ME 204 Thermodynamics I
... Internal Energy, Enthalpy, and Specıfıc Heats of Ideal Gases In general, for any substance the internal energy u depends on the two independent properties specifying the state. For a low-density gas, however, u depends primarily on T and much less on the second property, P or v. Internal Energy val ...
... Internal Energy, Enthalpy, and Specıfıc Heats of Ideal Gases In general, for any substance the internal energy u depends on the two independent properties specifying the state. For a low-density gas, however, u depends primarily on T and much less on the second property, P or v. Internal Energy val ...
Free Energy. Thermodynamic Identities. Phase
... internal energy is of principal importance because it is conserved; more precisely its change is controlled by the first law. A second energy type of quantity is the enthalpy H = U +P V which is the energy needed/yielded upon creation/destruction of the system with volume V in an environment at a fi ...
... internal energy is of principal importance because it is conserved; more precisely its change is controlled by the first law. A second energy type of quantity is the enthalpy H = U +P V which is the energy needed/yielded upon creation/destruction of the system with volume V in an environment at a fi ...
Energy Practice Exam
... ground level. Which of the following statements best describes the energy of the student and sled from point W to point Z? The total energy at point W is less than at point Z The total energy at point W is greater than at point Z The potential energy at point W becomes all kinetic energy at point Z ...
... ground level. Which of the following statements best describes the energy of the student and sled from point W to point Z? The total energy at point W is less than at point Z The total energy at point W is greater than at point Z The potential energy at point W becomes all kinetic energy at point Z ...
Chapter 20 - UCF Physics
... Latent Heat • The latent heat of fusion is used when the phase change is from solid to liquid • The latent heat of vaporization is used when the phase change is from liquid to gas • The positive sign is used when the energy is transferred into the system – This will result in melting or boiling ...
... Latent Heat • The latent heat of fusion is used when the phase change is from solid to liquid • The latent heat of vaporization is used when the phase change is from liquid to gas • The positive sign is used when the energy is transferred into the system – This will result in melting or boiling ...
Chapter 20 - UCF College of Sciences
... The addition of energy will cause the amplitude of the vibration of the molecules about their equilibrium position to increase At the melting point, the amplitude is great enough to break apart bonds between the molecules The molecules can move to new positions The molecules in the liquid are bound ...
... The addition of energy will cause the amplitude of the vibration of the molecules about their equilibrium position to increase At the melting point, the amplitude is great enough to break apart bonds between the molecules The molecules can move to new positions The molecules in the liquid are bound ...
12.1 Work Energy Power
... Energy can change from one form to another. Eventually all forms of energy change into heat which is lost to space. 4.18 J of any energy (work) will become 1 cal of heat (the amount of heat that raises the temperature of 1 g of water 1 celsius degree). Conservation of energy means that energy can no ...
... Energy can change from one form to another. Eventually all forms of energy change into heat which is lost to space. 4.18 J of any energy (work) will become 1 cal of heat (the amount of heat that raises the temperature of 1 g of water 1 celsius degree). Conservation of energy means that energy can no ...
Physical Science Day Starters
... 0.386. If equal masses of aluminum and copper wire are placed in a flame, which one will require more energy to raise its temperature by 1C? (A) aluminum (B) copper (C) both will increase at the same rate Which has more total thermal energy – a bathtub of cold water or a red-hot nail? (A) The batht ...
... 0.386. If equal masses of aluminum and copper wire are placed in a flame, which one will require more energy to raise its temperature by 1C? (A) aluminum (B) copper (C) both will increase at the same rate Which has more total thermal energy – a bathtub of cold water or a red-hot nail? (A) The batht ...
Lectures 21 and 22 - NUS Physics Department
... The addition of energy will cause the amplitude of the vibration of the molecules about their equilibrium position to increase At the melting point, the amplitude is great enough to break apart bonds between the molecules The molecules can move to new positions The molecules in the liquid are bound ...
... The addition of energy will cause the amplitude of the vibration of the molecules about their equilibrium position to increase At the melting point, the amplitude is great enough to break apart bonds between the molecules The molecules can move to new positions The molecules in the liquid are bound ...
- Philsci
... the thermodynamic limit. Basically, the infinite size makes shape irrelevant for SM’s pressure. Similarly the infinite system with realistic4 interactions among its constituents makes SM’s entropy and internal energy truly extensive because the ratio of the summation of bulk interactions to that of ...
