Situational crime prevention and worldwide piracy: a cross
... Situational crime prevention is particularly relevant to piracy, since it assists in identifying measures that are effective in disrupting the opportunity for an attack (Clarke 1980, 1997, 2013). SCP is informed by the three separate theories of environmental criminology, which, when taken together, ...
... Situational crime prevention is particularly relevant to piracy, since it assists in identifying measures that are effective in disrupting the opportunity for an attack (Clarke 1980, 1997, 2013). SCP is informed by the three separate theories of environmental criminology, which, when taken together, ...
chapter 1
... Explain why police officers are allowed discretionary powers. List the three primary purposes of police patrol. Indicate some investigation strategies that are considered aggressive. Describe how forensic experts use DNA fingerprinting to solve crimes. Explain why differential response strategies en ...
... Explain why police officers are allowed discretionary powers. List the three primary purposes of police patrol. Indicate some investigation strategies that are considered aggressive. Describe how forensic experts use DNA fingerprinting to solve crimes. Explain why differential response strategies en ...
chapter 5 - MHHE.com
... 4,000 U.S. researchers said they had witnessed research misconduct (including such acts as plagiarism and falsifying data) among other faculty, and 13 to 33 percent reported various types of misconduct among graduate students (Decoo, 2002). The motive typically is career enhancement, but the desire ...
... 4,000 U.S. researchers said they had witnessed research misconduct (including such acts as plagiarism and falsifying data) among other faculty, and 13 to 33 percent reported various types of misconduct among graduate students (Decoo, 2002). The motive typically is career enhancement, but the desire ...
The Effect of Prison Population
... prison populations on crime is two to three times greater than previous estimates would imply. Prior to instrumenting, I obtain estimates that are actually slightly smaller than those in past research: elasticities of crime with respect to prisoner populations of approximately —0.10. The IV estimate ...
... prison populations on crime is two to three times greater than previous estimates would imply. Prior to instrumenting, I obtain estimates that are actually slightly smaller than those in past research: elasticities of crime with respect to prisoner populations of approximately —0.10. The IV estimate ...
Outcome 3 Safety MTSF Chapter
... in people in South Africa, especially vulnerable groups such as women, children, older persons and people with disabilities, living in fear and feeling unsafe. It also impacts negatively on the country’s economic development and undermines the wellbeing of people in the country and hinders their abi ...
... in people in South Africa, especially vulnerable groups such as women, children, older persons and people with disabilities, living in fear and feeling unsafe. It also impacts negatively on the country’s economic development and undermines the wellbeing of people in the country and hinders their abi ...
SYG 2323 Study Guide
... 3. Explain the origin of radical criminology. 4. Discuss some of the critical perspectives that have emerged over the past decade, including radical feminist theory, left realism, abolitionist and anarchist criminology, and peacemaking criminology. CHAPTER 10: Violent Crimes 1. Differentiate amongs ...
... 3. Explain the origin of radical criminology. 4. Discuss some of the critical perspectives that have emerged over the past decade, including radical feminist theory, left realism, abolitionist and anarchist criminology, and peacemaking criminology. CHAPTER 10: Violent Crimes 1. Differentiate amongs ...
The Fear Factor Stephen Harper’s “Tough on Crime” Agenda Paula Mallea >
... from prison. According to the Roadmap, Canadians need to be very afraid of violent recidivism. And yet statistics show that the rate of reoffending (both violent and non-violent) has been dropping steadily for years from an already low rate.13 For example, in 2006–2007, only 117 violent offences (0. ...
... from prison. According to the Roadmap, Canadians need to be very afraid of violent recidivism. And yet statistics show that the rate of reoffending (both violent and non-violent) has been dropping steadily for years from an already low rate.13 For example, in 2006–2007, only 117 violent offences (0. ...
Crime and Deviance
... – Police statistics always underreport the actual amount of crime – Reporting of crime is inconsistent from place to place and from time to time – Example: Why such an increase of domestic violence in Winnipeg from 1444 in 1990 to 3387 in 1996? Not that there was actually more violence in 1996, but ...
... – Police statistics always underreport the actual amount of crime – Reporting of crime is inconsistent from place to place and from time to time – Example: Why such an increase of domestic violence in Winnipeg from 1444 in 1990 to 3387 in 1996? Not that there was actually more violence in 1996, but ...
