
SPH 3U Lesson 6
... We can use a solenoid to make an electrically powered bar magnet- an electromagnet, which is a device that produces a magnetic field when current is passed through it. The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by increasing the number of loops in the coil, increasing the current, or putting ...
... We can use a solenoid to make an electrically powered bar magnet- an electromagnet, which is a device that produces a magnetic field when current is passed through it. The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by increasing the number of loops in the coil, increasing the current, or putting ...
Lecture Notes Y F Chapter 29
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: Lenz’s Law The direction of any magnetic induct ...
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: Lenz’s Law The direction of any magnetic induct ...
Electromagnetic Fields - Mr. Gabrielse`s Physics Class
... 5. Expectation: The student will use appropriate methods for communicating in writing and orally the processes and results of scientific investigation. 7. Expectation: The student will show that connections exist both within the various fields of science and among science and other disciplines inclu ...
... 5. Expectation: The student will use appropriate methods for communicating in writing and orally the processes and results of scientific investigation. 7. Expectation: The student will show that connections exist both within the various fields of science and among science and other disciplines inclu ...
Physics 20800 - Section ST and ST2, Spring 2008
... 7. solve simple direct-current circuits by combining series and parallel resistors and by using Kirchoff’s laws and be able to calculate the behavior of simple R-C, L-R, and L-C circuits 8. calculate the magnetic force on a point charge moving in a magnetic field 9. calculate the magnetic fields ass ...
... 7. solve simple direct-current circuits by combining series and parallel resistors and by using Kirchoff’s laws and be able to calculate the behavior of simple R-C, L-R, and L-C circuits 8. calculate the magnetic force on a point charge moving in a magnetic field 9. calculate the magnetic fields ass ...
Magnetic Flux and Faraday`s Law of Induction
... A transformer is a device specifically designed to alter the voltage in an altering current (AC) circuit. The “adapter” used to charge a cell phone is example of a transformer. The transformer is very efficient at doing what is does do to the lack of moving parts (hence very little friction). It is ...
... A transformer is a device specifically designed to alter the voltage in an altering current (AC) circuit. The “adapter” used to charge a cell phone is example of a transformer. The transformer is very efficient at doing what is does do to the lack of moving parts (hence very little friction). It is ...
How the solar motor works. - Solar
... case that is mounted so as to be stationary. The action of the magnetic forces created inside the motor make the spindle spin. An electric motor harnesses this phenomenon to force a shaft to turn. Connecting the motor to another mechanism transfers torque (turning force). Materials: The stack contai ...
... case that is mounted so as to be stationary. The action of the magnetic forces created inside the motor make the spindle spin. An electric motor harnesses this phenomenon to force a shaft to turn. Connecting the motor to another mechanism transfers torque (turning force). Materials: The stack contai ...
Synchronous Machines
... the difficulty involved in transmitting large currents via the brushes, limit the maximum power output and the generated electromagnetic field (emf). This type is only used in small units, and its main application is as the main exciter in large alternators with brushless excitation systems. 2.2. Ro ...
... the difficulty involved in transmitting large currents via the brushes, limit the maximum power output and the generated electromagnetic field (emf). This type is only used in small units, and its main application is as the main exciter in large alternators with brushless excitation systems. 2.2. Ro ...
Electromagnetic Experiments
... 2. Pickup coil -- again see field lines and light bulb -- using your mouse, move the magnet in and out of the coil -- see what happens -- change a few variables on tool box -- record what happens with each change. What conclusions do you draw? 3. Electromagnet -- Look familiar??!! Predict what will ...
... 2. Pickup coil -- again see field lines and light bulb -- using your mouse, move the magnet in and out of the coil -- see what happens -- change a few variables on tool box -- record what happens with each change. What conclusions do you draw? 3. Electromagnet -- Look familiar??!! Predict what will ...
Write-up - Community Science Workshop Network
... © 2012 Watsonville Environmental Science Workshop. All Rights Reserved worldwide. When linking to or using WESW content, images, or videos, credit MUST be included. ...
