Chapter 14 Bentley
... (48) As the Islamic world expanded into other regions, it brought its faith and traditions to those societies but it also adopted traditions that it encountered. ________________ adaptations were made in the areas of administrative techniques and kingship responsibilities. ___________ alos became th ...
... (48) As the Islamic world expanded into other regions, it brought its faith and traditions to those societies but it also adopted traditions that it encountered. ________________ adaptations were made in the areas of administrative techniques and kingship responsibilities. ___________ alos became th ...
File - World History with Miss Bunnell
... The Sunni majority, on the other hand, believe that Mohammed did not appoint a successor and instead recognize the first four caliphs— Abu Bakr, father-in-law of Muhammad; Umar I; Uthman ibn Affan; and Ali, son-in-law of Muhammad—as the rightful successors to Muhammad. The first caliph was elected b ...
... The Sunni majority, on the other hand, believe that Mohammed did not appoint a successor and instead recognize the first four caliphs— Abu Bakr, father-in-law of Muhammad; Umar I; Uthman ibn Affan; and Ali, son-in-law of Muhammad—as the rightful successors to Muhammad. The first caliph was elected b ...
Ch 5 Study Guide
... 10. Comparing and Contrasting How did the Sunni and Shia differ? What beliefs did they share? ___________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 11. How did the Sunni feel about the Umayyad caliphs? _________________ ___________________________ ...
... 10. Comparing and Contrasting How did the Sunni and Shia differ? What beliefs did they share? ___________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 11. How did the Sunni feel about the Umayyad caliphs? _________________ ___________________________ ...
Chapter 5 Byzantium and Islam
... Who was the founder of organized Byzantine monastic communities which adopted his idea of a single rule of life? Saint Basil of Caesarea Who were the Fatamids who weakened the Abbasid Caliphate? What did they conquer? The Fatamids believed that they were the descendants of Fatima, the daughter of M ...
... Who was the founder of organized Byzantine monastic communities which adopted his idea of a single rule of life? Saint Basil of Caesarea Who were the Fatamids who weakened the Abbasid Caliphate? What did they conquer? The Fatamids believed that they were the descendants of Fatima, the daughter of M ...
Guide to Responding to the Umayyad and Abbasid Empires
... Umayyad armies. This conquest began in the 8th century and ended in the 15th. For approximately 7 centuries, Islam was the dominant force in Spain. The Muslim period in Spain is often described as a 'golden age' of learning as the Umayyad rulers established libraries, colleges, and public baths. Lit ...
... Umayyad armies. This conquest began in the 8th century and ended in the 15th. For approximately 7 centuries, Islam was the dominant force in Spain. The Muslim period in Spain is often described as a 'golden age' of learning as the Umayyad rulers established libraries, colleges, and public baths. Lit ...
Name___________________________________ Per____
... recognize one creator god—Allah—who rewards or punishes believers after death according to how they led their lives. umma The community of all Muslims. A major innovation against the background of seventh-century Arabia, where traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a co ...
... recognize one creator god—Allah—who rewards or punishes believers after death according to how they led their lives. umma The community of all Muslims. A major innovation against the background of seventh-century Arabia, where traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a co ...
WHAP Teacher Copy Sharia Sufis and Cultural Encounters in the
... civilizationnon-Arab Persians played a prominent role 1. Persian cultural influence was reflected in a new title for the caliph, “the shadow of God on earth” B. But the political unity of the Abbasid Empire did not last long 1. Formal allegiance to the caliph in Baghdad but fractured politically in ...
... civilizationnon-Arab Persians played a prominent role 1. Persian cultural influence was reflected in a new title for the caliph, “the shadow of God on earth” B. But the political unity of the Abbasid Empire did not last long 1. Formal allegiance to the caliph in Baghdad but fractured politically in ...
The Why of Islamic Art
... he died. Third most sacred site: al-Aqsa mosque and nearby Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem. Muslims believe it is the site that Muhammad rose into heaven. This is also site that Abraham almost sacrificed Isaac (Mt. Moriah) and the site of the first and second temple of the Hebrews (both destroyed: onl ...
... he died. Third most sacred site: al-Aqsa mosque and nearby Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem. Muslims believe it is the site that Muhammad rose into heaven. This is also site that Abraham almost sacrificed Isaac (Mt. Moriah) and the site of the first and second temple of the Hebrews (both destroyed: onl ...
The Islamic World 600 to 1500 A.D.
... • Ismaili’is (Seveners) recognize son of 6th Imam as 7th Imam • Revolutionaries control Eastern Arabia, Iraq, Syria in 900’s ◊ Dominant Group (Twelvers) believes in 12 Imams descended through a different Son of the 6th Imam • The 12th was taken to heaven and will reemerge • This will be the Mahdi an ...
