1PP Examination Autumn 2002_postMod_2
... Sketch and label a graph showing how the angular velocity, , varies as a function of the radial distance r such that v is kept constant. Show the minimum and maximum angular velocities on the graph. Using the information given above, calculate the total length of the helical data track for a standa ...
... Sketch and label a graph showing how the angular velocity, , varies as a function of the radial distance r such that v is kept constant. Show the minimum and maximum angular velocities on the graph. Using the information given above, calculate the total length of the helical data track for a standa ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms.
... (I have colored ‘v’ (velocity) red to distinguish it from ‘v’ (frequency) ...
... (I have colored ‘v’ (velocity) red to distinguish it from ‘v’ (frequency) ...
Conservation Laws I - Department of Physics, HKU
... (a) In this universe laws are not constant in time. As time progresses electric charges increase with time. The spring shown compresses – building potential energy (not conserved) – this could be released to drive an engine. (b) An electric field is placed across this universe – making space anisotr ...
... (a) In this universe laws are not constant in time. As time progresses electric charges increase with time. The spring shown compresses – building potential energy (not conserved) – this could be released to drive an engine. (b) An electric field is placed across this universe – making space anisotr ...
pdf file - High Point University
... Because the force on the alpha particle by the electric eld is in the same direction as the velocity of the particle, then the particle will speed up as it travels toward the negatively charged plate. As a result, its kinetic energy increases. Conservation of Energy tells us that this must be accom ...
... Because the force on the alpha particle by the electric eld is in the same direction as the velocity of the particle, then the particle will speed up as it travels toward the negatively charged plate. As a result, its kinetic energy increases. Conservation of Energy tells us that this must be accom ...
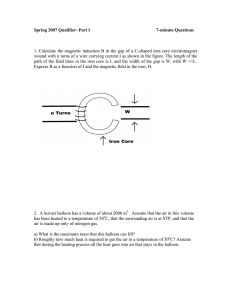
Spring 2007 Qualifier- Part I 7-minute Questions
... b) Derive the equation of motion. c) Linearize the equation of motion for small φ <<1 and calculate the frequency of ...
... b) Derive the equation of motion. c) Linearize the equation of motion for small φ <<1 and calculate the frequency of ...
1 - gtbit
... A plane 200 MHz wave is traveling in a medium for which σ = 0, μ r = 2, εr = 4. If average Poynting vector is 5 W/m2, Find Erms, Hrms, phase velocity and impedance of the medium. ...
... A plane 200 MHz wave is traveling in a medium for which σ = 0, μ r = 2, εr = 4. If average Poynting vector is 5 W/m2, Find Erms, Hrms, phase velocity and impedance of the medium. ...
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... the result to explain why nearly all H atoms are in the ground state at room temperature, and hence emit no light. ...
... the result to explain why nearly all H atoms are in the ground state at room temperature, and hence emit no light. ...
Interactions
... If electrons are not ejected from atoms but merely raised to higher energy levels (outer shells), the process is termed excitation, and the atom is said to be “excited.” Charged particles such as electrons, protons, and atomic nuclei are directly ionizing radiations because they can eject electrons ...
... If electrons are not ejected from atoms but merely raised to higher energy levels (outer shells), the process is termed excitation, and the atom is said to be “excited.” Charged particles such as electrons, protons, and atomic nuclei are directly ionizing radiations because they can eject electrons ...
1 Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
... Roughly, if < x|Ψ > has a narrow distribution, then < p|Ψ > will have a spread out distribution and vice versa. Heisenberg’s original paper on uncertainty concerned a much more physical picture. The example he used was that of determining the location of an electron with an uncertainty δx, by having ...
... Roughly, if < x|Ψ > has a narrow distribution, then < p|Ψ > will have a spread out distribution and vice versa. Heisenberg’s original paper on uncertainty concerned a much more physical picture. The example he used was that of determining the location of an electron with an uncertainty δx, by having ...
Ch 24: Quantum Mechanics
... 21. The momentum of an electron is measured to an accuracy of ± 5.1 × 10-24 kg·m/s. What is the corresponding uncertainty in the position of the same electron at the same moment? Express your answer in Angstroms (1 Å = 10-10 m, about the size of a typical atom). 22. Thor, a baseball player, passes o ...
... 21. The momentum of an electron is measured to an accuracy of ± 5.1 × 10-24 kg·m/s. What is the corresponding uncertainty in the position of the same electron at the same moment? Express your answer in Angstroms (1 Å = 10-10 m, about the size of a typical atom). 22. Thor, a baseball player, passes o ...
Unit 2: Atoms and their Electrons
... 7.58 x 1020 photons = 4.34 x 10-7m , f = 6.91 x 1014 s-1 , E = 4.58 x 10-19 J the principle quantum number n ...
... 7.58 x 1020 photons = 4.34 x 10-7m , f = 6.91 x 1014 s-1 , E = 4.58 x 10-19 J the principle quantum number n ...
Recitation 3
... that most of the mass of an atom is in a very small nucleus, whith electrons in orbit around it, in his planetary model of the atom. Assume that an alpha particle, initially very far from a gold nucleus, is fired with a velocity v = 2.00 · 107 m/s directly toward the nucleus (charge Q = +79e). How c ...
... that most of the mass of an atom is in a very small nucleus, whith electrons in orbit around it, in his planetary model of the atom. Assume that an alpha particle, initially very far from a gold nucleus, is fired with a velocity v = 2.00 · 107 m/s directly toward the nucleus (charge Q = +79e). How c ...