Document
... atmosphere distort the view of telescopes on the ground, no matter how large or scientifically advanced those telescopes are. This "atmospheric distortion" is the reason that the stars seem to twinkle when you look up at the sky. The atmosphere also partially blocks or absorbs certain wavelengths of ...
... atmosphere distort the view of telescopes on the ground, no matter how large or scientifically advanced those telescopes are. This "atmospheric distortion" is the reason that the stars seem to twinkle when you look up at the sky. The atmosphere also partially blocks or absorbs certain wavelengths of ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... • The sum of all space, matter, and energy that exists, has existed, or will exist • There is only one • You are part of it too! • We see it as it was in the past • Contains many other galaxies • Most of it is empty space ...
... • The sum of all space, matter, and energy that exists, has existed, or will exist • There is only one • You are part of it too! • We see it as it was in the past • Contains many other galaxies • Most of it is empty space ...
ppt of lecture - July Lectures
... Einstein’s Greatest Blunder? He included it in the equations because he didn’t realise the universe was expanding. Then he wanted to get rid of it. ...
... Einstein’s Greatest Blunder? He included it in the equations because he didn’t realise the universe was expanding. Then he wanted to get rid of it. ...
History of the Universe and Solar System
... No, gravitational forces have slowed down the galaxies since the Big Bang. (Note: Recent observations suggest this was the case for the first 2/3 of the Universe’s history. The expansion rate now seems to have increased for the last 1/3 of the Universe’s history. This is explained by “dark phantom e ...
... No, gravitational forces have slowed down the galaxies since the Big Bang. (Note: Recent observations suggest this was the case for the first 2/3 of the Universe’s history. The expansion rate now seems to have increased for the last 1/3 of the Universe’s history. This is explained by “dark phantom e ...
Distant galaxies and quasars The ages of things Light
... • Quasars (the most luminous Active Galactic Nuclei, or AGN) have evolved dramatically over cosmic time • Because they are easy to see to large distances, this (unlike galaxy evolution) has been clearly known for several decades • In the past they were both much more numerous and substantially more ...
... • Quasars (the most luminous Active Galactic Nuclei, or AGN) have evolved dramatically over cosmic time • Because they are easy to see to large distances, this (unlike galaxy evolution) has been clearly known for several decades • In the past they were both much more numerous and substantially more ...
ppt
... • That is, nearby galaxies are moving away from us slowly, but distant galaxies are rushing away from us • This recessional movement is called the Hubble flow ...
... • That is, nearby galaxies are moving away from us slowly, but distant galaxies are rushing away from us • This recessional movement is called the Hubble flow ...
24.1 The Study of Light
... been set out to rise for a few hours. As the dough doubles in size, so does the distance between all the raisins. Those objects located father apart move away from each other more ...
... been set out to rise for a few hours. As the dough doubles in size, so does the distance between all the raisins. Those objects located father apart move away from each other more ...
Not a limitation
... was in a small point and exploded and is moving from that point out. • Was called Big Bang to make fun of it and the name stuck! ...
... was in a small point and exploded and is moving from that point out. • Was called Big Bang to make fun of it and the name stuck! ...
ITB - In the Beginning
... These particles formed in the first few minutes. The first atoms to form were; Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), and Beryllium (Be) These formed after ~ 600,000 years. ...
... These particles formed in the first few minutes. The first atoms to form were; Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), and Beryllium (Be) These formed after ~ 600,000 years. ...
Lecture 20, PPT version
... • if universe has been expanding at constant rate for all time, then all galaxies would have been on top of each other at time equal to 1/H0 Distance between any two galaxy clusters at the present day: distance = speed x time (the standard formula) speed = H0 x distance (Hubble’s Law, specifically) ...
... • if universe has been expanding at constant rate for all time, then all galaxies would have been on top of each other at time equal to 1/H0 Distance between any two galaxy clusters at the present day: distance = speed x time (the standard formula) speed = H0 x distance (Hubble’s Law, specifically) ...
Ch. 28 Test Topics
... -Know that the faster the source of light is moving the greater the shift of light. -Know that Edwin Hubble discovered that the farther away a galaxy was, the faster it was moving away from Earth. -Know the universe is continually expanding and how we know this. -Be able to describe the Big Bang the ...
... -Know that the faster the source of light is moving the greater the shift of light. -Know that Edwin Hubble discovered that the farther away a galaxy was, the faster it was moving away from Earth. -Know the universe is continually expanding and how we know this. -Be able to describe the Big Bang the ...
Lecture24
... are the superposition of millions or billions of stellar spectra. For all but a few of the nearest galaxies, the absorption and emission lines are redshifted relative to the solar ...
... are the superposition of millions or billions of stellar spectra. For all but a few of the nearest galaxies, the absorption and emission lines are redshifted relative to the solar ...
Astronomy Honors Mid term Study Guide
... 23. What is the Hubble Law? 24. What are the Hubble Constant and its currently most accepted value ( in the commonly used units for this constant)? 25. Describe Olber’s Paradox and its resolution (explanation) 26. Describe evidence for the Universe being open, closed , or flat. 27. What is the cosmo ...
... 23. What is the Hubble Law? 24. What are the Hubble Constant and its currently most accepted value ( in the commonly used units for this constant)? 25. Describe Olber’s Paradox and its resolution (explanation) 26. Describe evidence for the Universe being open, closed , or flat. 27. What is the cosmo ...
Chapter 7 Review Answers
... 4. (a) A galaxy is a collection of hundreds of billions of stars held together by gravity. (b) We live in the Milky Way galaxy. 5. The four types of galaxies are: (i) spiral (ii) barred spiral (iii) elliptical (iv) irregular 6. (a) This is an irregular galaxy. (b) This is a spiral galaxy. 7. (a) Hub ...
... 4. (a) A galaxy is a collection of hundreds of billions of stars held together by gravity. (b) We live in the Milky Way galaxy. 5. The four types of galaxies are: (i) spiral (ii) barred spiral (iii) elliptical (iv) irregular 6. (a) This is an irregular galaxy. (b) This is a spiral galaxy. 7. (a) Hub ...
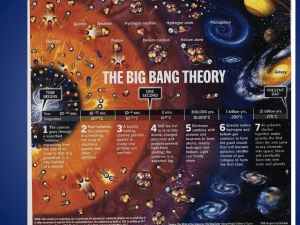
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 • We observe stars millions/billions of light-years away • A light-year is the distance that light travels in 1 year – the light we see today from a star 500 light years away is 500 years old • The ...
18-3 constellations RG
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
Class 28, 27 July
... • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • This leads to OSCILLATIONS! • Size of oscillations measures geometry of universe (know physical size, angle, so can measure geometry) ...
... • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • This leads to OSCILLATIONS! • Size of oscillations measures geometry of universe (know physical size, angle, so can measure geometry) ...
PRACTICE MINI-EXAM
... 6) A newly formed zircon crystal contains 1000 uranium-238 atoms. How many uranium-238 atoms will be left after two half-lives? ...
... 6) A newly formed zircon crystal contains 1000 uranium-238 atoms. How many uranium-238 atoms will be left after two half-lives? ...
13800000000 Years Ago The First Sky
... What do they tell us ? Age of the Universe = 13800000000 Years Size of our Universe = 13800000000 Light Years = 100000000000000000000000 kilo-meters !!! ...
... What do they tell us ? Age of the Universe = 13800000000 Years Size of our Universe = 13800000000 Light Years = 100000000000000000000000 kilo-meters !!! ...
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 ...