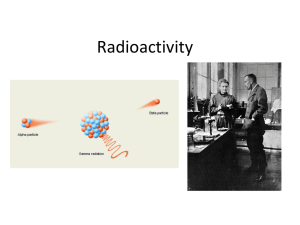
Radioactivity
... • Certain isotopes, because of their size and/or ratio of protons and neutrons are not stable. • Radioisotopes have unstable, high energy nuclei • Radioisotopes lose energy by emitting radiation and matter ...
... • Certain isotopes, because of their size and/or ratio of protons and neutrons are not stable. • Radioisotopes have unstable, high energy nuclei • Radioisotopes lose energy by emitting radiation and matter ...
Nuclear Chemistry - VCC Library
... PARTICLES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR REACTIONS The three principal emissions from the nuclei of radioactive elements are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. There are also other particles that show up in nuclear reactions like neutrons and protons. It is important to know the mass number, char ...
... PARTICLES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR REACTIONS The three principal emissions from the nuclei of radioactive elements are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. There are also other particles that show up in nuclear reactions like neutrons and protons. It is important to know the mass number, char ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
What do these food items have in common?
... technique in which food products are exposed briefly to highenergy radiation to control insects, mold, bacteria, and spoilage. ...
... technique in which food products are exposed briefly to highenergy radiation to control insects, mold, bacteria, and spoilage. ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
Topic 6 – Benefits and drawbacks of using radioactive materials
... Handling radioactive sources: The risk of harm decreases with distance from the sourceradioactive substances are always handled with tongs, and kept away from other people Protective clothing is worn in case the radioactive source happens to come into contact with the skin The most penetrating radi ...
... Handling radioactive sources: The risk of harm decreases with distance from the sourceradioactive substances are always handled with tongs, and kept away from other people Protective clothing is worn in case the radioactive source happens to come into contact with the skin The most penetrating radi ...
Isotope Half-Life Radiation Emitted
... 2. Dating rocks 3. Finding a safe isotope to put in someone’s body ...
... 2. Dating rocks 3. Finding a safe isotope to put in someone’s body ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... number 19 have stable nuclei. Elements with higher atomic number (20-83) consist of a mixture isotopes, some of which may have unstable nuclei. When the nucleus of an isotope is unstable, it is radioactive, which means that it will spontaneously emit energy to become more stable. This energy, called ...
... number 19 have stable nuclei. Elements with higher atomic number (20-83) consist of a mixture isotopes, some of which may have unstable nuclei. When the nucleus of an isotope is unstable, it is radioactive, which means that it will spontaneously emit energy to become more stable. This energy, called ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • The husband and wife team of Pierre and Marie Curie became interested in Becquereal's discovery. While experimenting with their own uranium-containing ore, they came up with the term "radioactivity" to describe the spontaneous emissions that they studied. This word is still used today to describe ...
... • The husband and wife team of Pierre and Marie Curie became interested in Becquereal's discovery. While experimenting with their own uranium-containing ore, they came up with the term "radioactivity" to describe the spontaneous emissions that they studied. This word is still used today to describe ...
Chapter 10
... with a half-life of 12 hours. How much will remain in the body after 2.0 days, assuming that radioactive decay is the only path for removal of the isotope form the body. ...
... with a half-life of 12 hours. How much will remain in the body after 2.0 days, assuming that radioactive decay is the only path for removal of the isotope form the body. ...
Alpha
... 4. Which of the three radioactive emissions best fit the following statements? Write the correct symbol/s on the lines. a) These emissions are charged. ____________ b) This emission is the most massive (heaviest). ____________ c) This emission is the most charged. ____________ d) This emission is mo ...
... 4. Which of the three radioactive emissions best fit the following statements? Write the correct symbol/s on the lines. a) These emissions are charged. ____________ b) This emission is the most massive (heaviest). ____________ c) This emission is the most charged. ____________ d) This emission is mo ...
Document
... 30. When the _nuclear strong force_ is not large enough to hold a nucleus together tightly, the nucleus can become radioactive 31. Nuclei with more than 83 protons are always unstable, no matter how many _neutrons_ they have. 32. Explain the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. nuc ...
... 30. When the _nuclear strong force_ is not large enough to hold a nucleus together tightly, the nucleus can become radioactive 31. Nuclei with more than 83 protons are always unstable, no matter how many _neutrons_ they have. 32. Explain the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. nuc ...
Beyond Element 83 are very unstable (radioactive)
... unstable (radioactive) • No amount neutrons can hold nucleus together once it has 83+ protons • All Elements 83 and above on PT are radioactive • Other elements may have radioactive isotopes applet ...
