Lesson 1 Intro to Evolution Adaptation and - Blyth-Biology11
... genes/alleles, genotypes/phenotypes) of species (or populations of a species) over time. • Throughout this unit, you will see that three main processes determine the rate of evolution: – 1) variation within a species (i.e. the fact that no one is an identical clone to another person) – 2) reproducti ...
... genes/alleles, genotypes/phenotypes) of species (or populations of a species) over time. • Throughout this unit, you will see that three main processes determine the rate of evolution: – 1) variation within a species (i.e. the fact that no one is an identical clone to another person) – 2) reproducti ...
Evidence supporting evolution
... shared ancestry and how organisms and the environment have changed over time. Biogeography Differences and similarities between organisms in different locations around the world. Provides evidence of how modern species share a common ancestor but have evolved to fit environments in different l ...
... shared ancestry and how organisms and the environment have changed over time. Biogeography Differences and similarities between organisms in different locations around the world. Provides evidence of how modern species share a common ancestor but have evolved to fit environments in different l ...
Spheres of Earth - Red Hook Central Schools
... Atmosphere: Shell of gases that surrounds a planet, for example, Earth a. Earth’s atmosphere is unique because it contains oxygen b. Atmosphere = Air Lithosphere(also known as Geosphere): Solid portion of Earth below the atmosphere and the hydrosphere a. Includes: rocks, mountains and beaches ...
... Atmosphere: Shell of gases that surrounds a planet, for example, Earth a. Earth’s atmosphere is unique because it contains oxygen b. Atmosphere = Air Lithosphere(also known as Geosphere): Solid portion of Earth below the atmosphere and the hydrosphere a. Includes: rocks, mountains and beaches ...
key
... In prior grades students learned how the traits of organisms are passed on through the transfer of genetic information during reproduction. In grades 9-11 students learn about the factors that underlie biological evolution: variability of offspring, population growth, a finite supply of resources, a ...
... In prior grades students learned how the traits of organisms are passed on through the transfer of genetic information during reproduction. In grades 9-11 students learn about the factors that underlie biological evolution: variability of offspring, population growth, a finite supply of resources, a ...
ASK Biology Review
... • Eukaryotic-cells with membrane (“skin”) bound nucleus • These are more complex cells than prokaryotic • Seen in the protist, fungi, plant, and animal kingdoms ...
... • Eukaryotic-cells with membrane (“skin”) bound nucleus • These are more complex cells than prokaryotic • Seen in the protist, fungi, plant, and animal kingdoms ...
File
... successfully modeled in the laboratory. d. No other alternative hypotheses have been introduced. ____ 22. What discovery supports the hypothesis that RNA was the genetic material in the earliest organisms? a. Ribozymes are RNA that can self-replicate. b. DNA does not require enzymes to replicate. c. ...
... successfully modeled in the laboratory. d. No other alternative hypotheses have been introduced. ____ 22. What discovery supports the hypothesis that RNA was the genetic material in the earliest organisms? a. Ribozymes are RNA that can self-replicate. b. DNA does not require enzymes to replicate. c. ...
Historical Geology
... 1. Extinction strikes in both the land and the sea. 2. On the land, while animals suffer repeatedly, plants tend to be highly resistant to mass extinctions. 3. Preferential disappearance of tropical forms of life during mass extinctions. 4. Tendency of certain groups of animals to experience them re ...
... 1. Extinction strikes in both the land and the sea. 2. On the land, while animals suffer repeatedly, plants tend to be highly resistant to mass extinctions. 3. Preferential disappearance of tropical forms of life during mass extinctions. 4. Tendency of certain groups of animals to experience them re ...
Evolution Evidence and Fossil Records
... • remains of structures/organs that ONCE had an importance in organism’s ancestors – Example: tailbones in humans, appendix, wings on ostrich, wisdom teeth in humans, nipples in male mammals, femur and pelvis in whales ...
... • remains of structures/organs that ONCE had an importance in organism’s ancestors – Example: tailbones in humans, appendix, wings on ostrich, wisdom teeth in humans, nipples in male mammals, femur and pelvis in whales ...
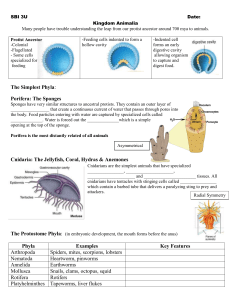
Kingdom Animalia
... Many people have trouble understanding the leap from our protist ancestor around 700 mya to animals. -Feeding cells indented to form a hollow cavity ...
... Many people have trouble understanding the leap from our protist ancestor around 700 mya to animals. -Feeding cells indented to form a hollow cavity ...
1. Relative dating is using comparison to date rocks or fossils. Law
... 1. Relative dating is using comparison to date rocks or fossils. Law of superposition and index fossils are both examples of relative dating. Relative dating provides an estimate of age versus absolute dating that gives an exact age based on radioactive decay of Carbon-14 or Uranium-235. Absolute da ...
