PDF (Chapter 5. Thermodynamics and Equations of State)
... probably can be treated with classical solid-state physics concepts. I say "probably" because the interior of the Earth is at simultaneous high temperature and high pressure and these are competing effects. The quantization of lattice vibrations and the departures from classical behavior that are of ...
... probably can be treated with classical solid-state physics concepts. I say "probably" because the interior of the Earth is at simultaneous high temperature and high pressure and these are competing effects. The quantization of lattice vibrations and the departures from classical behavior that are of ...
Grade 8 Physical Science 2015 Unit 1
... o The term “heat” as used in everyday language refers both to thermal energy (the motion of atoms or molecules within a substance) and the transfer of that thermal energy from one object to another. In science, heat is used only for this second meaning; it refers to the energy transferred due to the ...
... o The term “heat” as used in everyday language refers both to thermal energy (the motion of atoms or molecules within a substance) and the transfer of that thermal energy from one object to another. In science, heat is used only for this second meaning; it refers to the energy transferred due to the ...
Kinetic energy
... Mechanical energy is the total amount of kinetic and potential energy in a system. In any given situation, energy may change from one form to another, but the total amount of energy remains constant: energy is conserved. The law of conservation of energy states that energy may change form but it c ...
... Mechanical energy is the total amount of kinetic and potential energy in a system. In any given situation, energy may change from one form to another, but the total amount of energy remains constant: energy is conserved. The law of conservation of energy states that energy may change form but it c ...
Heat and Properties of Matter
... The density of liquids and gases can be calculated the same way as in solids. If the mass and volume of a liquid is known, the density can be calculated. We can often determine which liquid has a greater density by mixing two liquids and seeing how they settle. The more dense liquid will fall toward ...
... The density of liquids and gases can be calculated the same way as in solids. If the mass and volume of a liquid is known, the density can be calculated. We can often determine which liquid has a greater density by mixing two liquids and seeing how they settle. The more dense liquid will fall toward ...
Chapter 13 Energy, Heat, and Chemical Change
... The neon atoms, more massive than helium, develop a lower speed given the same amount of kinetic energy ($mv2). 10. Total thermal energy is an extensive property, scaling with the number of molecules. The average thermal energy per molecule, an intensive property, is independent of total amount and ...
... The neon atoms, more massive than helium, develop a lower speed given the same amount of kinetic energy ($mv2). 10. Total thermal energy is an extensive property, scaling with the number of molecules. The average thermal energy per molecule, an intensive property, is independent of total amount and ...
Questions
... closer to her body, it is observed that her angular velocity increases. Ignore any effects due to friction and air resistance. Her angular velocity increases because... (A) her moment of inertia increases. (C) her rotational kinetic energy decreases. (E) her moment of inertia decreases. ...
... closer to her body, it is observed that her angular velocity increases. Ignore any effects due to friction and air resistance. Her angular velocity increases because... (A) her moment of inertia increases. (C) her rotational kinetic energy decreases. (E) her moment of inertia decreases. ...
Basic Concepts and Definitions
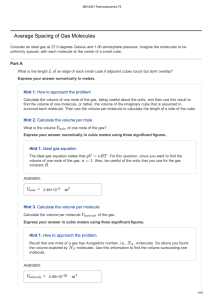
... The results of macroscopic thermodynamics are obtained from microscopic study of matter. For example, consider a cube of 25 mm side and containing a monatomic gas at atmospheric pressure and temperature. Suppose, this volume contains 1020 atoms. In order to describe position and velocity of each ato ...
... The results of macroscopic thermodynamics are obtained from microscopic study of matter. For example, consider a cube of 25 mm side and containing a monatomic gas at atmospheric pressure and temperature. Suppose, this volume contains 1020 atoms. In order to describe position and velocity of each ato ...
Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance
... also higher under cloudy skies that under clear skies, as cloud bases act like blackbody emitters. Trees are also very nearly blackbodies, such that Lin is higher under a forest canopy than an adjacent open field. In most cases, outgoing longwave radiation exceeds incoming longwave radiation i.e., L ...
... also higher under cloudy skies that under clear skies, as cloud bases act like blackbody emitters. Trees are also very nearly blackbodies, such that Lin is higher under a forest canopy than an adjacent open field. In most cases, outgoing longwave radiation exceeds incoming longwave radiation i.e., L ...
kinetic theory
... chemically to yield another gas, their volumes are in the ratios of small integers. Avogadro’s law (or hypothesis) says: Equal volumes of all gases at equal temperature and pressure have the same number of molecules. Avogadro’s law, when combined with Dalton’s theory explains Gay Lussac’s law. Since ...
... chemically to yield another gas, their volumes are in the ratios of small integers. Avogadro’s law (or hypothesis) says: Equal volumes of all gases at equal temperature and pressure have the same number of molecules. Avogadro’s law, when combined with Dalton’s theory explains Gay Lussac’s law. Since ...