Kansas City, Missouri Smart Policing Initiative
... beneficial impact on subjective outcomes, such as citizen satisfaction with the police and fear of crime, but there was little evidence regarding its impact on crime (e.g., the Newark Foot Patrol Experiment; the Neighborhood Foot Patrol Program).10 One possible explanation for the lack of crime impa ...
... beneficial impact on subjective outcomes, such as citizen satisfaction with the police and fear of crime, but there was little evidence regarding its impact on crime (e.g., the Newark Foot Patrol Experiment; the Neighborhood Foot Patrol Program).10 One possible explanation for the lack of crime impa ...
1 - Khayelitsha Commission of Inquiry
... a site to relocate the African population of Cape Town. The area originally was a sand dune area owned by the defense force. The area was cleared and laid out for settlement. The relative security of tenure attracted residents who were at the time living in backyard shacks. Khayelitsha started as a ...
... a site to relocate the African population of Cape Town. The area originally was a sand dune area owned by the defense force. The area was cleared and laid out for settlement. The relative security of tenure attracted residents who were at the time living in backyard shacks. Khayelitsha started as a ...
The role of Forensic science in Criminal investigation in
... The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules are the genetic material of all living cells and many viruses11. It encodes an organism’s genetic blueprint and DNA is unique to each person except identical twins. It may be used for solving crimes, paternity test, identification of missing persons and unid ...
... The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules are the genetic material of all living cells and many viruses11. It encodes an organism’s genetic blueprint and DNA is unique to each person except identical twins. It may be used for solving crimes, paternity test, identification of missing persons and unid ...
sociology_powerpoint_chapter_8
... Bribing a U.S. Senator to pass a tax bill that they benefit from. People without power, on the other hand, commit deviant acts for one of two reasons. They turn to deviance either to obtain economic rewards or because they have low self-esteem and feelings of powerlessness. ► Begging for money o ...
... Bribing a U.S. Senator to pass a tax bill that they benefit from. People without power, on the other hand, commit deviant acts for one of two reasons. They turn to deviance either to obtain economic rewards or because they have low self-esteem and feelings of powerlessness. ► Begging for money o ...
Fear of Crime Among Chinese Immigrants - ScholarWorks
... English version of the questionnaire was translated by a university-level Chinese instructor. Then, the translated Chinese version was back-translated into English. The original English and the back-translated English version were then compared with each other by bilingual faculty members. Correctio ...
... English version of the questionnaire was translated by a university-level Chinese instructor. Then, the translated Chinese version was back-translated into English. The original English and the back-translated English version were then compared with each other by bilingual faculty members. Correctio ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES DRAWN INTO VIOLENCE:
... Era draft eligible inmates in prison to the fraction expected based on cohorts not subjected to the drafts, he finds imprecise effects effects on overall rates of incarceration. Our study offers several advantages over this work. First, we improve precision by using within cohort variation provided ...
... Era draft eligible inmates in prison to the fraction expected based on cohorts not subjected to the drafts, he finds imprecise effects effects on overall rates of incarceration. Our study offers several advantages over this work. First, we improve precision by using within cohort variation provided ...
ECONOMIC AND ORGANIZED CRIME: Challenges for Criminal
... frequently “computer crime” is singled out as a prime new area of concern. But it really boils down to a series of traditional criminal acts (e.g. extortion, counterfeiting or fraud) that happen today to be assisted by the use of computers. The crimes remain the same. The only difference is the tech ...
... frequently “computer crime” is singled out as a prime new area of concern. But it really boils down to a series of traditional criminal acts (e.g. extortion, counterfeiting or fraud) that happen today to be assisted by the use of computers. The crimes remain the same. The only difference is the tech ...
Zero tolerance policing - Office of Crime Statistics and Research
... responsible for the decline in the crime rate (‘Crime is down in New York City: blame the police’ –Bratton, 1997). Brereton (1999) suggests that recent reductions in the New York crime rate are part of a downward trend which commenced in 1990, some three years before Bratton became Police Commission ...
... responsible for the decline in the crime rate (‘Crime is down in New York City: blame the police’ –Bratton, 1997). Brereton (1999) suggests that recent reductions in the New York crime rate are part of a downward trend which commenced in 1990, some three years before Bratton became Police Commission ...
