and the Crusades - Norwell Public Schools
... hese negotiations continued till our men had procured the money and the number of prisoners that they were to deliver to the Christians at the end of the first period in accordance with the treaty. The first instalment was to consist of the Holy Cross, 100,000 dinars [unit of money] and 1,600 prisoner ...
... hese negotiations continued till our men had procured the money and the number of prisoners that they were to deliver to the Christians at the end of the first period in accordance with the treaty. The first instalment was to consist of the Holy Cross, 100,000 dinars [unit of money] and 1,600 prisoner ...
Digital Presentation The Crusades
... was crowned Pope in 1088 at the age of 46. We may never know what was said by the Pope on November 27th, 1095, as the many accounts of that speech are varied. More important, however are the reasons the crusade was called in the first place. ...
... was crowned Pope in 1088 at the age of 46. We may never know what was said by the Pope on November 27th, 1095, as the many accounts of that speech are varied. More important, however are the reasons the crusade was called in the first place. ...
Socratic Seminar: The Crusades Background: Beginning in 1096
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
Lesson Plan #79
... Men and women, knights and peasants, answered the Pope’s call. People from all over Western Europe left their homes to reclaim the Holy Land of Palestine for Christianity. These people, who agreed to fight the Muslims, were known as Crusaders (people who fought in the Crusades). Many of these Crusad ...
... Men and women, knights and peasants, answered the Pope’s call. People from all over Western Europe left their homes to reclaim the Holy Land of Palestine for Christianity. These people, who agreed to fight the Muslims, were known as Crusaders (people who fought in the Crusades). Many of these Crusad ...
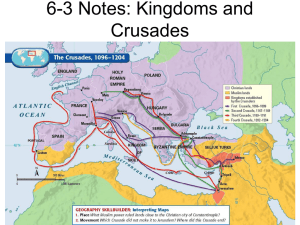
6-3 Kings and Crusades Notes
... 1480 - Ivan finally drove the Mongols out of Russia Expanded his territory to the north and west too before dying in 1505 ...
... 1480 - Ivan finally drove the Mongols out of Russia Expanded his territory to the north and west too before dying in 1505 ...
The Crusades
... traveled by sea to the Holy Land with their forces, Frederick’s army was too large and was forced to march overland. Moving through Hungary, Serbia, and the Byzantine Empire, they crossed the Bosporus into Anatolia. After fighting two battles, they arrived at the Saleph River in southeast Anatol ...
... traveled by sea to the Holy Land with their forces, Frederick’s army was too large and was forced to march overland. Moving through Hungary, Serbia, and the Byzantine Empire, they crossed the Bosporus into Anatolia. After fighting two battles, they arrived at the Saleph River in southeast Anatol ...
File
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
... petty territorial disputes The king or emperor of any region - was quarrelling over investiture (one of those mangy disputes where the king and pope are fighting over the election of bishops) Byzantines are rapidly losing land to the Muslims So what is all the trouble… Christians have made pilgrimag ...
The Crusades of the Holy Roman Empire
... Holy Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire respectively, believed in their own eyes that they were Christian Empires. The Crusades. The Crusades were military expeditions, organized mainly to recapture Palestine during the Middle Ages. Palestine, also called the Holy Land, was important to Christians be ...
... Holy Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire respectively, believed in their own eyes that they were Christian Empires. The Crusades. The Crusades were military expeditions, organized mainly to recapture Palestine during the Middle Ages. Palestine, also called the Holy Land, was important to Christians be ...
Why the Crusades Failed? NarratiNg the episode aFter the Fall oF
... ii. Among the crusaders, only 20 percent were able to return home; the rest died from wounds or were killed in the fighting.4 The property they left in Europe was handled by local bishops and churches and many were desperate to gain ...
... ii. Among the crusaders, only 20 percent were able to return home; the rest died from wounds or were killed in the fighting.4 The property they left in Europe was handled by local bishops and churches and many were desperate to gain ...
Middle Ages - Crusades
... Palestine, the land where Christ was born. • Several crusades (9 officially) between 1096 and 1291 failed to win the Holy Land, but nevertheless had important results for the people of Western Europe. ...
... Palestine, the land where Christ was born. • Several crusades (9 officially) between 1096 and 1291 failed to win the Holy Land, but nevertheless had important results for the people of Western Europe. ...