Fundamental Concepts, Definitions and Zeroth
... 2. Microscopic approach–(Micro means small) The state or condition of the system can be completely described by measured values of pressure, temperature and volume which are called macroscopic or time–averaged variables. In the classical ...
... 2. Microscopic approach–(Micro means small) The state or condition of the system can be completely described by measured values of pressure, temperature and volume which are called macroscopic or time–averaged variables. In the classical ...
Ch06CQ5e
... at the top of the second hill. As the roller coaster descends the first hill, its total mechanical energy remains constant at all times. Its gravitational potential energy at the top of the hill is converted entirely into kinetic energy at the bottom. When the roller coaster ascends the second hill, ...
... at the top of the second hill. As the roller coaster descends the first hill, its total mechanical energy remains constant at all times. Its gravitational potential energy at the top of the hill is converted entirely into kinetic energy at the bottom. When the roller coaster ascends the second hill, ...
Phase Transformations
... • Provide a fine distribution of alloy carbides during tempering • ↑ resistance to softening on tempering • ↑ corrosion and oxidation resistance • ↑ strength at high temperatures • Strengthen steels that cannot be quenched • Make easier to obtain the properties throughout a larger section • ↑ Elasti ...
... • Provide a fine distribution of alloy carbides during tempering • ↑ resistance to softening on tempering • ↑ corrosion and oxidation resistance • ↑ strength at high temperatures • Strengthen steels that cannot be quenched • Make easier to obtain the properties throughout a larger section • ↑ Elasti ...
Introduction to SOLID STATE PHYSICS
... A hydrogen atom, having one electron, can be covalently bonded to only one atom. However, the hydrogen atom can involve itself in an additional electrostatic bond with a second atom of highly electronegative character such as fluorine or oxygen. This second bond permits a hydrogen bond between two a ...
... A hydrogen atom, having one electron, can be covalently bonded to only one atom. However, the hydrogen atom can involve itself in an additional electrostatic bond with a second atom of highly electronegative character such as fluorine or oxygen. This second bond permits a hydrogen bond between two a ...
Physical Science Day Starters
... 0.386. If equal masses of aluminum and copper wire are placed in a flame, which one will require more energy to raise its temperature by 1C? (A) aluminum (B) copper (C) both will increase at the same rate Which has more total thermal energy – a bathtub of cold water or a red-hot nail? (A) The batht ...
... 0.386. If equal masses of aluminum and copper wire are placed in a flame, which one will require more energy to raise its temperature by 1C? (A) aluminum (B) copper (C) both will increase at the same rate Which has more total thermal energy – a bathtub of cold water or a red-hot nail? (A) The batht ...
Chap8
... its work equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle it obeys Newton's second law it obeys Newton's third law its work depends on the end points of the motion, not this the path between it is not a frictional force ...
... its work equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle it obeys Newton's second law it obeys Newton's third law its work depends on the end points of the motion, not this the path between it is not a frictional force ...
Work, Energy and Power
... • Determine the kinetic energy of a 625-kg roller coaster car that is moving with a speed of 18.3 m/s. • If the roller coaster car in the above problem were moving with twice the speed, then what would be its new kinetic energy? • Missy Diwater, the former platform diver for the Ringling Brother's C ...
... • Determine the kinetic energy of a 625-kg roller coaster car that is moving with a speed of 18.3 m/s. • If the roller coaster car in the above problem were moving with twice the speed, then what would be its new kinetic energy? • Missy Diwater, the former platform diver for the Ringling Brother's C ...
chapter3lecturepost
... Thermal energy is the kinetic and potential energy associated with the random motion of the atoms inside a material that is heated. There are two ideas here: 1. All ordinary matter is made of atoms. (In extraordinary environments, such as the interior of the sun, the atoms are broken up into consti ...
... Thermal energy is the kinetic and potential energy associated with the random motion of the atoms inside a material that is heated. There are two ideas here: 1. All ordinary matter is made of atoms. (In extraordinary environments, such as the interior of the sun, the atoms are broken up into consti ...
Dissipative particle dynamics with energy conservation
... only deal with isothermal conditions since dissipative and Brownian forces cause no energy conservation in the particleÈ particle interaction. The equation for the energy transport is then of the relaxation type7 and, therefore, heat Ñow, related to the energy conservation at the microscopic scale, ...
... only deal with isothermal conditions since dissipative and Brownian forces cause no energy conservation in the particleÈ particle interaction. The equation for the energy transport is then of the relaxation type7 and, therefore, heat Ñow, related to the energy conservation at the microscopic scale, ...
temperature 2015 10 13
... This place of hotness is specific to substance, but is insensitive to pressure. ...
... This place of hotness is specific to substance, but is insensitive to pressure. ...