1.1 What has to be explained by Quantum mechanics?
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
... • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave function, quantum number, ...... ...
Wave-Particle Duality - the Principle of Complementarity The
... Answer: This role is played by the wave function, Ψ. The square of the absolute value of the wave function at any point is proportional to the number of electrons expected to be found there. For a single electron, the wave function is the probability of finding the electron at that point. In the cla ...
... Answer: This role is played by the wave function, Ψ. The square of the absolute value of the wave function at any point is proportional to the number of electrons expected to be found there. For a single electron, the wave function is the probability of finding the electron at that point. In the cla ...
Lec-22_Strachan
... Example: Find the de Broglie wavelength of a 1500-kg car whose speed is 30 m/s. Solution: The car’s wavelength is l=h/mv=6.63x10-34 J•s/(1.5x103)(30m/s) = 1.5x10-38 m The wavelength is so small compared to the car’s dimension that no wave behavior is to be expected. ...
... Example: Find the de Broglie wavelength of a 1500-kg car whose speed is 30 m/s. Solution: The car’s wavelength is l=h/mv=6.63x10-34 J•s/(1.5x103)(30m/s) = 1.5x10-38 m The wavelength is so small compared to the car’s dimension that no wave behavior is to be expected. ...
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics AEP3610 Professor Scott
... atom of atomic number Z with only one electron left on it, to get KE (m is reduced mass, which is almost the electron mass but slightly less): ...
... atom of atomic number Z with only one electron left on it, to get KE (m is reduced mass, which is almost the electron mass but slightly less): ...
Mid Semester paper
... (b) A particle of mass m moves under a force F (x) = −cx3 , where c is a positive constant. Find the potential energy function. If the particle starts from rest at x = −a, what is the velocity when it reaches x = 0? Where with subsequent motion does it come to rest? 8. (a) Show that for an isolated ...
... (b) A particle of mass m moves under a force F (x) = −cx3 , where c is a positive constant. Find the potential energy function. If the particle starts from rest at x = −a, what is the velocity when it reaches x = 0? Where with subsequent motion does it come to rest? 8. (a) Show that for an isolated ...
Please look over the following review questions
... An excited atom decays to its ground state and emits a photon of green light. If instead the atom decays to an intermediate state, then the light could be a. b. c. d. e. ...
... An excited atom decays to its ground state and emits a photon of green light. If instead the atom decays to an intermediate state, then the light could be a. b. c. d. e. ...
Slide 1
... but like photons are quanta of electromagnetic energy, all particle states are the physical manifestation of quantum mechanical wave functions (fields). Not only does each atomic electron exist trapped within quantized energy levels or spin states, but its mass, its physical existence, is a quantum ...
... but like photons are quanta of electromagnetic energy, all particle states are the physical manifestation of quantum mechanical wave functions (fields). Not only does each atomic electron exist trapped within quantized energy levels or spin states, but its mass, its physical existence, is a quantum ...
Chemistry Science Notebook
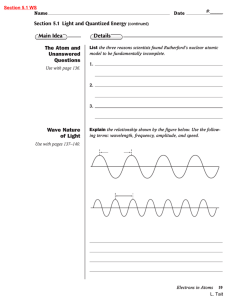
... Explain the relationship shown by the figure below. Use the following terms: wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed. ...
... Explain the relationship shown by the figure below. Use the following terms: wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed. ...
The Particulate Nature of Light
... to consist of tiny massless particles called photons. These photons can be considered to be packets of energy and each photon is called a quantum of energy. The energy associated with each photon is given by ...
... to consist of tiny massless particles called photons. These photons can be considered to be packets of energy and each photon is called a quantum of energy. The energy associated with each photon is given by ...
Spectroscopy - Birmingham City Schools
... o 4 quantum numbers resulting from spectral lines: n = principle quantum number (energy level) l = orbital quantum number (shape of orbit) ml = magnetic quantum number ...
... o 4 quantum numbers resulting from spectral lines: n = principle quantum number (energy level) l = orbital quantum number (shape of orbit) ml = magnetic quantum number ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI M.Sc. THIRD
... 9. Plot the probability density of a linear harmonic oscillator in its ground state. 10. Write down the eigenvalues of ( ) for the eigenstate *+,, -, . . ...
... 9. Plot the probability density of a linear harmonic oscillator in its ground state. 10. Write down the eigenvalues of ( ) for the eigenstate *+,, -, . . ...
Handout
... Black body radiation Light comes in individual particles, explaining deviation from Rayleigh-Jeans law at short wavelengths - waves are particles! ...
... Black body radiation Light comes in individual particles, explaining deviation from Rayleigh-Jeans law at short wavelengths - waves are particles! ...
Lesson 1 - Tarleton State University
... wave but interacts as a particle as claimed by Einstein then particles must also have wave properties! Furthermore, the basic equations must be analogous since all particles are waves and vice-versa. B. ...
... wave but interacts as a particle as claimed by Einstein then particles must also have wave properties! Furthermore, the basic equations must be analogous since all particles are waves and vice-versa. B. ...