Syllabus for Semesters I to VI For Physics (Hons.) for 2011-2014
... refraction. Interference of light waves: Young’s experiment, spatial and temporal coherence, intensity distribution, Fresnel’s biprism, interference in thin films, Newton’s ring, Michelson interferometer, application in fine structure study. Diffraction: Fresnel and Fraunhofer class, Fresnel’s half ...
... refraction. Interference of light waves: Young’s experiment, spatial and temporal coherence, intensity distribution, Fresnel’s biprism, interference in thin films, Newton’s ring, Michelson interferometer, application in fine structure study. Diffraction: Fresnel and Fraunhofer class, Fresnel’s half ...
Formulae and Data Booklet - SCSA
... This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that it is not changed and that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the ...
... This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that it is not changed and that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the ...
Cutoff conditions for transverse circularly polarized electromagnetic
... equations. The cutoff condition for transverse circularly polarized electromagnetic waves is obtained from the derived dispersion relation. The variation of the cutoff frequency CO,,with the static electric field Es, magnetostatic field B,, the electron number density N and the electron gas temperat ...
... equations. The cutoff condition for transverse circularly polarized electromagnetic waves is obtained from the derived dispersion relation. The variation of the cutoff frequency CO,,with the static electric field Es, magnetostatic field B,, the electron number density N and the electron gas temperat ...
2002 - The Physics Teacher
... magnetic flux. (ii) State Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction. Lenz’s Law states that the direction of the induced emf is always such as to oppose the change producing it. (iii) In an experiment, a coil was connected in series with an ammeter and an a.c. power supply as shown in the diagram. Exp ...
... magnetic flux. (ii) State Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction. Lenz’s Law states that the direction of the induced emf is always such as to oppose the change producing it. (iii) In an experiment, a coil was connected in series with an ammeter and an a.c. power supply as shown in the diagram. Exp ...
Слайд 1 - TU Muenchen
... Note1: If electron – hole pairs are being produced in a bound state (exciton), they are also polarized free electrons, but this process is more complicated and is not enough studied. ...
... Note1: If electron – hole pairs are being produced in a bound state (exciton), they are also polarized free electrons, but this process is more complicated and is not enough studied. ...
Set #4
... 4. A long time ago, in a galaxy far, far away, electric charge had not yet been invented, and atoms were held together by gravitational forces. Compute the Bohr radius and the n=2 to n = 1 transition energy in a gravitationally hound hydrogen atom. (Krane, P33, pg. 204) 5. The fine structure constan ...
... 4. A long time ago, in a galaxy far, far away, electric charge had not yet been invented, and atoms were held together by gravitational forces. Compute the Bohr radius and the n=2 to n = 1 transition energy in a gravitationally hound hydrogen atom. (Krane, P33, pg. 204) 5. The fine structure constan ...
Optical Pumping of Rubidium Vapor
... hyperfine constant and is given in units of Hertz. µB is the Bohr magneton. h̄J~ and h̄I~ are the electron and nuclear angular momentum operators. gJ and gF can be found via a classical vector coupling model or a more detailed quantum mechanical calculation to be: J(J + 1) + L(L + 1) − S(S + 1) ...
... hyperfine constant and is given in units of Hertz. µB is the Bohr magneton. h̄J~ and h̄I~ are the electron and nuclear angular momentum operators. gJ and gF can be found via a classical vector coupling model or a more detailed quantum mechanical calculation to be: J(J + 1) + L(L + 1) − S(S + 1) ...
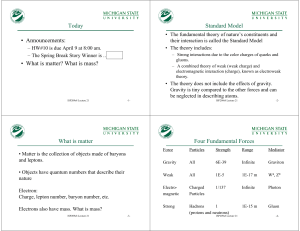
ppt - HEP Educational Outreach
... The Connection: Expected that whatever the “New Physics” is that addresses SM questions also provides a candidate particle that forms the Dark Matter in the Universe ...
... The Connection: Expected that whatever the “New Physics” is that addresses SM questions also provides a candidate particle that forms the Dark Matter in the Universe ...
On the Energisation Mechanism of Charged Particles in ABC
... not actually being radiation, consist of charged particles with energies up to 1020 eV impacting the surface of the Earth at great velocities [2, 3]. In comparison, the highest energies currently produced in particle accelerators are in the order of 1013 eV [4]. The particles include protons, electr ...
... not actually being radiation, consist of charged particles with energies up to 1020 eV impacting the surface of the Earth at great velocities [2, 3]. In comparison, the highest energies currently produced in particle accelerators are in the order of 1013 eV [4]. The particles include protons, electr ...
Lecture notes, part 5
... The Raman effect is the scattering of a photon by a molecule. In scattering, the photon transfers some (but not all) of its energy to the molecule. This is different than absorption spectroscopy in which the photon transfers all of its energy to the molecule. Raman spectroscopy complements absorptio ...
... The Raman effect is the scattering of a photon by a molecule. In scattering, the photon transfers some (but not all) of its energy to the molecule. This is different than absorption spectroscopy in which the photon transfers all of its energy to the molecule. Raman spectroscopy complements absorptio ...
Learning material
... Rutherford was able to obtain a formula for the number of alpha particles scattered through an angle greater or equal to , by assuming that there was no transfer of momentum from the alpha particle to the atom. Rutherford’s formula depends on ...
... Rutherford was able to obtain a formula for the number of alpha particles scattered through an angle greater or equal to , by assuming that there was no transfer of momentum from the alpha particle to the atom. Rutherford’s formula depends on ...
Review for Exam 1
... Angular momentum, J, is a vector quantity, meaning it has both direction and magnitude. Classically the magnitude of the J, is related to Erot by Erot = J2/(2I), where I is the moment of inertia or Erot = L2/2I ...........................(F) Comparing Eqns. (E) and (F) leads to the conclusion that t ...
... Angular momentum, J, is a vector quantity, meaning it has both direction and magnitude. Classically the magnitude of the J, is related to Erot by Erot = J2/(2I), where I is the moment of inertia or Erot = L2/2I ...........................(F) Comparing Eqns. (E) and (F) leads to the conclusion that t ...
Bonding homework
... false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ...
... false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ...
Establishing the Riemannian structure of space-time by
... Ehlers, Pirani, and Schild (EPS) ’ have proposed a constructive space-time axiomatics based on light rays and freely falling classical point particles as primitive objects. For a further elaboration of this approach, see Coleman and Korte.’ Based on these primitive objects and appropriate basic expe ...
... Ehlers, Pirani, and Schild (EPS) ’ have proposed a constructive space-time axiomatics based on light rays and freely falling classical point particles as primitive objects. For a further elaboration of this approach, see Coleman and Korte.’ Based on these primitive objects and appropriate basic expe ...