetic inheritance on a. the patterns of inheritance of chromosomes during mitosis. b. the patterns of inheritance of chromosomes during meiosis. c. mathematical models of the number of factors required to explain his crossing results. d. a d ...
S7L2_Genetics and S7L5_Theory of Evolution (Thrower)
... B. other living things can look like clams. C. clams became extinct, and then new ones grew. D. clams have been on Earth for a very long time. 20. Polar bears and brown bears are related. Over time, polar bears and brown bears have developed different appearances. Which of these MOST LIKELY caused t ...
... B. other living things can look like clams. C. clams became extinct, and then new ones grew. D. clams have been on Earth for a very long time. 20. Polar bears and brown bears are related. Over time, polar bears and brown bears have developed different appearances. Which of these MOST LIKELY caused t ...
Document
... 20. Incomplete dominance- 2 alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. They both contribute to the phenotype In 4 O’clock flowers Ex. Red x white flowers = pink ...
... 20. Incomplete dominance- 2 alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. They both contribute to the phenotype In 4 O’clock flowers Ex. Red x white flowers = pink ...
do not open the examination paper until you are told by the
... As the vascular cambium divides, differentiation of cambium cells toward the exterior of the cambium layer gives rise to the phloem. As the vascular cambium divides, differentiation of cambium cells toward the exterior of the cambium layer gives rise to the xylem. As the vascular cambium divides, di ...
... As the vascular cambium divides, differentiation of cambium cells toward the exterior of the cambium layer gives rise to the phloem. As the vascular cambium divides, differentiation of cambium cells toward the exterior of the cambium layer gives rise to the xylem. As the vascular cambium divides, di ...
WINK Meiosis and Genetics
... Theme: Sex cells are formed by a process of cell division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is halved after replication. With the exception of sex chromosomes, for each chromosome in the body cells of a multicellular organism, there is a second similar, but not identical, chromosome. Altho ...
... Theme: Sex cells are formed by a process of cell division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is halved after replication. With the exception of sex chromosomes, for each chromosome in the body cells of a multicellular organism, there is a second similar, but not identical, chromosome. Altho ...
lecture 16 - reproductive isolation - Cal State LA
... Less related species can’t hybridize (more fully isolated), so they aren’t under selection to spawn at different times ...
... Less related species can’t hybridize (more fully isolated), so they aren’t under selection to spawn at different times ...
Chapter 13
... determining the recombination frequency between a gene and an anonymous marker Anonymous markers such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be detected by molecular techniques. ...
... determining the recombination frequency between a gene and an anonymous marker Anonymous markers such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be detected by molecular techniques. ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype. • Mendel studied autosomal gene traits, like hair texture. ...
... Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype. • Mendel studied autosomal gene traits, like hair texture. ...
Meiosis Student Notes • Organisms have tens of thousands of
... A cell that contains ____________ of each kind of chromosome is called a haploid cell. ...
... A cell that contains ____________ of each kind of chromosome is called a haploid cell. ...
Speciation - OpenStax CNX
... occurs occasionally in animals, most chromosomal abnormalities in animals are lethal; it takes place most commonly in plants. Scientists have discovered more than 1/2 of all plant species studied relate back to a species evolved through polyploidy. Sympatric speciation may also take place in ways ot ...
... occurs occasionally in animals, most chromosomal abnormalities in animals are lethal; it takes place most commonly in plants. Scientists have discovered more than 1/2 of all plant species studied relate back to a species evolved through polyploidy. Sympatric speciation may also take place in ways ot ...
Print Preview - D:\Temp\e3temp_3492\.aptcache\aea03492/tfa03492
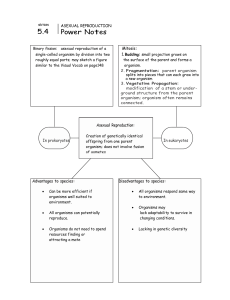
... Binary fission: asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism by division into two roughly equal parts; may sketch a figure similar to the Visual Vocab on page148 ...
... Binary fission: asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism by division into two roughly equal parts; may sketch a figure similar to the Visual Vocab on page148 ...
Exam Review Questions Part IIof2
... inherit the genes for blond hair, while other individuals with blood group A may inherit the genes for brown hair. This can be explained by the principle of A. dominance B. multiple alleles C. independent assortment D. incomplete dominance ...