... unstable (radioactive) • No amount neutrons can hold nucleus together once it has 83+ protons • All Elements 83 and above on PT are radioactive • Other elements may have radioactive isotopes applet ...
Nuclear Hazards - SNS Courseware
... 1) Cosmic rays from outer space. The quantity depends on altitude and latitude; it is more at higher latitudes and high altitudes. 2) Emissions from radioactive materials from the Earth's crust. ...
... 1) Cosmic rays from outer space. The quantity depends on altitude and latitude; it is more at higher latitudes and high altitudes. 2) Emissions from radioactive materials from the Earth's crust. ...
2005 Nuclear FRQs - AP Chemistry Olympics
... (b) Alpha particles have a greater mass than beta par(b) Identify the type of decay expected for carbon-14 ticles. Thus, their speed (penetrating potential) is and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are ...
... (b) Alpha particles have a greater mass than beta par(b) Identify the type of decay expected for carbon-14 ticles. Thus, their speed (penetrating potential) is and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are ...
Grade 10S Physics T3W5 material
... in a leaf is magnesium used? If lead accumulates in the body until it kills, which part of the body does it destroy, and where is it stored? Are atoms of iodine able to leave solid iodine into a saturated solution of iodine? 5. When rocks form, a certain amount of radioactive material is locked up i ...
... in a leaf is magnesium used? If lead accumulates in the body until it kills, which part of the body does it destroy, and where is it stored? Are atoms of iodine able to leave solid iodine into a saturated solution of iodine? 5. When rocks form, a certain amount of radioactive material is locked up i ...
Average Atomic Mass
... • In the late 1890’s, scientists noticed that some substances spontaneously emitted radiation in a process called radioactivity. • The rays and particles emitted by a radioactive material were called radiation. ...
... • In the late 1890’s, scientists noticed that some substances spontaneously emitted radiation in a process called radioactivity. • The rays and particles emitted by a radioactive material were called radiation. ...
Nuclear Radiation and Decay File
... High energy electromagnetic radiation. Are not made of matter. No electric charge. Does not ionize material. However, gamma rays cause more damage to biological molecules as they pass through living tissue. • Can travel far through a material. ...
... High energy electromagnetic radiation. Are not made of matter. No electric charge. Does not ionize material. However, gamma rays cause more damage to biological molecules as they pass through living tissue. • Can travel far through a material. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... days after the accident, but not enough to cause any dose above background levels to local residents. • There were no injuries or adverse health effects from the Three Mile Island accident. ...
... days after the accident, but not enough to cause any dose above background levels to local residents. • There were no injuries or adverse health effects from the Three Mile Island accident. ...
File
... • A neutron breaks apart into a proton, which remains in the nucleus, and an electron, which is released 14 C ...
... • A neutron breaks apart into a proton, which remains in the nucleus, and an electron, which is released 14 C ...
Notes - Science With Horne
... • A neutron breaks apart into a proton, which remains in the nucleus, and an electron, which is released 14 C ...
... • A neutron breaks apart into a proton, which remains in the nucleus, and an electron, which is released 14 C ...
nuclear radiation
... radiation given off when an atom of one element underwent transmutation and became an atom of another element. The two types of radiation he found were: •The alpha particle (a) •The beta particle (b) A third type of radiation that was discovered later is called: ...
... radiation given off when an atom of one element underwent transmutation and became an atom of another element. The two types of radiation he found were: •The alpha particle (a) •The beta particle (b) A third type of radiation that was discovered later is called: ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... charge, so they do not alter the atomic number or the mass number • Gamma particles have the largest penetration ability ...
... charge, so they do not alter the atomic number or the mass number • Gamma particles have the largest penetration ability ...
Fallout shelter

A fallout shelter is an enclosed space specially designed to protect occupants from radioactive debris or fallout resulting from a nuclear explosion. Many such shelters were constructed as civil defense measures during the Cold War.During a nuclear explosion, matter vaporized in the resulting fireball is exposed to neutrons from the explosion, absorbs them, and becomes radioactive. When this material condenses in the rain, it forms dust and light sandy materials that resembles ground pumice. The fallout emits alpha and beta particles, as well as gamma rays.Much of this highly radioactive material falls to earth, subjecting anything within the line of sight to radiation, becoming a significant hazard. A fallout shelter is designed to allow its occupants to minimize exposure to harmful fallout until radioactivity has decayed to a safer level.