Characteristics of Life Notes Packet
... 9. Living Things have a life span Why can’t organisms just live forever? Over time there is damage to the DNA and cells (things wear out despite constant maintenance and repair). Organisms cannot always maintain homeostasis in all environmental conditions. If an organism cannot continue its metaboli ...
... 9. Living Things have a life span Why can’t organisms just live forever? Over time there is damage to the DNA and cells (things wear out despite constant maintenance and repair). Organisms cannot always maintain homeostasis in all environmental conditions. If an organism cannot continue its metaboli ...
File
... These offspring compete with one another for available resources Organisms of the same species from different populations vary The offspring with the most favourable traits are more likely to survive and produce more offspring 4. Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck: 18th century theorist who proposed tha ...
... These offspring compete with one another for available resources Organisms of the same species from different populations vary The offspring with the most favourable traits are more likely to survive and produce more offspring 4. Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck: 18th century theorist who proposed tha ...
8.L.5- Energy in Living Organisms - NHCS
... Why are all organisms connected to each other? How can understanding human body systems help you make informed decisions that affect your health? 8.L.5.1 Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. Organisms get energy by oxidizing their food, releasing some o ...
... Why are all organisms connected to each other? How can understanding human body systems help you make informed decisions that affect your health? 8.L.5.1 Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. Organisms get energy by oxidizing their food, releasing some o ...
Review Presentation
... • a form of asexual reproduction where a chromosome is copied before the cell divides to form two new cells • used by bacteria (which are unicellular and prokaryotes.) ...
... • a form of asexual reproduction where a chromosome is copied before the cell divides to form two new cells • used by bacteria (which are unicellular and prokaryotes.) ...
Evolution - Wikispaces
... function. These organisms DID NOT inherit their structural adaptations from a common ancestor. ...
... function. These organisms DID NOT inherit their structural adaptations from a common ancestor. ...
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification: A Darwinian
... between organisms and their environment, which may give rise to new species. 14. Explain the reasoning behind the phrase “survival of the fittest”. Individuals do not evolve. Populations evolve. 15. Explain how research on soapberry bugs demonstrates observable evolutionary change. Researchers have ...
... between organisms and their environment, which may give rise to new species. 14. Explain the reasoning behind the phrase “survival of the fittest”. Individuals do not evolve. Populations evolve. 15. Explain how research on soapberry bugs demonstrates observable evolutionary change. Researchers have ...
Adaptations Over Time
... •He introduced the idea that the environment caused changes in animals and these changes were inherited by the animals' offspring. •changes in an organism during its lifetime could be passed on to its offspring. •if an organism that used certain organs more than others, then the organ used the most ...
... •He introduced the idea that the environment caused changes in animals and these changes were inherited by the animals' offspring. •changes in an organism during its lifetime could be passed on to its offspring. •if an organism that used certain organs more than others, then the organ used the most ...
Evolution - Ms
... specimens and kept a journal with his thoughts and observations. During his travels Darwin started to believe that he was coming across a scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. ...
... specimens and kept a journal with his thoughts and observations. During his travels Darwin started to believe that he was coming across a scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. ...
Bio112_Ex2StudyGuide_F16
... b. a group of rooted plant cuttings from a single plant c. the cells produced by the asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism d. the offspring produced by two parents e. the buds on a flowering plant 17. Which process is absolutely necessary for sexual reproduction to occur in a life cycle b ...
... b. a group of rooted plant cuttings from a single plant c. the cells produced by the asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism d. the offspring produced by two parents e. the buds on a flowering plant 17. Which process is absolutely necessary for sexual reproduction to occur in a life cycle b ...
Evolution Unit Review
... 8. Which scientist first proved that lipid membranes could form around proteins and nucleic acids under the conditions of early earth? ...
... 8. Which scientist first proved that lipid membranes could form around proteins and nucleic acids under the conditions of early earth? ...
Unit 4 Test: Evolution and Classification Tracker
... b. The ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in any potential environment, compared to other individuals of that population. c. The ability of a species to survive in a certain environment, compared to other species. d. The ability of a species to survive over time, compared to other spe ...
... b. The ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in any potential environment, compared to other individuals of that population. c. The ability of a species to survive in a certain environment, compared to other species. d. The ability of a species to survive over time, compared to other spe ...
The Study of Life
... • BIOLOGY – the scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms • ORGANISM – any individual living thing – All share certain characteristics, but not all ...
... • BIOLOGY – the scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms • ORGANISM – any individual living thing – All share certain characteristics, but not all ...