China, Byzantine Empire, Islamic Empire, and The Crusades Test
... D. Many of the rulers of the dynasties were related to previous rulers so it allowed the Chinese to trust them as their leaders. ...
... D. Many of the rulers of the dynasties were related to previous rulers so it allowed the Chinese to trust them as their leaders. ...
Chapter 5—Fiefdom and Monastery - Wolverton
... Pope Urban II started the First Crusade for various reasons. One was to recapture shrines of Christianity in the Holy Land that now were under Arab Muslims starting in 638. However, the issue of primogeniture was also a main reason. Under primogeniture, only the first born male inherited the family ...
... Pope Urban II started the First Crusade for various reasons. One was to recapture shrines of Christianity in the Holy Land that now were under Arab Muslims starting in 638. However, the issue of primogeniture was also a main reason. Under primogeniture, only the first born male inherited the family ...
Powerpoint-Arabic/Church reform and the crusades
... Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states ...
... Pope promises Crusaders who die a place in heaven First Crusade: three armies gather at Constantinople in 1097 Crusaders capture Jerusalem in 1099 Captured lands along coast divided into four Crusader states ...
The Crusades were a series of wars during the Middle Ages where
... retake control of Jerusalem and the Holy Land from the Muslims. Why did they want to control Jerusalem? Jerusalem was important to a number of religions during the Middle Ages. It was important to Jewish people as it was the site of the original temple to God built by King Solomon. It was important ...
... retake control of Jerusalem and the Holy Land from the Muslims. Why did they want to control Jerusalem? Jerusalem was important to a number of religions during the Middle Ages. It was important to Jewish people as it was the site of the original temple to God built by King Solomon. It was important ...
Section 1 The High Middle Ages
... • Jerusalem in control of North African Muslims, Fatimids, late 1000s ...
... • Jerusalem in control of North African Muslims, Fatimids, late 1000s ...
Hist Lab SS.912.W.3.7 - socialsciences dadeschools net
... Source 3 – Excerpt from Ibn al-Athir’s account of the First Crusade, 1231 Ibn al-Athir (1160-1233) was an Arab historian who wrote a history of the first three crusades, though he only witnessed the third one. The passage below is a modified excerpt from his account of the siege of Jerusalem during ...
... Source 3 – Excerpt from Ibn al-Athir’s account of the First Crusade, 1231 Ibn al-Athir (1160-1233) was an Arab historian who wrote a history of the first three crusades, though he only witnessed the third one. The passage below is a modified excerpt from his account of the siege of Jerusalem during ...
Salah al-Din ~ Muslim
... now controlled Jerusalem, they never succeeded in chasing all the crusaders out of the Holy Land. Some crusader fortresses outside Jerusalem remained, and these helped the Christians to begin the Third Crusade two years later. The Third Crusade was difficult for Salah al-Din and his army. The crusad ...
... now controlled Jerusalem, they never succeeded in chasing all the crusaders out of the Holy Land. Some crusader fortresses outside Jerusalem remained, and these helped the Christians to begin the Third Crusade two years later. The Third Crusade was difficult for Salah al-Din and his army. The crusad ...
The Social Structure of the First Crusade Conor Kostick Arachne ID
... weapons, obtained freedom in the ranks of the army of God. Among the crowds were women, also present in their thousands. The presence of so many women dismayed the senior clergy, but popular preachers distributed alms to them, so that they could find husbands and protectors. Some women, though, had ...
... weapons, obtained freedom in the ranks of the army of God. Among the crowds were women, also present in their thousands. The presence of so many women dismayed the senior clergy, but popular preachers distributed alms to them, so that they could find husbands and protectors. Some women, though, had ...
HA Ch. 11 Historic People of the Crusades Info
... the crusaders was his intense devotion to Islam. An extremely religious man, he considered Christians and Jews spiritually similar to Muslims since they shared the belief in one God. Although he was a skilled and experienced soldier, Usamah did not put much faith in the value of military planning. “ ...
... the crusaders was his intense devotion to Islam. An extremely religious man, he considered Christians and Jews spiritually similar to Muslims since they shared the belief in one God. Although he was a skilled and experienced soldier, Usamah did not put much faith in the value of military planning. “ ...