... 1. Relative dating is using comparison to date rocks or fossils. Law of superposition and index fossils are both examples of relative dating. Relative dating provides an estimate of age versus absolute dating that gives an exact age based on radioactive decay of Carbon-14 or Uranium-235. Absolute da ...
Chapter 1 - SharpSchool
... • Cause diseases but also cure diseases • Can turn milk into different kinds of cheese. ...
... • Cause diseases but also cure diseases • Can turn milk into different kinds of cheese. ...
Evolution Jeopardy
... What type of adaptation is listed below? A. Camouflage B. Mimicry C. It’s the same species D. Natural Selection ...
... What type of adaptation is listed below? A. Camouflage B. Mimicry C. It’s the same species D. Natural Selection ...
File - Biology with Mrs. Mercaldi
... 3. Give three examples of artificial selection. Include examples of both animals and plants. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 4. Critical ...
... 3. Give three examples of artificial selection. Include examples of both animals and plants. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 4. Critical ...
Document
... 3. New __________can develop if organisms with common ancestors become __________ and natural selection causes them to differentiate in response to different environments a. Inherited traits that increase an organism’s chance of surviving and reproducing in a particular environment are called ______ ...
... 3. New __________can develop if organisms with common ancestors become __________ and natural selection causes them to differentiate in response to different environments a. Inherited traits that increase an organism’s chance of surviving and reproducing in a particular environment are called ______ ...
Evolution Notes
... inherited characteristics well-suited for an environment produce more offspring than do other individuals. ...
... inherited characteristics well-suited for an environment produce more offspring than do other individuals. ...
Concept 15.1: The diversity of life is based on
... IV. Continental Drift and Macroevolution A. Landmasses on different plates change position relative to one another known as _________________________ B. There are two major events of continental drift that had a major impact on the history of life 1. 250 million years ago all the plates moved toget ...
... IV. Continental Drift and Macroevolution A. Landmasses on different plates change position relative to one another known as _________________________ B. There are two major events of continental drift that had a major impact on the history of life 1. 250 million years ago all the plates moved toget ...
What is an inference
... What did Miller and Urey prove in their experiment? ...They proved that organic molecules could be formed from chemical reactions among the gases in the early atmosphere instituted by lightening. Gases in a special chamber were given an electric spark and ...
... What did Miller and Urey prove in their experiment? ...They proved that organic molecules could be formed from chemical reactions among the gases in the early atmosphere instituted by lightening. Gases in a special chamber were given an electric spark and ...
Evolution SOL Questions
... What did Miller and Urey prove in their experiment? ...They proved that organic molecules could be formed from chemical reactions among the gases in the early atmosphere instituted by lightening. Gases in a special chamber were given an electric spark and ...
... What did Miller and Urey prove in their experiment? ...They proved that organic molecules could be formed from chemical reactions among the gases in the early atmosphere instituted by lightening. Gases in a special chamber were given an electric spark and ...
5 chapter_test_b 5 chapter_test_b
... _____ 11. Darwin theorized that individuals having an advantage due to their traits or abilities will be more likely to survive and reproduce. His theory is known as a. evolution. b. speciation. ...
... _____ 11. Darwin theorized that individuals having an advantage due to their traits or abilities will be more likely to survive and reproduce. His theory is known as a. evolution. b. speciation. ...
Conditions on early Earth made the origin of life possible
... The fossil record documents the history of life The fossil record documents the main events in the history of life The geologic record is defined by major transitions in life on Earth ...
... The fossil record documents the history of life The fossil record documents the main events in the history of life The geologic record is defined by major transitions in life on Earth ...
File - Hanna Biology
... Voyage of the Beagle In 1831, Darwin set sail from England aboard the H.M.S. Beagle for a voyage around the world. During his travels, Darwin made numerous observations and collected evidence that led him to propose a hypothesis about the way life changes over time. That hypothesis has become the th ...
... Voyage of the Beagle In 1831, Darwin set sail from England aboard the H.M.S. Beagle for a voyage around the world. During his travels, Darwin made numerous observations and collected evidence that led him to propose a hypothesis about the way life changes over time. That hypothesis has become the th ...
Algae, Fungus, etc. 3 (3) Algae- plantlike protists and are extremely
... Water molds and downy molds- most are downy molds that live in water or moist places, grow as tiny thread that look like fuzz, and they attack many food crops, such as potatoes, corn, and grapes. Algal blooms- is the rapid of a population of algae. True or false question: Algal blooms can occur in f ...
... Water molds and downy molds- most are downy molds that live in water or moist places, grow as tiny thread that look like fuzz, and they attack many food crops, such as potatoes, corn, and grapes. Algal blooms- is the rapid of a population of algae. True or false question: Algal blooms can occur in f ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.