History of the Crusades
... pogroms. That may be. But if so, those roots are far deeper and more widespread than the Crusades. Jews perished during the Crusades, but the purpose of the Crusades was not to kill Jews. Quite the contrary: Popes, bishops, and preachers made it clear that the Jews of Europe were to be left unmolest ...
... pogroms. That may be. But if so, those roots are far deeper and more widespread than the Crusades. Jews perished during the Crusades, but the purpose of the Crusades was not to kill Jews. Quite the contrary: Popes, bishops, and preachers made it clear that the Jews of Europe were to be left unmolest ...
Transcript of Lesson Audio
... The pope also had mixed motives for his support of the Crusades. Urban hoped to increase his power in Europe and perhaps heal to split between the Roman and Byzantine churches. He also hoped that the Crusades would set Christian knights to fighting Muslims instead of one another. The First Crusade – ...
... The pope also had mixed motives for his support of the Crusades. Urban hoped to increase his power in Europe and perhaps heal to split between the Roman and Byzantine churches. He also hoped that the Crusades would set Christian knights to fighting Muslims instead of one another. The First Crusade – ...
From the 11th century until the beginning of the
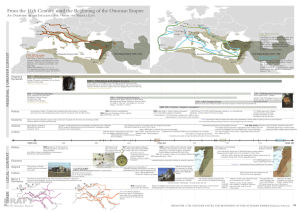
... Chief “Seljuk” of The Oghuz, sun of Duqaq, a turkish tribe from Asia, establishes the so named dynasty, Sunnite Muslims, big military power, invasing in Muslimic territory, support Calif from Bagdad versus the Fatimids, „Damascus: City of Monuments“ ...
... Chief “Seljuk” of The Oghuz, sun of Duqaq, a turkish tribe from Asia, establishes the so named dynasty, Sunnite Muslims, big military power, invasing in Muslimic territory, support Calif from Bagdad versus the Fatimids, „Damascus: City of Monuments“ ...
Document
... o Christians: Pope Urban II promised immediate salvation for all Christians killed while fighting in the Crusades. ...
... o Christians: Pope Urban II promised immediate salvation for all Christians killed while fighting in the Crusades. ...
Middle Middle Ages - Osborne High School
... Last successful invasion of England; Battle of Hastings ...
... Last successful invasion of England; Battle of Hastings ...
The Talisman
... Ayyubid Dynasty (r. 1171-1341) • Preserve Salah al-Din’s Sultanate • Egypt as new economic center • Egypt as new focus of crusade – 1197, 1217, 1229, and 1249 ...
... Ayyubid Dynasty (r. 1171-1341) • Preserve Salah al-Din’s Sultanate • Egypt as new economic center • Egypt as new focus of crusade – 1197, 1217, 1229, and 1249 ...
Challenges to Islam
... Urban to call for a “crusade” to recapture the Holy Land from the Muslims First Crusade (1096-1099) Captures Jerusalem in 1099 Crusader armies establish kingdoms in Syria and Palestine When the Crusaders capture Jerusalem, they celebrate by killing all Muslims, Jews, and even Orthodox Christia ...
... Urban to call for a “crusade” to recapture the Holy Land from the Muslims First Crusade (1096-1099) Captures Jerusalem in 1099 Crusader armies establish kingdoms in Syria and Palestine When the Crusaders capture Jerusalem, they celebrate by killing all Muslims, Jews, and even Orthodox Christia ...
antisemitism_class_i-7
... Crusades. 1096 is the year of the first Crusade (Rashi was 56 and in the prime of his writing years). The sudden outburst of violence against the Jewish communities of Europe at the hands nobles, ...
... Crusades. 1096 is the year of the first Crusade (Rashi was 56 and in the prime of his writing years). The sudden outburst of violence against the Jewish communities of Europe at the hands nobles, ...
Year 12 to 13 History Crusades Coursework
... changed and the role played by the Fourth Crusade in this. The concept of crusading as a method used against fellow Christians could be considered along with growing ...
... changed and the role played by the Fourth Crusade in this. The concept of crusading as a method used against fellow Christians could be considered along with growing ...
If YOU were there `~
... Although the Crusades failed, they changed Europe forever. Trade between Europe and Asia grew. Europeans who went to the Holy Land learned about products such as apricots, rice, and cotton cloth. Crusaders also brought ideas of Muslim thinkers to Europe. Politics in Europe also changed. Some kings i ...
... Although the Crusades failed, they changed Europe forever. Trade between Europe and Asia grew. Europeans who went to the Holy Land learned about products such as apricots, rice, and cotton cloth. Crusaders also brought ideas of Muslim thinkers to Europe. Politics in Europe also changed. Some kings i ...
The Arab World - Cloudfront.net
... •Jews, Muslims and Christians all lived together harmoniously. •Christians on pilgrimages to Jerusalem were freely allowed across to the Holy Places •When the Crusades arrived in Northern Turkey, the carnage began. •Lycea was captured and looted. •babies cut to pieces; •old people were tortured. •Un ...
... •Jews, Muslims and Christians all lived together harmoniously. •Christians on pilgrimages to Jerusalem were freely allowed across to the Holy Places •When the Crusades arrived in Northern Turkey, the carnage began. •Lycea was captured and looted. •babies cut to pieces; •old people were tortured. •Un ...
Reading Crusaders at the Wall
... “I am sorry. I want to believe,” said Robert. “But there are other things. I am very disappointed in the actions of many men on our side. They seem much more interested in looting the places they visit than in capturing the Holy Land for our religion. In our travels we were often cheated by our fell ...