The Crusades Predictions
... you think sacked Constantinople, Christians or Muslims? Explain. Give your self a point if you said the Christian Crusaders. Give yourself 5 points if you said that the Crusaders saw things that they did not have because they were coming from Western Europe in the Middle Ages. They decided to steal ...
... you think sacked Constantinople, Christians or Muslims? Explain. Give your self a point if you said the Christian Crusaders. Give yourself 5 points if you said that the Crusaders saw things that they did not have because they were coming from Western Europe in the Middle Ages. They decided to steal ...
The Crusades: A Jigsaw Activity
... even got to the Holy Land, let alone fight for Jerusalem. Many Christians had used the crusade as a means to plunder valuable goods from abroad; however, the Children’s Crusade seemed to put some Christian belief back into crusading. In 1212, two groups – one from France, the other from Germany – se ...
... even got to the Holy Land, let alone fight for Jerusalem. Many Christians had used the crusade as a means to plunder valuable goods from abroad; however, the Children’s Crusade seemed to put some Christian belief back into crusading. In 1212, two groups – one from France, the other from Germany – se ...
Was there a curse on King Tutankhamen`s tomb?
... In 600 CE, Arabs entered the city and took control. The Arabs allowed Christian and Jewish pilgrims to visit Jerusalem. In fact, Jews and Christians could live in Palestine as long as they paid their taxes like everyone else. The First Crusade: The Problem: Around 1095, a new group of Arabs took con ...
... In 600 CE, Arabs entered the city and took control. The Arabs allowed Christian and Jewish pilgrims to visit Jerusalem. In fact, Jews and Christians could live in Palestine as long as they paid their taxes like everyone else. The First Crusade: The Problem: Around 1095, a new group of Arabs took con ...
Crusades - Summary and King Richard powerpoint
... When the news reached Europe that Jerusalem and Acre had fallen, Richard was quick to take up the challenge of a crusade. Historians speculate that he had three main reasons for taking up the cross- to take part in the adventure of war, to have his name immortalised by the bards and troubadours of t ...
... When the news reached Europe that Jerusalem and Acre had fallen, Richard was quick to take up the challenge of a crusade. Historians speculate that he had three main reasons for taking up the cross- to take part in the adventure of war, to have his name immortalised by the bards and troubadours of t ...
From the 11th century until the beginning of the
... “Turn-Over” Pope Eugen III. calls for another crusade, King Ludwig VII. (France) becomes the leader of the mission Bernhard from Clairveaux, Hungary, Byanz, Sicilia and Germany declare their support Aim: recapturing Edessa, finally ended: Damascus crusaders were not successful ...
... “Turn-Over” Pope Eugen III. calls for another crusade, King Ludwig VII. (France) becomes the leader of the mission Bernhard from Clairveaux, Hungary, Byanz, Sicilia and Germany declare their support Aim: recapturing Edessa, finally ended: Damascus crusaders were not successful ...
First Crusade

The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a number of crusades that attempted to capture the Holy Lands, called by Pope Urban II in 1095. It started as a widespread pilgrimage in western christendom and ended as a military expedition by Roman Catholic Europe to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquests of the Levant (632–661), ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem in 1099. It was launched on 27 November 1095 by Pope Urban II with the primary goal of responding to an appeal from Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos, who requested that western volunteers come to his aid and help to repel the invading Seljuq Turks from Anatolia. An additional goal soon became the principal objective—the Christian reconquest of the sacred city of Jerusalem and the Holy Land and the freeing of the Eastern Christians from Muslim rule.During the crusade, knights, peasants and serfs from many nations of Western Europe travelled over land and by sea, first to Constantinople and then on towards Jerusalem. The Crusaders arrived at Jerusalem, launched an assault on the city, and captured it in July 1099, massacring many of the city's Muslim, Christian, and Jewish inhabitants. They also established the crusader states of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, and the County of Edessa.The First Crusade was followed by the Second to the Ninth Crusades. It was also the first major step towards reopening international trade in the West since the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Because the First Crusade was largely concerned with Jerusalem, a city which had not been under Christian dominion for 461 years, and the crusader army had refused to return the land to the control of the Byzantine Empire, the status of the First Crusade as defensive or as aggressive in nature remains controversial.