A clinical approach to paediatric conversion disorder: VEER in the
... By contrast, children and teens with CD usually withdraw from school and/or other activities (especially performance-athletic activities, such as dance, gymnastics, or figure skating). The young person will often verbally state a desire to be able to attend school and participate in activities, but ...
... By contrast, children and teens with CD usually withdraw from school and/or other activities (especially performance-athletic activities, such as dance, gymnastics, or figure skating). The young person will often verbally state a desire to be able to attend school and participate in activities, but ...
PowerPoint
... is a result of changes in brain chemistry. Like other disorders, you can’t just will it away. 4. Depression and anxiety are signs that the person is weak ...
... is a result of changes in brain chemistry. Like other disorders, you can’t just will it away. 4. Depression and anxiety are signs that the person is weak ...
Unit 12 Study Guide
... A) active; anxiety B) passive; depression C) active; antisocial conduct D) passive; alcohol abuse 31. Which of the following is not true concerning depression? A) Depression is more common in females than in males. B) Most depressive episodes appear not to be preceded by any particular factor or eve ...
... A) active; anxiety B) passive; depression C) active; antisocial conduct D) passive; alcohol abuse 31. Which of the following is not true concerning depression? A) Depression is more common in females than in males. B) Most depressive episodes appear not to be preceded by any particular factor or eve ...
Ch 12 Big Review backup.tst
... 10. The ________ model of mental illness holds that abnormal behavior is caused by physiological malfunction that is often attributable to hereditary factors. A) cognitive-behavioral B) psychodynamic C) biological D) naturalistic 11. Thousands of years ago, mental illness was nearly always attribut ...
... 10. The ________ model of mental illness holds that abnormal behavior is caused by physiological malfunction that is often attributable to hereditary factors. A) cognitive-behavioral B) psychodynamic C) biological D) naturalistic 11. Thousands of years ago, mental illness was nearly always attribut ...
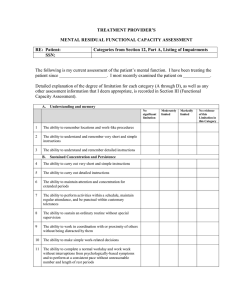
TREATMENT PROVIDER`S MENTAL RESIDUAL FUNCTIONAL
... manic and depressive syndromes (and currently characterized by either or both syndromes) ...
... manic and depressive syndromes (and currently characterized by either or both syndromes) ...
psychotic disorders
... Psychotic disorders form a diverse group of illnesses that are serious and often treatable. Psychotic disorders affect the way a person may act, think, see, hear or feel, and makes it difficult for them to distinguish between what is real and not real. There are different types of psychotic disorder ...
... Psychotic disorders form a diverse group of illnesses that are serious and often treatable. Psychotic disorders affect the way a person may act, think, see, hear or feel, and makes it difficult for them to distinguish between what is real and not real. There are different types of psychotic disorder ...
Psychological Disorders
... 1,000 mental patients 1 year after they were discharged from psychiatric facilities Monitored Group #2 (Control Group) Non-mental patients living in same neighborhood as the 1000 former mental patients Findings Former mental patients did not have a high rate of violence then the comparison gro ...
... 1,000 mental patients 1 year after they were discharged from psychiatric facilities Monitored Group #2 (Control Group) Non-mental patients living in same neighborhood as the 1000 former mental patients Findings Former mental patients did not have a high rate of violence then the comparison gro ...
Dissociative Disorders
... Dissociative disorders usually first develop as a response to a traumatic event to keep those memories under control. Stressful situations can worsen symptoms and cause problems with functioning in everyday activities. However, the symptoms a person experiences will depend on the type of dissociativ ...
... Dissociative disorders usually first develop as a response to a traumatic event to keep those memories under control. Stressful situations can worsen symptoms and cause problems with functioning in everyday activities. However, the symptoms a person experiences will depend on the type of dissociativ ...
Disruptive insights in psychiatry - Journal of Clinical Investigation
... If the medications were curative, this might have been revealing. But these medications, at best, ameliorate symptoms, and when they are effective, the effects usually require weeks of treatment. Indeed, the pharmacological effects have an unknown relationship to the pathophysiology of the mental di ...
... If the medications were curative, this might have been revealing. But these medications, at best, ameliorate symptoms, and when they are effective, the effects usually require weeks of treatment. Indeed, the pharmacological effects have an unknown relationship to the pathophysiology of the mental di ...
PSychiatric NurSing - Think Link
... Clients with PTSD who use cocaine or amphetamines are more vulnerable to paranoia and psychosis than those who do not use ...
... Clients with PTSD who use cocaine or amphetamines are more vulnerable to paranoia and psychosis than those who do not use ...
Disorders PP
... stressed, upset, fearful, panic, out of control. This leads to physical reactions (increase heart rate/breathing). ...
... stressed, upset, fearful, panic, out of control. This leads to physical reactions (increase heart rate/breathing). ...
malingering - Karen Tipton Murder
... factitious disorders. However, there are also distinct differences. A patient with a factitious disorder, like Munchausen’s, does not pretend to be sick in order to get drugs, money, or disability. No--they lie, exaggerate, and actually make themselves genuinely ill in order to simply be a patient. ...