Crime and Deviance - Outwood Academy Valley
... Describe one reason why there is argument and debate about levels of violent crime in society and explain why this might make it difficult to reduce the public’s fear of such crimes. (5 marks) Describe one recent approach to reduce the number of violent crimes committed by young people and explain w ...
... Describe one reason why there is argument and debate about levels of violent crime in society and explain why this might make it difficult to reduce the public’s fear of such crimes. (5 marks) Describe one recent approach to reduce the number of violent crimes committed by young people and explain w ...
Crime and Incarceration in the 1990s
... distribution of crimes reported to the police. The offenses included in the Crime Index are the violent crimes of murder and non-negligent manslaughter, forcible rape, robbery, and aggravated assault, and the property crimes of burglary, larceny-theft, and motor vehicle theft. The second measure of ...
... distribution of crimes reported to the police. The offenses included in the Crime Index are the violent crimes of murder and non-negligent manslaughter, forcible rape, robbery, and aggravated assault, and the property crimes of burglary, larceny-theft, and motor vehicle theft. The second measure of ...
Types of Crime
... White collar crimes are crimes committed by people in middle-class jobs like in businesses, offices and so on, which are related to their jobs. Another term used by sociologists which refer to the same situation is called occupational crime. Sociologists say that people have opportunities to commit ...
... White collar crimes are crimes committed by people in middle-class jobs like in businesses, offices and so on, which are related to their jobs. Another term used by sociologists which refer to the same situation is called occupational crime. Sociologists say that people have opportunities to commit ...
Study Chapter 07 copy
... Labeling Theory (cont.) • Primary deviance is when a person engages only in isolated acts of deviance. • Secondary deviance refers to deviance as a lifestyle and as a personal identity. ...
... Labeling Theory (cont.) • Primary deviance is when a person engages only in isolated acts of deviance. • Secondary deviance refers to deviance as a lifestyle and as a personal identity. ...
Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design
... Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design, CPTED, is based on the idea that the proper design and effective use of the built environment can lead to a reduction in the incidence and fear of crime, and an improvement in the quality of life. In other words, if a site is laid out well, the likeliho ...
... Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design, CPTED, is based on the idea that the proper design and effective use of the built environment can lead to a reduction in the incidence and fear of crime, and an improvement in the quality of life. In other words, if a site is laid out well, the likeliho ...
6a) Analyse/Evaluate prisons effectiveness in tackling crime and
... The Rape Crisis centre argues that ‘not proven’ encourages rape victims to come forward as the verdict doesn’t label them liars if there is an acquittal due to a lack of corroborating evidence. Double Jeopardy and the right to be tried once Double Jeopardy is a legal principle that prevents people b ...
... The Rape Crisis centre argues that ‘not proven’ encourages rape victims to come forward as the verdict doesn’t label them liars if there is an acquittal due to a lack of corroborating evidence. Double Jeopardy and the right to be tried once Double Jeopardy is a legal principle that prevents people b ...
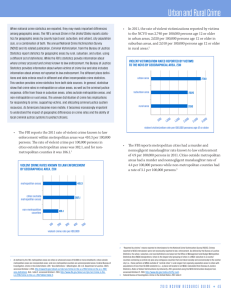
Urban and Rural Crime - National Center for Victims of Crime
... When national crime statistics are reported, they may mask important differences among geographic areas. The FBI’s annual Crime in the United States reports statistics for geographic areas by county type (rural, suburban, and urban), city population size, or a combination of both. The annual Nationa ...
... When national crime statistics are reported, they may mask important differences among geographic areas. The FBI’s annual Crime in the United States reports statistics for geographic areas by county type (rural, suburban, and urban), city population size, or a combination of both. The annual Nationa ...
preprint - Department of Economics
... we assume that changes in the level punishment entail no direct cost. (Note however that we do allow for some fixed cost associated with operating the punishment system). The society has another instrument at its disposal: the level of expenditure on policies, like enforcement, that have a direct re ...
... we assume that changes in the level punishment entail no direct cost. (Note however that we do allow for some fixed cost associated with operating the punishment system). The society has another instrument at its disposal: the level of expenditure on policies, like enforcement, that have a direct re ...