... the thermodynamic limit. Basically, the infinite size makes shape irrelevant for SM’s pressure. Similarly the infinite system with realistic4 interactions among its constituents makes SM’s entropy and internal energy truly extensive because the ratio of the summation of bulk interactions to that of ...
Study Guide for Final Exam
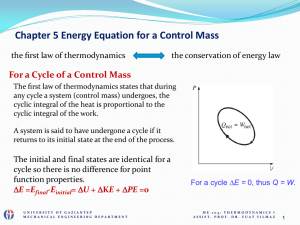
... control volume, which for a fixed mass is a control mass. Such a system can be isolated, exchanging neither mass, momentum, nor energy with its surroundings. A closed system versus an open system refers to the ability of mass exchange with the surroundings. If properties for a substance change, the ...
... control volume, which for a fixed mass is a control mass. Such a system can be isolated, exchanging neither mass, momentum, nor energy with its surroundings. A closed system versus an open system refers to the ability of mass exchange with the surroundings. If properties for a substance change, the ...
CHAPTER 4: PHASE TRANSITIONS
... example, solid ice, liquid water, and gaseous water vapor are separate phases of the same chemical species ( H 2O ) . Each phase can be distinguished with the density ρ of the constituent. For example, a portion of the Arctic Ocean in vicinity of the North Pole is frozen and consists of ice in a top ...
... example, solid ice, liquid water, and gaseous water vapor are separate phases of the same chemical species ( H 2O ) . Each phase can be distinguished with the density ρ of the constituent. For example, a portion of the Arctic Ocean in vicinity of the North Pole is frozen and consists of ice in a top ...
Objective 5 - Physics
... Heat is energy When you add heat to a substance, you are adding energy. • When heat (energy) goes into a substance one of two things can happen: • 1. The substance can experience a rise in temperature- an increase in the kinetic energy of the molecules.. • 2. The substance can change state. ...
... Heat is energy When you add heat to a substance, you are adding energy. • When heat (energy) goes into a substance one of two things can happen: • 1. The substance can experience a rise in temperature- an increase in the kinetic energy of the molecules.. • 2. The substance can change state. ...
Unit III: Laws of Motion
... Experiments Total Periods : 60 (Any 8 experiments out of the following to be performed by the Students) 1. To measure diameter of a small spherical/cylindrical body using Vernier Callipers. 2. To measure internal diameter and depth of a given beaker/calorimeter using Vernier Callipers and hence find ...
... Experiments Total Periods : 60 (Any 8 experiments out of the following to be performed by the Students) 1. To measure diameter of a small spherical/cylindrical body using Vernier Callipers. 2. To measure internal diameter and depth of a given beaker/calorimeter using Vernier Callipers and hence find ...
Document
... motion; Explain how Newton’s three laws of motion apply to real world situations (e.g., sports, transportation) ...
... motion; Explain how Newton’s three laws of motion apply to real world situations (e.g., sports, transportation) ...
EOCT Review (Extra Credit)
... 21. How can you find the weight of something using a mathematical formula? 22. What two things does momentum of an object depend on? 23. What is the definition of momentum? 24. What is the triangle formula for speed or velocity...and what is the SI unit for both? 25. What do unbalanced forces cause? ...
... 21. How can you find the weight of something using a mathematical formula? 22. What two things does momentum of an object depend on? 23. What is the definition of momentum? 24. What is the triangle formula for speed or velocity...and what is the SI unit for both? 25. What do unbalanced forces cause? ...
3.1 Thermal concepts (PPT)
... Thermal energy is a term often confused with that of heat. Simply put, heat is the flow of thermal energy. Thermal energy is the total internal energy of the system. This has to do with the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules, i.e. how fast the molecules are vibrating and their chemical ...
... Thermal energy is a term often confused with that of heat. Simply put, heat is the flow of thermal energy. Thermal energy is the total internal energy of the system. This has to do with the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules, i.e. how fast the molecules are vibrating and their chemical ...
chapter20
... Internal Energy and Other Energies The kinetic energy due to its motion through space is not included. ...
... Internal Energy and Other Energies The kinetic energy due to its motion through space is not included. ...