... “I am sorry. I want to believe,” said Robert. “But there are other things. I am very disappointed in the actions of many men on our side. They seem much more interested in looting the places they visit than in capturing the Holy Land for our religion. In our travels we were often cheated by our fell ...
The Crusades
... • Why might so many people have taken part in the Crusades, not only knights and soldiers but also ordinary people and even children? ...
... • Why might so many people have taken part in the Crusades, not only knights and soldiers but also ordinary people and even children? ...
Church Reform and the Crusades
... Hoped to win control of key trade routes to Asia from Muslim traders ...
... Hoped to win control of key trade routes to Asia from Muslim traders ...
THE CRUSADES
... The effects of the Crusades A legacy of distrust between Christians Summarize the causes Analyze the effects will impact the structure of and Muslims was left by the Crusades of the Crusades. of ...
... The effects of the Crusades A legacy of distrust between Christians Summarize the causes Analyze the effects will impact the structure of and Muslims was left by the Crusades of the Crusades. of ...
File - Ms. Peterman`s Class
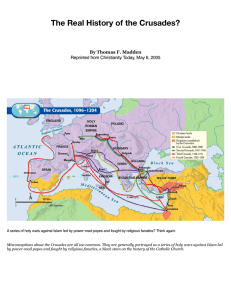
... ■ 1093, the Byzantine emperor Alexius Comnenus asked for help from Robert, Count of Flanders in fighting the Muslim Turks; they were threatening to conquer his capital. ■ Pope Urban II also read the letter and called for a crusade at the Council of Clermont to gain control of the Holy Land. ...
... ■ 1093, the Byzantine emperor Alexius Comnenus asked for help from Robert, Count of Flanders in fighting the Muslim Turks; they were threatening to conquer his capital. ■ Pope Urban II also read the letter and called for a crusade at the Council of Clermont to gain control of the Holy Land. ...
Hist Lab SS.912.W.3.7 - socialsciences dadeschools net
... Ibn al-Athir (1160-1233) was an Arab historian who wrote a history of the first three crusades, though he only witnessed the third one. The passage below is a modified excerpt from his account of the siege of Jerusalem during the First Crusade. Jerusalem was taken from the north on the morning of Ju ...
... Ibn al-Athir (1160-1233) was an Arab historian who wrote a history of the first three crusades, though he only witnessed the third one. The passage below is a modified excerpt from his account of the siege of Jerusalem during the First Crusade. Jerusalem was taken from the north on the morning of Ju ...
Why the Crusades Failed? NarratiNg the episode aFter the Fall oF
... When news of Ṣalaḥ al-Dīn’s death and the division of the empire among his three sons reached Europe, the then Pope Innocent III (1198-1216) began preparations for a new Crusade. On 15 August 1198, he issued a crusading bull, but he was not able to convince and recruit any kings - even Richard and P ...
... When news of Ṣalaḥ al-Dīn’s death and the division of the empire among his three sons reached Europe, the then Pope Innocent III (1198-1216) began preparations for a new Crusade. On 15 August 1198, he issued a crusading bull, but he was not able to convince and recruit any kings - even Richard and P ...
The Crusades
... Turks were a Central Asian people who had been migrating into Muslim lands for centuries. The Seljuks were named for a Turkish chieftain who converted to Islam in the mid-10th century. In 1055, his descendants took control of the Abbasid capital of Baghdad. A Seljuk sultan now ruled the old Abbasid ...
... Turks were a Central Asian people who had been migrating into Muslim lands for centuries. The Seljuks were named for a Turkish chieftain who converted to Islam in the mid-10th century. In 1055, his descendants took control of the Abbasid capital of Baghdad. A Seljuk sultan now ruled the old Abbasid ...
Crusades
... fight the Muslim leader (Saladin). • King Richard and Saladin admired each other and made compromises. Though King Richard conquered some lands, he left with Jerusalem in Muslim hands. ...
... fight the Muslim leader (Saladin). • King Richard and Saladin admired each other and made compromises. Though King Richard conquered some lands, he left with Jerusalem in Muslim hands. ...
First Crusade
... Second Crusade led by King Louis VII (France) and King Conrad III (Germany) Turks and Saladin take back all land captured by European Christian Crusaders during First Crusade. ...
... Second Crusade led by King Louis VII (France) and King Conrad III (Germany) Turks and Saladin take back all land captured by European Christian Crusaders during First Crusade. ...
BalthazarMonastery.com Roman Catholic Crusades III In May 1098
... Among the crusaders in the Crusade of 1101 were Stephen II, Count of Blois and Hugh of Vermandois, both of whom had returned home before reaching Jerusalem. This crusade was almost annihilated in Asia Minor by the Seljuqs, but the survivors helped to reinforce the kingdom upon their arrival in Jeru ...
... Among the crusaders in the Crusade of 1101 were Stephen II, Count of Blois and Hugh of Vermandois, both of whom had returned home before reaching Jerusalem. This crusade was almost annihilated in Asia Minor by the Seljuqs, but the survivors helped to reinforce the kingdom upon their arrival in Jeru ...
The Knight`s Templar and Bad Guys PPT
... Not unto us oh Lord, not unto us. But in Thy name, we “give glory”. ...
... Not unto us oh Lord, not unto us. But in Thy name, we “give glory”. ...
Background on the 1st Crusade: In 1095, Byzantine Emperor
... Ibn al-Athir (1160-1233) was an Arab historian who wrote a history of the first three crusades, though he only witnessed the third one. The passage below is a modified excerpt from his account of the siege of Jerusalem during the First Crusade. ...
... Ibn al-Athir (1160-1233) was an Arab historian who wrote a history of the first three crusades, though he only witnessed the third one. The passage below is a modified excerpt from his account of the siege of Jerusalem during the First Crusade. ...