Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry
... Section 25.2 Nuclear Transformations - In this section, you will learn about the decay rates of radioactive substances. 1. Nuclear Stability and Decay All nuclei contain protons and neutrons (exception - hydrogen-1 has no neutrons). Since protons are positively charged, it would be expected that the ...
... Section 25.2 Nuclear Transformations - In this section, you will learn about the decay rates of radioactive substances. 1. Nuclear Stability and Decay All nuclei contain protons and neutrons (exception - hydrogen-1 has no neutrons). Since protons are positively charged, it would be expected that the ...
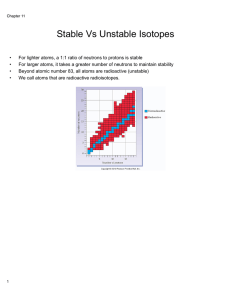
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... Co-60 is used in external beam radiation therapy. It undergoes beta decay which is accompanied by the emission of gamma rays. Write an equation to show this decay: ...
... Co-60 is used in external beam radiation therapy. It undergoes beta decay which is accompanied by the emission of gamma rays. Write an equation to show this decay: ...
radiation!!! - Mr Schmitt
... hold the nucleus together= NUCLEAR FORCE Sometimes there are not enough neutrons in the nucleus. This means the balance between repulsive forces and nuclear forces is off! ...
... hold the nucleus together= NUCLEAR FORCE Sometimes there are not enough neutrons in the nucleus. This means the balance between repulsive forces and nuclear forces is off! ...
1 0 +1 0 - davis.k12.ut.us
... occur in nature, can you list a few? Technetium, neptunium, elements 93 and up… 10. How can synthetic elements be produced? Bombarding an atom with a neutron or alpha particle. 11. A 5.0 g sample of Lead-210 decays to approximately .63 g. How much time has passed if Lead-210 has a half-life of 22 ye ...
... occur in nature, can you list a few? Technetium, neptunium, elements 93 and up… 10. How can synthetic elements be produced? Bombarding an atom with a neutron or alpha particle. 11. A 5.0 g sample of Lead-210 decays to approximately .63 g. How much time has passed if Lead-210 has a half-life of 22 ye ...
Radioactivity - Williamstown Independent Schools
... • Mass defect is the difference between the mass of all the particles in an atom and the actual mass of the atom. • This “missing mass” comes about when the nucleus forms and a small amount of mass is converted to energy. ...
... • Mass defect is the difference between the mass of all the particles in an atom and the actual mass of the atom. • This “missing mass” comes about when the nucleus forms and a small amount of mass is converted to energy. ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Mona Shores Blogs
... • Because of the size issue, there is a point beyond which all elements are radioactive. • Once they become large enough, the repulsive forces overcome. This occurs with all nuclei with 83 or more protons. • Therefore, all elements with an atomic number greater than 83 are radioactive! ...
... • Because of the size issue, there is a point beyond which all elements are radioactive. • Once they become large enough, the repulsive forces overcome. This occurs with all nuclei with 83 or more protons. • Therefore, all elements with an atomic number greater than 83 are radioactive! ...
Chapter 1
... • Emitted from the nucleus as a neutron, is converted to a proton • Higher speed particles, more penetrating than alpha particles ...
... • Emitted from the nucleus as a neutron, is converted to a proton • Higher speed particles, more penetrating than alpha particles ...
radioactivity-ppt
... Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
... Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
Radioactivity
... Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
... Rocks on Earth have been dated to 3.7 bil yrs old Rocks on Moon dated to 4.2 bil yrs old The Earth has been dated to 4.6 bil yrs old ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • Atom releases a beta particle with zero mass & negative charge • Atomic number increases (becomes new element!) ...
... • Atom releases a beta particle with zero mass & negative charge • Atomic number increases (becomes new element!) ...
Chapter 16 Notes - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... acquire electrons, and become helium atoms. 2. Paper, clothing, and skin will protect you from alpha particles. 3. Beta particles have a very small mass and move much faster and farther than alpha particles, traveling as much as several meters through air. 4. Beta particles can penetrate as far as 4 ...
... acquire electrons, and become helium atoms. 2. Paper, clothing, and skin will protect you from alpha particles. 3. Beta particles have a very small mass and move much faster and farther than alpha particles, traveling as much as several meters through air. 4. Beta particles can penetrate as far as 4 ...
Topic 6 Radioactivity Core Questions
... released particles after and the atomic number (proton number) before with the total atomic numbers (proton numbers) of the new isotope and released particles after. When is gamma radiation emitted? When a radioisotope undergoes decay by alpha or beta (+ or -) emission, the nuclear rearrangement usu ...
... released particles after and the atomic number (proton number) before with the total atomic numbers (proton numbers) of the new isotope and released particles after. When is gamma radiation emitted? When a radioisotope undergoes decay by alpha or beta (+ or -) emission, the nuclear rearrangement usu ...
The Cold War in America
... tapped into Americans’ fears of nuclear fallout • Government used propaganda to teach Americans how to deal with the threat • Encouraged people to build their own shelters • Interstate highway system doubled as defense system ...
