Criteria for Depressive Disorder (summary of the guideline)
... Depressed mood or moody impression because of little eye contact, monotonous speech and slow motor system. ...
... Depressed mood or moody impression because of little eye contact, monotonous speech and slow motor system. ...
Mood Disorders
... restlessness, agitation, sleeplessness, pressured speech, flight of ideas, sexual disinhibition, inflated self-esteem, reckless behavior several DSM subtypes, based on whether youngster displays a manic, mixed, or hypomanic episode ...
... restlessness, agitation, sleeplessness, pressured speech, flight of ideas, sexual disinhibition, inflated self-esteem, reckless behavior several DSM subtypes, based on whether youngster displays a manic, mixed, or hypomanic episode ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint
... • What is dissociation? – literally a dis-association of memory – person suddenly becomes unaware of some aspect of their identity or history – unable to recall except under special ...
... • What is dissociation? – literally a dis-association of memory – person suddenly becomes unaware of some aspect of their identity or history – unable to recall except under special ...
Co-Occurring Disorders
... Substance abuse and substance dependence no longer exist as a diagnosis Instead, substance diagnoses fall into four categories that describe ...
... Substance abuse and substance dependence no longer exist as a diagnosis Instead, substance diagnoses fall into four categories that describe ...
An Overview of Psychiatric Disorders Commonly Seen in
... Depression ranks among the most burdensome diseases in the world. The lifetime prevalence of Major Depression in the U.S. is reported to be between 16 % and 20%. Approximately 5% -10% of primary care patients meet DSM-IV criteria for Major Depression and 3%-5% for ...
... Depression ranks among the most burdensome diseases in the world. The lifetime prevalence of Major Depression in the U.S. is reported to be between 16 % and 20%. Approximately 5% -10% of primary care patients meet DSM-IV criteria for Major Depression and 3%-5% for ...
Disorders and treatment – KEY TERMS 1. Hallucinations 2
... disorders: medical model, psychoanalytic, humanistic, cognitive, biological, and sociocultural. • Identify the positive and negative consequences of diagnostic labels (e.g., the Rosenhan study). • Discuss the intersection between psychology and the legal system (e.g., confidentiality, insanity defen ...
... disorders: medical model, psychoanalytic, humanistic, cognitive, biological, and sociocultural. • Identify the positive and negative consequences of diagnostic labels (e.g., the Rosenhan study). • Discuss the intersection between psychology and the legal system (e.g., confidentiality, insanity defen ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... Possible Origins and Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder The cause of Borderline Personality disorder is still unclear. Research shows that chemical imbalances in the brain and other biological factors may be involved, such as heredity. Childhood trauma, such as abuse and neglect, have also be ...
... Possible Origins and Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder The cause of Borderline Personality disorder is still unclear. Research shows that chemical imbalances in the brain and other biological factors may be involved, such as heredity. Childhood trauma, such as abuse and neglect, have also be ...
PSYCHOLOGY MID-TERM REVIEW GUIDE
... 28. What is the purpose of the myelin sheath? 29. What does the endocrine system regulate in the human body? 30. Which neurons carry messages from the central nervous system (CNS) to glands and muscles? 31. Due to Phineas Gage’s accident, what do we know about the frontal lobes? 32. Which region of ...
... 28. What is the purpose of the myelin sheath? 29. What does the endocrine system regulate in the human body? 30. Which neurons carry messages from the central nervous system (CNS) to glands and muscles? 31. Due to Phineas Gage’s accident, what do we know about the frontal lobes? 32. Which region of ...
Mental Health - Jones College Prep
... • An unhealthy way to cope with emotions, stress, or traumatic events • Self-injury can be a symptom of a mood disorder, anxiety disorder, or eating disorder • Most people aren’t attempting suicide, but it is done to feel better in a situation – Some people may attempt suicide, but this is due to em ...
... • An unhealthy way to cope with emotions, stress, or traumatic events • Self-injury can be a symptom of a mood disorder, anxiety disorder, or eating disorder • Most people aren’t attempting suicide, but it is done to feel better in a situation – Some people may attempt suicide, but this is due to em ...
Psychological (or Mental) Disorders
... • Severe cases fairly rare but experiencing some somatic symptoms much more common ...
... • Severe cases fairly rare but experiencing some somatic symptoms much more common ...
handout
... This term is used in children who are over the age of 5 when assessment of the degree of intellectual disability is difficult or impossible. • This could be due to a lack of locally available procedures or due to physical impairments such as blindness or deafness. • There also could be severe behavi ...
... This term is used in children who are over the age of 5 when assessment of the degree of intellectual disability is difficult or impossible. • This could be due to a lack of locally available procedures or due to physical impairments such as blindness or deafness. • There also could be severe behavi ...
Somatization: Principles of Clinical Management
... menses, excessive menstrual bleeding, vomiting throughout pregnancy) 4 one pseudoneurological symptom: a history of at least one symptom or deficit suggesting a neurological condition not limited to pain (conversion symptoms such as impaired coordination or balance, paralysis or localized weakness, ...
... menses, excessive menstrual bleeding, vomiting throughout pregnancy) 4 one pseudoneurological symptom: a history of at least one symptom or deficit suggesting a neurological condition not limited to pain (conversion symptoms such as impaired coordination or balance, paralysis or localized weakness, ...
Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Depression and Anxiety
... • Major Depressive Disorder is a clinical diagnosis • No diagnostic blood test or brain scan • Insight needed for optimal self-report • Optimal assessment involves skilled clinical assessment and information from an outside informant ...
... • Major Depressive Disorder is a clinical diagnosis • No diagnostic blood test or brain scan • Insight needed for optimal self-report • Optimal assessment involves skilled clinical assessment and information from an outside informant ...
Somato Form PPT
... menses, excessive menstrual bleeding, vomiting throughout pregnancy) 4 one pseudoneurological symptom: a history of at least one symptom or deficit suggesting a neurological condition not limited to pain (conversion symptoms such as impaired coordination or balance, paralysis or localized weakness, ...
... menses, excessive menstrual bleeding, vomiting throughout pregnancy) 4 one pseudoneurological symptom: a history of at least one symptom or deficit suggesting a neurological condition not limited to pain (conversion symptoms such as impaired coordination or balance, paralysis or localized weakness, ...
The sections in the book that correspond to this quiz are modules 29
... 17. According to the medical model, psychological disorders are: A) learned habits that need to be extinguished. B) maladaptive responses to a troubling environment. C) purely imaginary symptoms of distress. D) sicknesses that need to be diagnosed and cured. 18. Nonmedical therapy is known as: A) th ...
... 17. According to the medical model, psychological disorders are: A) learned habits that need to be extinguished. B) maladaptive responses to a troubling environment. C) purely imaginary symptoms of distress. D) sicknesses that need to be diagnosed and cured. 18. Nonmedical therapy is known as: A) th ...
PSY240H1S Introduction to Abnormal Psychology
... • AND one month of concern about additional attacks • OR... worry about the implications of the attack or its consequences • OR... a significant change in behaviour related to the attacks ...
... • AND one month of concern about additional attacks • OR... worry about the implications of the attack or its consequences • OR... a significant change in behaviour related to the attacks ...
Ch 12
... 26. How can depression be a vicious cycle? In your discussion incorporate Martin Seligman’s concept of “learned helplessness.” 27. What does the cognitive approach to depression suggest as being an appropriate therapy for depression? 28. Why do depression rates tend to be higher in men than in women ...
... 26. How can depression be a vicious cycle? In your discussion incorporate Martin Seligman’s concept of “learned helplessness.” 27. What does the cognitive approach to depression suggest as being an appropriate therapy for depression? 28. Why do depression rates tend to be higher in men than in women ...
Friday, October 29
... Manic episode Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Differences in rates of depression between men & women Explaining depressive disorders (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
... Manic episode Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Differences in rates of depression between men & women Explaining depressive disorders (psychoanalytic theory, biological theory, social-cognitive theory ((ex. attributional theory)), humanistic) ...
ANXIETY DISORDERS
... behaviour ( counting, checking, avoiding) most common; washing, checking, counting, need to ask or confess, symmetry ) Ego-dystonic ( the person knows that its excessive, irrational, and does not want ) %2-3, ~ 20 years. Serotonergic system, orbitofrontal cortex, caudates and thalamus. %20-30 improv ...
... behaviour ( counting, checking, avoiding) most common; washing, checking, counting, need to ask or confess, symmetry ) Ego-dystonic ( the person knows that its excessive, irrational, and does not want ) %2-3, ~ 20 years. Serotonergic system, orbitofrontal cortex, caudates and thalamus. %20-30 improv ...
BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT IMPORTANT IN DIAGNOSIS
... model tends to restrict one's view of the patient's condition to specific abnormalities, signs and symptoms, while the biopsychosocial model offers a more holistic approach. Diamant encourages doctors to think beyond the physical, neurological, pathological and biochemical aspects of treatment and t ...
... model tends to restrict one's view of the patient's condition to specific abnormalities, signs and symptoms, while the biopsychosocial model offers a more holistic approach. Diamant encourages doctors to think beyond the physical, neurological, pathological and biochemical aspects of treatment and t ...
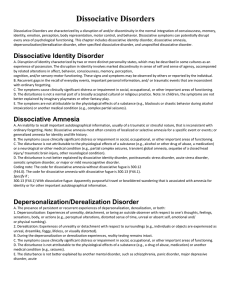
Dissociative Disorders
... B. The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. C. The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., alcohol or other drug of abuse, a medication) or a neurological or other med ...
... B. The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. C. The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., alcohol or other drug of abuse, a medication) or a neurological or other med ...
Slide 1
... - low grade depression with less severe symptoms - chronic – longer than 2 years - able to function Cyclothymic Disorder -low grade bipolar – less severe mood swings I lied – a fifth mood disorder – Seasonal Affective Disorder – SAD - related to seasonal conditions - depression symptoms ...
... - low grade depression with less severe symptoms - chronic – longer than 2 years - able to function Cyclothymic Disorder -low grade bipolar – less severe mood swings I lied – a fifth mood disorder – Seasonal Affective Disorder – SAD - related to seasonal conditions - depression symptoms ...
Psychological Disorders Review Sheet (Chapter 15)
... argues disorders are maladaptive behaviors LEARNED from inappropriate rewards and/or punishments. ...
... argues disorders are maladaptive behaviors LEARNED from inappropriate rewards and/or punishments. ...