17. Some Examples and Applications of Time
... constant angular velocity CJ.).It can be obtained by two perpendicular stationary coils with -equal currents shifted 900 in phase, or by three stationary coils at 1200 angle with symmetrical three-phase currents. In synchronous motors, the rotating part (the rotor) is a permanent magnet, which rotat ...
... constant angular velocity CJ.).It can be obtained by two perpendicular stationary coils with -equal currents shifted 900 in phase, or by three stationary coils at 1200 angle with symmetrical three-phase currents. In synchronous motors, the rotating part (the rotor) is a permanent magnet, which rotat ...
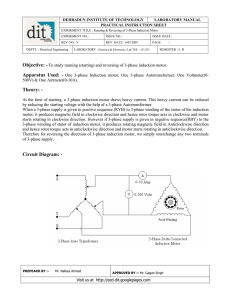
DEHRADUN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY MANUAL PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET
... Objective: - To study running (starting) and reversing of 3-phase induction motor. Apparatus Used: - One 3-phase Induction motor, One 3-phase Autotransformer, One Voltmeter(0500V) & One Ammeter(0-10A). Theory: At the time of starting, a 3-phase induction motor draws heavy current. This heavy current ...
... Objective: - To study running (starting) and reversing of 3-phase induction motor. Apparatus Used: - One 3-phase Induction motor, One 3-phase Autotransformer, One Voltmeter(0500V) & One Ammeter(0-10A). Theory: At the time of starting, a 3-phase induction motor draws heavy current. This heavy current ...
di/dt - s3.amazonaws.com
... in the circuit if the loop is a conductor. (b) If the loop is replaced by one made of an insulator, what effect does this have on the induces emf and induced current? ...
... in the circuit if the loop is a conductor. (b) If the loop is replaced by one made of an insulator, what effect does this have on the induces emf and induced current? ...
Physics 203 Sample Exam 1
... (a) constant electric and magnetic fields. (b) oscillating electric and magnetic fields in the same direction. (c) electric and magnetic fields at various angles. (d) oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles. [8] Magnetic fields can be produced by (a) electric currents (b) changing e ...
... (a) constant electric and magnetic fields. (b) oscillating electric and magnetic fields in the same direction. (c) electric and magnetic fields at various angles. (d) oscillating electric and magnetic fields at right angles. [8] Magnetic fields can be produced by (a) electric currents (b) changing e ...
Electricity generators
... current that alternates in direction as the armature revolves. Such alternating current is advantageous for electric power transmission , and hence most large electric generators are of the AC type. In its simplest form, an AC generator differs from a DC generator in only two particulars: the ends o ...
... current that alternates in direction as the armature revolves. Such alternating current is advantageous for electric power transmission , and hence most large electric generators are of the AC type. In its simplest form, an AC generator differs from a DC generator in only two particulars: the ends o ...
induced current. - University of Iowa Physics
... windings. • If the current in the primary windings were DC, there would be NO induced current in the secondary circuit. ...
... windings. • If the current in the primary windings were DC, there would be NO induced current in the secondary circuit. ...
magnetic field
... circular coils of wire uniformly wound in the shape of a cylinder through which electric current flows. Magnetic field pattern produced by a current in a solenoid is almost identical to that of a bar magnet. ...
... circular coils of wire uniformly wound in the shape of a cylinder through which electric current flows. Magnetic field pattern produced by a current in a solenoid is almost identical to that of a bar magnet. ...
Alternator
... speed, output of diode trio is fed back to the regulator and serves as the source of the field current. ...
... speed, output of diode trio is fed back to the regulator and serves as the source of the field current. ...
COMPARISON OF SCALAR AND VECTOR CONTROL
... the technique is used as Volts/Hertz constant control. Vector control is a more complex control technique, the evolution of which was inevitable, too, since scalar control cannot be applied for controlling systems with dynamic behaviour. The vector control technique works with vector quantities, con ...
... the technique is used as Volts/Hertz constant control. Vector control is a more complex control technique, the evolution of which was inevitable, too, since scalar control cannot be applied for controlling systems with dynamic behaviour. The vector control technique works with vector quantities, con ...
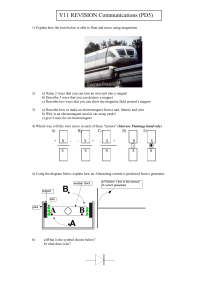
Comms Revision Questions
... a) Describe how to make an electromagnet from a nail, battery and wire b) Why is an electromagnet used in car scrap yards? c) give 6 uses for an electromagnet ...
... a) Describe how to make an electromagnet from a nail, battery and wire b) Why is an electromagnet used in car scrap yards? c) give 6 uses for an electromagnet ...
File
... Directions: Play around with the website so that you can answer the questions about the solenoid. 1. What happens to the compass as the current is increased? 2. What happens when the “current direction” box is checked? 3. What happens when the “magnetic field vector” box is checked? 4. What happens ...
... Directions: Play around with the website so that you can answer the questions about the solenoid. 1. What happens to the compass as the current is increased? 2. What happens when the “current direction” box is checked? 3. What happens when the “magnetic field vector” box is checked? 4. What happens ...