... factitious disorders. However, there are also distinct differences. A patient with a factitious disorder, like Munchausen’s, does not pretend to be sick in order to get drugs, money, or disability. No--they lie, exaggerate, and actually make themselves genuinely ill in order to simply be a patient. ...
Title of Presentation
... someone/? makes any inquiries about me; please follow this legality. [student’s name], is on Social Security Disability Insurance. I qualify under the protection of the Department of Justice. This entitlement is provided through the ‘Americans With Disabilities Act’ and the United Stated Department ...
... someone/? makes any inquiries about me; please follow this legality. [student’s name], is on Social Security Disability Insurance. I qualify under the protection of the Department of Justice. This entitlement is provided through the ‘Americans With Disabilities Act’ and the United Stated Department ...
2. Misconceptions about Psychological Disorders
... Monitored Group #2 (Control Group) Non-mental patients living in same neighborhood as the 1000 former mental patients Findings Former mental patients did not have a high rate of violence then the comparison group Stronger predictors of violence are… 1. Living in impoverished neighborhoods 2. D ...
... Monitored Group #2 (Control Group) Non-mental patients living in same neighborhood as the 1000 former mental patients Findings Former mental patients did not have a high rate of violence then the comparison group Stronger predictors of violence are… 1. Living in impoverished neighborhoods 2. D ...
Psychological
... Enlarged cerebral ventricles MRI shows damage to frontal and temporal areas. Dopamine hypothesis: elevated levels of dopamine. Thalamus appears smaller and there seems less metabolic activity. ...
... Enlarged cerebral ventricles MRI shows damage to frontal and temporal areas. Dopamine hypothesis: elevated levels of dopamine. Thalamus appears smaller and there seems less metabolic activity. ...
Prevalence and characteristics of depression in a Japanese
... Regarding suicide, adolescent suicide was most common during the early to middle periods of the leprosarium’s history. While a large number of residents were suspected of attempting suicide, the lack of precise clinical records makes it impossible to determine the number of residents who attempted s ...
... Regarding suicide, adolescent suicide was most common during the early to middle periods of the leprosarium’s history. While a large number of residents were suspected of attempting suicide, the lack of precise clinical records makes it impossible to determine the number of residents who attempted s ...
F91 Conduct Disorders
... Attentive and answers frankly but was somehow defensive in some personal questions ...
... Attentive and answers frankly but was somehow defensive in some personal questions ...
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder - SPARK: Scholarship at Parkland
... *Experiencing a sense of panic that something bad is about to happen. ...
... *Experiencing a sense of panic that something bad is about to happen. ...
Conversion Disorder in the Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology 2
... and neuropsychological alterations reflect causative, maintaining, or consequential factors of conversion symptoms. ...
... and neuropsychological alterations reflect causative, maintaining, or consequential factors of conversion symptoms. ...
Will the Real Pseudodementia Please Stand Up?
... depression,” were much less prevalent than previously thought. A meta-analysis of 39 studies from 1987 to 20027 identified potentially reversible dementias in 9% of patients but only 0.6% actually reversed and only 0.31% Table 1 ...
... depression,” were much less prevalent than previously thought. A meta-analysis of 39 studies from 1987 to 20027 identified potentially reversible dementias in 9% of patients but only 0.6% actually reversed and only 0.31% Table 1 ...
Introduction to Psychology
... depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. ...
... depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. ...
Center for Disease Control- National Depression Screening Day
... Mental Disorders in America Mental disorders are common in the United States and internationally. An estimated 26.2 percent of Americans ages 18 and older — about one in four adults — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year.1 When applied to the 2004 U.S. Census residential populat ...
... Mental Disorders in America Mental disorders are common in the United States and internationally. An estimated 26.2 percent of Americans ages 18 and older — about one in four adults — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year.1 When applied to the 2004 U.S. Census residential populat ...
19834 Mylan CNS SADAG Booklet rF.indd
... Depression is one of the most treatable mental illnesses. Eight out ten depressed people respond to treatment and nearly all depressed people who receive treatment see at least some relief from their symptoms. Treatment for depression can include cognitive behavioural therapy, that teaches you to vi ...
... Depression is one of the most treatable mental illnesses. Eight out ten depressed people respond to treatment and nearly all depressed people who receive treatment see at least some relief from their symptoms. Treatment for depression can include cognitive behavioural therapy, that teaches you to vi ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... Lack of empathy, inflated self-appraisal, and superficial charm are features that have been commonly included in traditional conceptions of psychopathy and may be particularly distinguishing of Antisocial Personality Disorder in prison or forensic settings where criminal, delinquent, or aggressive a ...
... Lack of empathy, inflated self-appraisal, and superficial charm are features that have been commonly included in traditional conceptions of psychopathy and may be particularly distinguishing of Antisocial Personality Disorder in prison or forensic settings where criminal, delinquent, or aggressive a ...