... • Ismaili’is (Seveners) recognize son of 6th Imam as 7th Imam • Revolutionaries control Eastern Arabia, Iraq, Syria in 900’s ◊ Dominant Group (Twelvers) believes in 12 Imams descended through a different Son of the 6th Imam • The 12th was taken to heaven and will reemerge • This will be the Mahdi an ...
Chapter Seven: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic
... Islamic civilization was enriched by Indian culture, while Indian achievements were passed to Arabs Muslims came as conquerors but interactions with Indians were generally peaceful, while the main carriers of Islam were conquerors, traders, and Sufi mystics. Additionally, colonies of Arab traders se ...
... Islamic civilization was enriched by Indian culture, while Indian achievements were passed to Arabs Muslims came as conquerors but interactions with Indians were generally peaceful, while the main carriers of Islam were conquerors, traders, and Sufi mystics. Additionally, colonies of Arab traders se ...
Spread of Islam to South and South East Asia
... Islamic civilization was enriched by Indian culture, while Indian achievements were passed to Arabs Muslims came as conquerors but interactions with Indians were generally peaceful, while the main carriers of Islam were conquerors, traders, and Sufi mystics. Additionally, colonies of Arab traders se ...
... Islamic civilization was enriched by Indian culture, while Indian achievements were passed to Arabs Muslims came as conquerors but interactions with Indians were generally peaceful, while the main carriers of Islam were conquerors, traders, and Sufi mystics. Additionally, colonies of Arab traders se ...
Chapter 6--Rise and Spread of Islam
... lost the support of his most radical adherents, the Umayyads won the renewed hostilities The Umayyad leader, Mu’awiya, was proclaimed caliph in 660. Ali was assassinated in 661 His son, Husayn, was killed at Karbala in 680. The dispute left a permanent division within Islam. The Shi’a, eventually di ...
... lost the support of his most radical adherents, the Umayyads won the renewed hostilities The Umayyad leader, Mu’awiya, was proclaimed caliph in 660. Ali was assassinated in 661 His son, Husayn, was killed at Karbala in 680. The dispute left a permanent division within Islam. The Shi’a, eventually di ...
Islam
... Ways to regulate everyday life to make it easier for Muslims to follow will of God Rules to help create the umma – uniform laws that united Muslims throughout caliphate Protection for the weak Respect for women (divorce, property) But unequal power in society & relationships ...
... Ways to regulate everyday life to make it easier for Muslims to follow will of God Rules to help create the umma – uniform laws that united Muslims throughout caliphate Protection for the weak Respect for women (divorce, property) But unequal power in society & relationships ...
325 Glossary of Islamic Terms
... University of Haifa. Among his fields of specialization are: the ArabIsraeli conflict; inter-Arab relations and the Palestinian question; international terrorism and fundamental Islam; theoretical issues and political applications in the Middle-East; Asad’s foreign policy toward Israel and Lebanon; th ...
... University of Haifa. Among his fields of specialization are: the ArabIsraeli conflict; inter-Arab relations and the Palestinian question; international terrorism and fundamental Islam; theoretical issues and political applications in the Middle-East; Asad’s foreign policy toward Israel and Lebanon; th ...
Chapter 7: The World of Islam
... d. referred to the individual who was the temporal successor of Muhammad and who also was generally considered to be an imam. e. both b and c ____ 20. Among possible reasons for Arabic expansion accepted by historians is a. acceptance of the militaristic culture of the Roman Empire by the population ...
... d. referred to the individual who was the temporal successor of Muhammad and who also was generally considered to be an imam. e. both b and c ____ 20. Among possible reasons for Arabic expansion accepted by historians is a. acceptance of the militaristic culture of the Roman Empire by the population ...
Democracy and the Muslims - Al
... The Muslim Brotherhood stressed that no government established by force can be accepted, for consultation is mandatory according to Sura 42 verse 35 of the Koran. Hence military regimes produced by coups are unIslamic. (Militant Islam, New York) It is, therefore, the consensus of the Sunni scholars ...
... The Muslim Brotherhood stressed that no government established by force can be accepted, for consultation is mandatory according to Sura 42 verse 35 of the Koran. Hence military regimes produced by coups are unIslamic. (Militant Islam, New York) It is, therefore, the consensus of the Sunni scholars ...
I. The Sasanid Empire, 224–651 A. Politics and Society 1. The
... Mesopotamia. The Sasanids confronted Arab pastoralists on their Euphrates border and the Byzantine Empire on the west. Relations with the Byzantines alternated between war and peaceful trading relationships. In times of peace, the Byzantine cities of Syria and the Arab nomads who guided caravans bet ...