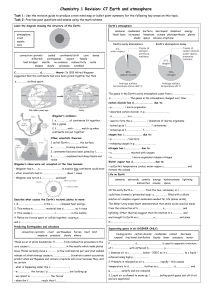
C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
C7 Revision Earth and Atmosphere
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
... These occur at plate boundaries. H………..…. from radioactive processes in the core causes c……….……………………. c……………………. in the mantle which make plates move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately pre ...
Photo by “davemee” flickr creative commons
... observable characteristics of an organism, such that individuals with favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce than those with less favorable phenotypes. • The phenotype's genetic basis, the genotype associated with the favorable phenotype, will increase in frequency over the fo ...
... observable characteristics of an organism, such that individuals with favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce than those with less favorable phenotypes. • The phenotype's genetic basis, the genotype associated with the favorable phenotype, will increase in frequency over the fo ...
Chapter 22 - Bio-Guru
... 2. Struggle for existence: there will be a struggle for survival a.k.a COMPETITION 3. Genetic Variation: The organisms that possess a variation that will help them in this struggle, will ...
... 2. Struggle for existence: there will be a struggle for survival a.k.a COMPETITION 3. Genetic Variation: The organisms that possess a variation that will help them in this struggle, will ...
Charles Darwin - Paradise Primary School
... his ideas), so Darwin spent many years thinking about what he had seen and how he could explain it and give evidence He asked himself questions such as: why were there so many different types of plants and animals, and why were there similar, but not identical plants/creatures in different places? ...
... his ideas), so Darwin spent many years thinking about what he had seen and how he could explain it and give evidence He asked himself questions such as: why were there so many different types of plants and animals, and why were there similar, but not identical plants/creatures in different places? ...
An Introduction to Evolution
... ___________________: the process through which traits that provide a reproductive advantage to an individual organism grow more common in populations of organisms over successive generations ...
... ___________________: the process through which traits that provide a reproductive advantage to an individual organism grow more common in populations of organisms over successive generations ...
chapter 21
... Earth’s layers differentiated based on density Densest went to the core (iron) Lightest to the crust (granite) Formed the plates, which have moved throughout time due to convection currents in the mantle ...
... Earth’s layers differentiated based on density Densest went to the core (iron) Lightest to the crust (granite) Formed the plates, which have moved throughout time due to convection currents in the mantle ...
Honors Biology Ch. 14 Notes The Origin of Species Concepts of species
... Females choose based on different factors. 14.10 Describe the circumstances that led to the adaptive radiation of the Galapagos finches. Adaptive Radiation: The evolution of many diverse species from a common ancestor. Example: Darwin’s Finches Typically occurs when a few organisms colonize new, u ...
... Females choose based on different factors. 14.10 Describe the circumstances that led to the adaptive radiation of the Galapagos finches. Adaptive Radiation: The evolution of many diverse species from a common ancestor. Example: Darwin’s Finches Typically occurs when a few organisms colonize new, u ...
The Nature of Zoology
... Fortunately, there are other sources and you can get a wide variety of traits from all of the previous generations! ...
... Fortunately, there are other sources and you can get a wide variety of traits from all of the previous generations! ...
Early Earth and Evolution
... could not explain how traits were passed down through generations. • We now can apply our understanding of genetics and apply them to evolutionary theory. ...
... could not explain how traits were passed down through generations. • We now can apply our understanding of genetics and apply them to evolutionary theory. ...
Evolution Test
... 11. The number and location of bones of many fossil vertebrates are similar to those in living vertebrates. Most biologists would probably explain this fact on the basis of a. the needs of the organisms. c. the struggle for existence. b. a common ancestor. d. the inheritance of acquired traits. 12. ...
... 11. The number and location of bones of many fossil vertebrates are similar to those in living vertebrates. Most biologists would probably explain this fact on the basis of a. the needs of the organisms. c. the struggle for existence. b. a common ancestor. d. the inheritance of acquired traits. 12. ...
Sea Page 66
... Continental Shelf Gradually sloping area of land that begins at the shore and continues under the ocean. Continental Slope Steeply sloping area of land located beneath the ocean. Crustaceans Mostly aquatic class of animals that includes shrimp, lobsters, crabs, krill and others. Colonial Animal Anim ...
... Continental Shelf Gradually sloping area of land that begins at the shore and continues under the ocean. Continental Slope Steeply sloping area of land located beneath the ocean. Crustaceans Mostly aquatic class of animals that includes shrimp, lobsters, crabs, krill and others. Colonial Animal Anim ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.










![C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001217671_1-b9cc347117db8dff9935614904a55b09-300x300.png)