... © 2012 Watsonville Environmental Science Workshop. All Rights Reserved worldwide. When linking to or using WESW content, images, or videos, credit MUST be included. ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... magnetic field while keeping it uniform in space and direction ! An electric field is induced as shown by the red loops ! The magnitude of the electric field is constant along each loop and the direction is tangential to each loop ! Note that the induced electric field points in the opposite dire ...
... magnetic field while keeping it uniform in space and direction ! An electric field is induced as shown by the red loops ! The magnitude of the electric field is constant along each loop and the direction is tangential to each loop ! Note that the induced electric field points in the opposite dire ...
Sound Systems, Computer Memory, Seismograph, GFCI Inductance
... the opposite direction to the original field if the flux is increasing; in the same direction if it is decreasing; and is zero if the flux is not changing. 3. Use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the current. 4. Remember that the external field and the field due to the induced curre ...
... the opposite direction to the original field if the flux is increasing; in the same direction if it is decreasing; and is zero if the flux is not changing. 3. Use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the current. 4. Remember that the external field and the field due to the induced curre ...
EE4302 Fl04 Class Sy..
... EMAG 1 in Bold – EMAG 2 not bolded Section 1 Basic concepts and basic Mathematics History Maxwell’s equations in point and integral form Concept, Nature and sources of vector fields Proof of Divergence and stokes theorems Concept of vector and scalar potential Section II – Static electric and magnet ...
... EMAG 1 in Bold – EMAG 2 not bolded Section 1 Basic concepts and basic Mathematics History Maxwell’s equations in point and integral form Concept, Nature and sources of vector fields Proof of Divergence and stokes theorems Concept of vector and scalar potential Section II – Static electric and magnet ...
Make an electric motor
... wire when the wire is connected in a circuit from one battery terminal to the other. The negatively charged electrons in the wire move away from the negative terminal of the battery towards the positive terminal. The movement of electrons through a conductor is called an electric current. A magnet i ...
... wire when the wire is connected in a circuit from one battery terminal to the other. The negatively charged electrons in the wire move away from the negative terminal of the battery towards the positive terminal. The movement of electrons through a conductor is called an electric current. A magnet i ...
22.1,2,3,4,5,6
... 1.Determine whether the magnetic flux that penetrates a coil is increasing or decreasing. 2.Find what the direction of the induced magnetic field must be so that it can oppose the change in flux by adding to or subtracting from the original field. 3.Having found the direction of the induced magnetic ...
... 1.Determine whether the magnetic flux that penetrates a coil is increasing or decreasing. 2.Find what the direction of the induced magnetic field must be so that it can oppose the change in flux by adding to or subtracting from the original field. 3.Having found the direction of the induced magnetic ...
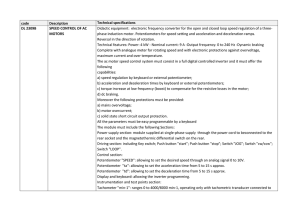
4. numerical results - Scientific Bulletin of Electrical Engineering
... 2.1 Electric motors. Star – delta starting All indirect starting methods are used to reduce the starting current. In the case of a star – delta starting the network voltage is applied directly to the star connected to a three phase winding coil.[4] When the motor reaches a rotation speed of 90 % of ...
... 2.1 Electric motors. Star – delta starting All indirect starting methods are used to reduce the starting current. In the case of a star – delta starting the network voltage is applied directly to the star connected to a three phase winding coil.[4] When the motor reaches a rotation speed of 90 % of ...
Week of Dec. 5
... Essential Question(s): What are magnetic fields? Learning Target(s): I can demonstrate my knowledge of electric cirucits and energy transformations. I can create a magnetic field using magnets, an iron bolt, and compass. 1. Students will briefly review for their quiz. 2. Students will complete a bri ...
... Essential Question(s): What are magnetic fields? Learning Target(s): I can demonstrate my knowledge of electric cirucits and energy transformations. I can create a magnetic field using magnets, an iron bolt, and compass. 1. Students will briefly review for their quiz. 2. Students will complete a bri ...




















![L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001482032_1-b69d1eb7a0f8c001e0e2a09bf26d62d2-300x300.png)