... inherit the genes for blond hair, while other individuals with blood group A may inherit the genes for brown hair. This can be explained by the principle of A. dominance B. multiple alleles C. independent assortment D. incomplete dominance ...
BIOL 1406 chapter 13 assessment: Modern Understanding of
... 6.What is the term for the failure of chromosome separation in meiosis? Nondisjunction Genetic linkage Translocations Mutations 7.Which of the following statements about nondisjunction is true? Nondisjunction only results in gametes with n+1 or n-1 chromosomes Nondisjunction occurring during meiosis ...
... 6.What is the term for the failure of chromosome separation in meiosis? Nondisjunction Genetic linkage Translocations Mutations 7.Which of the following statements about nondisjunction is true? Nondisjunction only results in gametes with n+1 or n-1 chromosomes Nondisjunction occurring during meiosis ...
Meiosis
... Each organism must inherit one copy of every gene from both parents. Each organism has 2 complete sets of genes. Those two sets must be separated so that each gamete produced contains just one set of genes. ...
... Each organism must inherit one copy of every gene from both parents. Each organism has 2 complete sets of genes. Those two sets must be separated so that each gamete produced contains just one set of genes. ...
Genetics-Chapter-10with
... Metaphase II-individual chromosomes line up at the equatorial plane Anaphase II-centromeres of each chromosome divides allowing the sister chromatids to be pulled apart in an equational division (mitosis-like) by spindle fibers. Telophase II-Cytokinesis divides each cell into 2 progeny cells o ...
... Metaphase II-individual chromosomes line up at the equatorial plane Anaphase II-centromeres of each chromosome divides allowing the sister chromatids to be pulled apart in an equational division (mitosis-like) by spindle fibers. Telophase II-Cytokinesis divides each cell into 2 progeny cells o ...
CHERCHER PREPARATORY SCHOOL Department of Natural
... Worksheet on Genetic crosses for Grade 12 Natural Science Students, 2005/2012 1. If a plant cell having 16 chromosomes undergoes meiotic cell division, how many chromosomes would the resulting daughter cells have? 2. What percentage of tall plants results from a cross between hybrid tall and pure sh ...
... Worksheet on Genetic crosses for Grade 12 Natural Science Students, 2005/2012 1. If a plant cell having 16 chromosomes undergoes meiotic cell division, how many chromosomes would the resulting daughter cells have? 2. What percentage of tall plants results from a cross between hybrid tall and pure sh ...
無投影片標題 - MADANIA
... studying seven traits: plant height, pod shape, pod color, seed shape, seed color, flower color, and flower location. • Pea plants develop individuals that are homozygous for particular characteristics. These populations are known as pure lines. ...
... studying seven traits: plant height, pod shape, pod color, seed shape, seed color, flower color, and flower location. • Pea plants develop individuals that are homozygous for particular characteristics. These populations are known as pure lines. ...
Hybrid (biology)

In biology a hybrid, also known as cross breed, is the result of mixing, through sexual reproduction, two animals or plants of different breeds, varieties, species or genera. Using genetic terminology, it may be defined as follows. Hybrid generally refers to any offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals, which usually will result in a high degree of heterozygosity, though hybrid and heterozygous are not, strictly speaking, synonymous. a genetic hybrid carries two different alleles of the same gene a structural hybrid results from the fusion of gametes that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities a numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes a permanent hybrid is a situation where only the heterozygous genotype occurs, because all homozygous combinations are lethal.From a taxonomic perspective, hybrid refers to: Offspring resulting from the interbreeding between two animal species or plant species. See also hybrid speciation. Hybrids between different subspecies within a species (such as between the Bengal tiger and Siberian tiger) are known as intra-specific hybrids. Hybrids between different species within the same genus (such as between lions and tigers) are sometimes known as interspecific hybrids or crosses. Hybrids between different genera (such as between sheep and goats) are known as intergeneric hybrids. Extremely rare interfamilial hybrids have been known to occur (such as the guineafowl hybrids). No interordinal (between different orders) animal hybrids are known. The third type of hybrid consists of crosses between populations, breeds or cultivars within a single species. This meaning is often used in plant and animal breeding, where hybrids are commonly produced and selected, because they have desirable characteristics not found or inconsistently present in the parent individuals or populations.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