... Mesopotamia. The Sasanids confronted Arab pastoralists on their Euphrates border and the Byzantine Empire on the west. Relations with the Byzantines alternated between war and peaceful trading relationships. In times of peace, the Byzantine cities of Syria and the Arab nomads who guided caravans bet ...
Arabic Islamic World PPT Powerpoint presentation
... Mecca, Medina, Yemeni cities, cities of Palmyra, Arab Petropolis Center of the city was a market place often shared with religious center Cities designed with human-environment interaction in mind Nomads came to city to trade, city often settled by whole tribes Arabs had settled in cities in Syria, ...
... Mecca, Medina, Yemeni cities, cities of Palmyra, Arab Petropolis Center of the city was a market place often shared with religious center Cities designed with human-environment interaction in mind Nomads came to city to trade, city often settled by whole tribes Arabs had settled in cities in Syria, ...
ISLAM
... Mecca, Medina, Yemeni cities, cities of Palmyra, Arab Petropolis Center of the city was a market place often shared with religious center Cities designed with human-environment interaction in mind Nomads came to city to trade, city often settled by whole tribes Arabs had settled in cities in Syria, ...
... Mecca, Medina, Yemeni cities, cities of Palmyra, Arab Petropolis Center of the city was a market place often shared with religious center Cities designed with human-environment interaction in mind Nomads came to city to trade, city often settled by whole tribes Arabs had settled in cities in Syria, ...
I. The Sasanid Empire, 224–651 A. Politics and Society 1. The
... Mesopotamia. The Sasanids confronted Arab pastoralists on their Euphrates border and the Byzantine Empire on the west. Relations with the Byzantines alternated between war and peaceful trading relationships. In times of peace, the Byzantine cities of Syria and the Arab nomads who guided caravans bet ...
... Mesopotamia. The Sasanids confronted Arab pastoralists on their Euphrates border and the Byzantine Empire on the west. Relations with the Byzantines alternated between war and peaceful trading relationships. In times of peace, the Byzantine cities of Syria and the Arab nomads who guided caravans bet ...
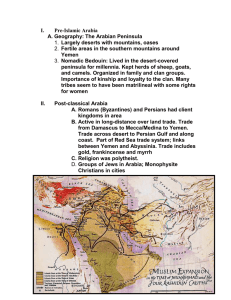
I. Pre-Islamic Arabia
... 4. Became a merchant at age 30, exposed to various faiths B. Muhammad's spiritual transformation 1. At age 40, he experienced visions 2. There was only one true god, Allah ("the god") 3. Allah would soon bring judgment on the world 4. The archangel Gabriel delivered these revelations to Muhammad 5. ...
... 4. Became a merchant at age 30, exposed to various faiths B. Muhammad's spiritual transformation 1. At age 40, he experienced visions 2. There was only one true god, Allah ("the god") 3. Allah would soon bring judgment on the world 4. The archangel Gabriel delivered these revelations to Muhammad 5. ...
Middle East History - Politics and Societies of the Middle East
... Ali lead an army to crush the rebellion of Mu`awiyah who refused to step down as the governor of Syria and accept Ali's replacement. Mu`awiyyah, fearing an eventual defeat, called for arbitration which ended up inconclusive. Ali's acceptance of arbitration angered loyal supporters of Ali and lead to ...
... Ali lead an army to crush the rebellion of Mu`awiyah who refused to step down as the governor of Syria and accept Ali's replacement. Mu`awiyyah, fearing an eventual defeat, called for arbitration which ended up inconclusive. Ali's acceptance of arbitration angered loyal supporters of Ali and lead to ...
click here
... message; they became known as the “______________ _______________ _________________” 3. The first caliph was Muhammad’s friend and father-in-law, _________ ____________; his goal was to keep Muslims under his government (the “____________________”) a. He used __________________ to control and expand ...
... message; they became known as the “______________ _______________ _________________” 3. The first caliph was Muhammad’s friend and father-in-law, _________ ____________; his goal was to keep Muslims under his government (the “____________________”) a. He used __________________ to control and expand ...
Islamic Golden Age

The Islamic Golden Age refers to the period in Islam's history during the Middle Ages from the 8th century to the 13th century when much of the historically Arabic-speaking world was ruled by various caliphates, experiencing a scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid (786 to 809) with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, where scholars from various parts of the world with different cultural backgrounds were mandated to gather and translate all of the world's classical knowledge into Arabic. It is said to have ended with the collapse of the Abbasid Caliphate with the Mongol invasions and the Sack of Baghdad in 1258. Several contemporary scholars, however, place the end of the Islamic Golden Age to be around the 16th to 17th centuries.