Languages - Computer Science@IUPUI
... Evolution of Operating Systems Batch processing: do only one job or task at a time Operating systems: manage transitions between jobs and Increase throughput (amount of work computers process) Multiprogramming: Computer resources are shared by many jobs or tasks Timesharing: Technique used to implem ...
... Evolution of Operating Systems Batch processing: do only one job or task at a time Operating systems: manage transitions between jobs and Increase throughput (amount of work computers process) Multiprogramming: Computer resources are shared by many jobs or tasks Timesharing: Technique used to implem ...
2. Computers: The Machines Behind Computing
... Secondary Storage Devices (e.g. hard drive) Slots - connecting specialty processors ___________ - connecting input/output devices A-7 ...
... Secondary Storage Devices (e.g. hard drive) Slots - connecting specialty processors ___________ - connecting input/output devices A-7 ...
Introduction to Computing
... The hardware doesn’t know if a sequence of bits represents a character or a number. In the ASCII code, upper case letters are sequential, lower case letters are sequential, and digits are sequential. In most programming languages the expression (‘A’ + 1 ) has the same value as ‘B’. ...
... The hardware doesn’t know if a sequence of bits represents a character or a number. In the ASCII code, upper case letters are sequential, lower case letters are sequential, and digits are sequential. In most programming languages the expression (‘A’ + 1 ) has the same value as ‘B’. ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programming, and C++
... A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits. Memory is like a work area for programs. Before a program is executed, it is brought into the memory. RAM stands for random-access memory. It is called RAM because a memory cell can be accessed directly. Memory size is measured in bytes ...
... A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits. Memory is like a work area for programs. Before a program is executed, it is brought into the memory. RAM stands for random-access memory. It is called RAM because a memory cell can be accessed directly. Memory size is measured in bytes ...
Slides4
... instruction to be executed The next instruction is fetched and place into the instruction register The control unit decodes the instructions – interprets the op-code, finds the operands The instruction is executed – the control unit causes the ALU to do the proper operation based on the op-code A Ju ...
... instruction to be executed The next instruction is fetched and place into the instruction register The control unit decodes the instructions – interprets the op-code, finds the operands The instruction is executed – the control unit causes the ALU to do the proper operation based on the op-code A Ju ...
CPS120 - Washtenaw Community College
... PowerPC, etc.) – includes Bus Interface Unit, Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, registers – motherboard is simply the main circuit board that contains most of these parts – the CPU (central processing unit) is considered to be most of these parts taken as a whole ...
... PowerPC, etc.) – includes Bus Interface Unit, Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, registers – motherboard is simply the main circuit board that contains most of these parts – the CPU (central processing unit) is considered to be most of these parts taken as a whole ...
Homework #1 (with paper and pencil)
... Algorithm: step-by-step problem-solving process in which a solution is arrived at in a finite amount of time Assembler: program that translates a program written in assembly language into an equivalent program in machine language American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII): most commo ...
... Algorithm: step-by-step problem-solving process in which a solution is arrived at in a finite amount of time Assembler: program that translates a program written in assembly language into an equivalent program in machine language American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII): most commo ...
Slide 1
... Data hazards (Data Dependency Conflicts): An instruction scheduled to be executed in the pipeline requires the result of a previous instruction, which is not yet available. ...
... Data hazards (Data Dependency Conflicts): An instruction scheduled to be executed in the pipeline requires the result of a previous instruction, which is not yet available. ...
F21/1947/2012 ANGELA WAITHERA NABA FEB 116 ASSIGNMENT
... speed of the computers. They were relatively smaller and cheaper than the previous generation. Fourth generation-were developed between 1972 and 1984. There was development of large scale and very large scale integrated circuits. There was development of programming languages like functional program ...
... speed of the computers. They were relatively smaller and cheaper than the previous generation. Fourth generation-were developed between 1972 and 1984. There was development of large scale and very large scale integrated circuits. There was development of programming languages like functional program ...
cs1026_topic1 - Computer Science
... A bit is a binary digit – a 0 or 1 A string of 8 bits are a byte A kilobit is 1000 bits, a megabit is 1,000,000 and so on Computers can only do on or off, and a certain number of these at a time – hence a 64 bit processor a 32 bit processor, etc.. ...
... A bit is a binary digit – a 0 or 1 A string of 8 bits are a byte A kilobit is 1000 bits, a megabit is 1,000,000 and so on Computers can only do on or off, and a certain number of these at a time – hence a 64 bit processor a 32 bit processor, etc.. ...
Generations of Computers
... These perform multi-tasking and allow many terminals to be connected to their services. Business, to process large amount of data. PRICE: between $15,000 $150,000 ...
