To P or not to P: on the evidential nature of P
... scientific inference is so extreme that few who read that passage can believe that they have grasped its true meaning. Certainly it is difficult to accept the consequences of the passage, for how could the result of an experiment fail to tell the experimenter about the local state of the world? The ...
... scientific inference is so extreme that few who read that passage can believe that they have grasped its true meaning. Certainly it is difficult to accept the consequences of the passage, for how could the result of an experiment fail to tell the experimenter about the local state of the world? The ...
lecture notes
... proof by contradiction, vacuous proof, trivial proof, and proof by cases. We start with a direct proof. Such a proof shows, using the rule of inferences that we just learned, that if p is true, then q must be true. Any established mathematical fact proved before, axioms (facts assumed to be true at ...
... proof by contradiction, vacuous proof, trivial proof, and proof by cases. We start with a direct proof. Such a proof shows, using the rule of inferences that we just learned, that if p is true, then q must be true. Any established mathematical fact proved before, axioms (facts assumed to be true at ...
Math 140 Notes and Activity Packet (Word) Hypothesis Testing
... population value, that it causes us to think that the population value may be wrong. (i.e. The sample data is not what we would expect by random chance!) How can we answer this key question we need to simulate a distribution based on the null hypothesis. This is often called a randomized simulation ...
... population value, that it causes us to think that the population value may be wrong. (i.e. The sample data is not what we would expect by random chance!) How can we answer this key question we need to simulate a distribution based on the null hypothesis. This is often called a randomized simulation ...
Statistical Inference with SCILAB
... A population constitutes the collection of all conceivable results of a random process, while a sample is a sub-set of a population. Typically, it is very difficult or impractical to evaluate the entire population for a given parameter. Therefore, we select one or more samples out of the population ...
... A population constitutes the collection of all conceivable results of a random process, while a sample is a sub-set of a population. Typically, it is very difficult or impractical to evaluate the entire population for a given parameter. Therefore, we select one or more samples out of the population ...
Part VIII - Tests of Significance - Chapters 26, 28, and 29
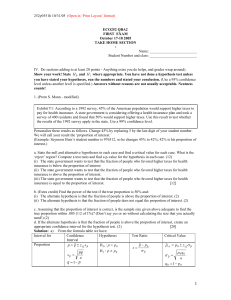
... Significance Level: The significance level, α, is a fixed constant which denotes the critical P-value which we regard to be decisive. This amounts to announcing in advance how much evidence against H0 we will require to reject H0 . The most frequently used values of α are 0.1, 0.05 or 0.01. Rules of ...
... Significance Level: The significance level, α, is a fixed constant which denotes the critical P-value which we regard to be decisive. This amounts to announcing in advance how much evidence against H0 we will require to reject H0 . The most frequently used values of α are 0.1, 0.05 or 0.01. Rules of ...
ch8 - German Vargas
... level, a power of at least 0.80 is a common requirement for determining that a hypothesis test is effective. (Some statisticians argue that the power should be higher, such as 0.85 or 0.90.) When designing an experiment, we might consider how much of a difference between the claimed value of a param ...
... level, a power of at least 0.80 is a common requirement for determining that a hypothesis test is effective. (Some statisticians argue that the power should be higher, such as 0.85 or 0.90.) When designing an experiment, we might consider how much of a difference between the claimed value of a param ...
Rules of inference
... Arguments A formal proof of a conclusion C, given premises p1, p2,…,pn consists of a sequence of steps, each of which applies some inference rule to premises or to previously-proven statements (as hypotheses) to yield a new true statement (the conclusion). A proof demonstrates that if the premis ...
... Arguments A formal proof of a conclusion C, given premises p1, p2,…,pn consists of a sequence of steps, each of which applies some inference rule to premises or to previously-proven statements (as hypotheses) to yield a new true statement (the conclusion). A proof demonstrates that if the premis ...
Testing
... This tells us that there is a 8.9% chance of observing the data that we see when the null is true. Since 8.9% is relatively large, we say that the data could have been sampled when the null is true. The null hypothesis is plausible and there is no evidence to reject the null (we cannot prove the alt ...
... This tells us that there is a 8.9% chance of observing the data that we see when the null is true. Since 8.9% is relatively large, we say that the data could have been sampled when the null is true. The null hypothesis is plausible and there is no evidence to reject the null (we cannot prove the alt ...
CHAPTER 9
... Decision: Since |tSTAT| < 2.1448, do not reject H 0 . There is not enough evidence to conclude that the mean amount spent for lunch is different from $6.50. The p-value is 0.1245. If the population mean is indeed $6.50, the probability of obtaining a test statistic that is more than 1.6344 standard ...
... Decision: Since |tSTAT| < 2.1448, do not reject H 0 . There is not enough evidence to conclude that the mean amount spent for lunch is different from $6.50. The p-value is 0.1245. If the population mean is indeed $6.50, the probability of obtaining a test statistic that is more than 1.6344 standard ...
2% - Project Maths
... Go Fast Airlines provides internal flights in Ireland, short haul flights to Europe and long haul flights to America and Asia. Each month the company carries out a survey among 1000 passengers. The company repeatedly advertises that 70% of their customers are satisfied with their overall service. 66 ...
... Go Fast Airlines provides internal flights in Ireland, short haul flights to Europe and long haul flights to America and Asia. Each month the company carries out a survey among 1000 passengers. The company repeatedly advertises that 70% of their customers are satisfied with their overall service. 66 ...
Document
... The Chi-Square Test for Goodness of Fit • Chi-square (χ2) test Tests for statistical significance. Is particularly appropriate for testing hypotheses ...
... The Chi-Square Test for Goodness of Fit • Chi-square (χ2) test Tests for statistical significance. Is particularly appropriate for testing hypotheses ...