... tapped into Americans’ fears of nuclear fallout • Government used propaganda to teach Americans how to deal with the threat • Encouraged people to build their own shelters • Interstate highway system doubled as defense system ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... number 19 have stable nuclei. Elements with higher atomic number (20-83) consist of a mixture isotopes, some of which may have unstable nuclei. When the nucleus of an isotope is unstable, it is radioactive, which means that it will spontaneously emit energy to become more stable. This energy, called ...
... number 19 have stable nuclei. Elements with higher atomic number (20-83) consist of a mixture isotopes, some of which may have unstable nuclei. When the nucleus of an isotope is unstable, it is radioactive, which means that it will spontaneously emit energy to become more stable. This energy, called ...
Physics 535 lectures notes: 1 * Sep 4th 2007
... a) Why did we observe the nuclear masses that we see? For instance, why was Helium four times more massive than hydrogen rather than twice? b) How did you bind the positively charged particles together when they should have a strong electromagnetic repulsion? c) How to explain other “radiation” emit ...
... a) Why did we observe the nuclear masses that we see? For instance, why was Helium four times more massive than hydrogen rather than twice? b) How did you bind the positively charged particles together when they should have a strong electromagnetic repulsion? c) How to explain other “radiation” emit ...
Section G23: Atoms and Radioactivity
... (min), second (s). 7.2 describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols such as C 14 6 to describe particular nuclei 7.3 understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma ...
... (min), second (s). 7.2 describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols such as C 14 6 to describe particular nuclei 7.3 understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma ...
Chemistry (B) HW Chapter 25
... a. It slows down the reaction. b. It speeds up the reaction. c. It increases the rate of heat absorption. d. It recycles the fuel. ____ 42. Control rods made of ____. a. carbon c. plutonium b. liquid sodium d. cadmium ____ 43. What substances are used as moderators in a nuclear reactor? a. carbon an ...
... a. It slows down the reaction. b. It speeds up the reaction. c. It increases the rate of heat absorption. d. It recycles the fuel. ____ 42. Control rods made of ____. a. carbon c. plutonium b. liquid sodium d. cadmium ____ 43. What substances are used as moderators in a nuclear reactor? a. carbon an ...
What is “Radiation”?
... (electrons or betas) are decelerated by a strong electrostatic field, such as that found near the nuclei of heavy metals (tungsten, lead). ...
... (electrons or betas) are decelerated by a strong electrostatic field, such as that found near the nuclei of heavy metals (tungsten, lead). ...
(or radioactive isotopes).
... • Gamma rays are used to kill bacteria, mould and insects in food. They are also used to kill bacteria on hospital equipment, dressings and bandages. • This is useful particularly on packaged food or on plastic items which would be damaged by heat sterilisation. • There are arguments for using cobal ...
... • Gamma rays are used to kill bacteria, mould and insects in food. They are also used to kill bacteria on hospital equipment, dressings and bandages. • This is useful particularly on packaged food or on plastic items which would be damaged by heat sterilisation. • There are arguments for using cobal ...
Chapter 25 Radioactivity
... and move faster. Beta particles have more penetrating power than alpha particle Sheet of aluminum foil will stop beta part. (diagram courtesy of the University of Michigan Student Chapter of the Health Physics Society) ...
... and move faster. Beta particles have more penetrating power than alpha particle Sheet of aluminum foil will stop beta part. (diagram courtesy of the University of Michigan Student Chapter of the Health Physics Society) ...
Chapter 9: Nuclear Changes
... - nuclear ________- the particles that are released from the nucleus during radioactive decay - may have effects on other materials 4 Types of Nuclear Radiation 1) ____________ particles (___) - positively charged - more massive than any other type of nuclear radiation - made of 2 protons and 2 neut ...
... - nuclear ________- the particles that are released from the nucleus during radioactive decay - may have effects on other materials 4 Types of Nuclear Radiation 1) ____________ particles (___) - positively charged - more massive than any other type of nuclear radiation - made of 2 protons and 2 neut ...
Ch 10 Nuclear Chemistry
... • Fusion is a process in which the nuclei of two atoms combine to form a larger nucleus. • During fusion a small fraction of the reactant mass is converted into energy. • Inside the sun an estimated 600 millions tons of hydrogen undergo fusion each second ...
... • Fusion is a process in which the nuclei of two atoms combine to form a larger nucleus. • During fusion a small fraction of the reactant mass is converted into energy. • Inside the sun an estimated 600 millions tons of hydrogen undergo fusion each second ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... 1. Gamma rays () are high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state 2. Gamma emission usually follows other types of decay that leave the nucleus in an excited state ...
... 1. Gamma rays () are high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state 2. Gamma emission usually follows other types of decay that leave the nucleus in an excited state ...
Fallout shelter

A fallout shelter is an enclosed space specially designed to protect occupants from radioactive debris or fallout resulting from a nuclear explosion. Many such shelters were constructed as civil defense measures during the Cold War.During a nuclear explosion, matter vaporized in the resulting fireball is exposed to neutrons from the explosion, absorbs them, and becomes radioactive. When this material condenses in the rain, it forms dust and light sandy materials that resembles ground pumice. The fallout emits alpha and beta particles, as well as gamma rays.Much of this highly radioactive material falls to earth, subjecting anything within the line of sight to radiation, becoming a significant hazard. A fallout shelter is designed to allow its occupants to minimize exposure to harmful fallout until radioactivity has decayed to a safer level.