... These perform multi-tasking and allow many terminals to be connected to their services. Business, to process large amount of data. PRICE: between $15,000 $150,000 ...
Instruction Set Architecture
... • Digital logic works by performing Boolean functions (and, or, not) • The basic boolean functions are implemented by creating circuits using transistors (and sometimes resistors), depending on the ...
... • Digital logic works by performing Boolean functions (and, or, not) • The basic boolean functions are implemented by creating circuits using transistors (and sometimes resistors), depending on the ...
History of Computer Science
... Konrad Zuse German engineering student, 1930’s Never allowed to complete his computer ...
... Konrad Zuse German engineering student, 1930’s Never allowed to complete his computer ...
Document
... – Arithmetic calculations are performed using the Arithmetic/Logical Unit or ALU – Control unit decodes and executes instructions – Registers hold information and instructions for CPU to process ...
... – Arithmetic calculations are performed using the Arithmetic/Logical Unit or ALU – Control unit decodes and executes instructions – Registers hold information and instructions for CPU to process ...
EECS 252 Graduate Computer Architecture Lec 01
... • Make input and output easier than wiring circuit boards and reading lights • Make programming easier by developing higher level programming languages, so that users did not need to use binary machine code instructions – First compilers in late 1950’s, for Fortran and Cobol ...
... • Make input and output easier than wiring circuit boards and reading lights • Make programming easier by developing higher level programming languages, so that users did not need to use binary machine code instructions – First compilers in late 1950’s, for Fortran and Cobol ...
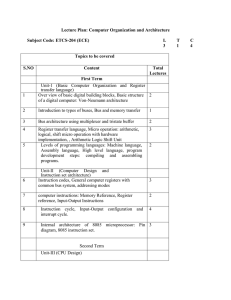
COA -ECE - Lecture plan
... logical, shift micro operation with hardware implementation, , Arithmetic Logic Shift Unit Levels of programming languages: Machine language, Assembly language, High level language, program development steps: compiling and assembling programs. ...
... logical, shift micro operation with hardware implementation, , Arithmetic Logic Shift Unit Levels of programming languages: Machine language, Assembly language, High level language, program development steps: compiling and assembling programs. ...
Computer Architecture
... • understand the hardware operation of digital computers: • It presents the various digital components used in the organization and design of digital computers. • Introduces the detailed steps that a designer must go through in order to design an elementary basic computer. • Presents the organizatio ...
... • understand the hardware operation of digital computers: • It presents the various digital components used in the organization and design of digital computers. • Introduces the detailed steps that a designer must go through in order to design an elementary basic computer. • Presents the organizatio ...
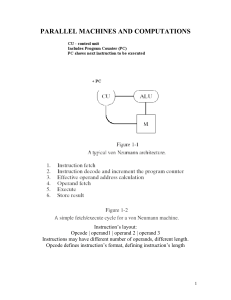
Parallel Machines and Computations (P1)
... SISD computers are the conventional von Neumann’s machines. In SIMD computers same operations are to be performed on disjoint data items, which may be viewed as vectors. For example, a single vector add operation is used to produce new vector C = A + B, whose elements are component wise addition of ...
... SISD computers are the conventional von Neumann’s machines. In SIMD computers same operations are to be performed on disjoint data items, which may be viewed as vectors. For example, a single vector add operation is used to produce new vector C = A + B, whose elements are component wise addition of ...
General information:
... into memory to be run Advanced issues modify simplified model: 1. Dynamic linking/loading 2. Virtual memory ...
... into memory to be run Advanced issues modify simplified model: 1. Dynamic linking/loading 2. Virtual memory ...
CPS120 - Washtenaw Community College
... PowerPC, etc.) – includes Bus Interface Unit, Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, registers – motherboard is simply the main circuit board that contains most of these parts – the CPU (central processing unit) is considered to be most of these parts taken as a whole ...
... PowerPC, etc.) – includes Bus Interface Unit, Arithmetic & Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, registers – motherboard is simply the main circuit board that contains most of these parts – the CPU (central processing unit) is considered to be most of these parts taken as a whole ...
ILLIAC IV

The ILLIAC IV was one of the first attempts to build a massively parallel computer. One of a series of research machines (the ILLIACs from the University of Illinois), the ILLIAC IV design featured fairly high parallelism with up to 256 processors, used to allow the machine to work on large data sets in what would later be known as vector processing. After several delays and redesigns, the computer was delivered to NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Airfield in Mountain View, California in 1971. After thorough testing and four years of NASA use, ILLIAC IV was connected to the ARPANet for distributed use in November 1975, becoming the first network-available supercomputer, beating Cray's Cray-1 by nearly 12 months.