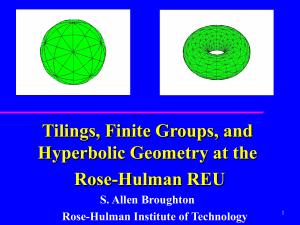
student
... Theorem 6.2 – Polygon Exterior Angles Sum: The sum of the exterior angle measures of a convex polygon, one angle at each vertex, is _________ degrees. ...
... Theorem 6.2 – Polygon Exterior Angles Sum: The sum of the exterior angle measures of a convex polygon, one angle at each vertex, is _________ degrees. ...
Unit 6 Review Packet
... ____________12. Opposite angles of a parallelogram are supplementary. ____________13. A trapezoid has exactly one pair of parallel sides. ____________14. The diagonals of a square are congruent. ...
... ____________12. Opposite angles of a parallelogram are supplementary. ____________13. A trapezoid has exactly one pair of parallel sides. ____________14. The diagonals of a square are congruent. ...
Quadrilaterals Study Guide
... - A parallelogram has two pairs of opposite _______________ angles. - The consecutive (same-side interior) angles of a parallelogram are ________________________. - The diagonals of a parallelogram ___________ each other, meaning they _____________________________________. ...
... - A parallelogram has two pairs of opposite _______________ angles. - The consecutive (same-side interior) angles of a parallelogram are ________________________. - The diagonals of a parallelogram ___________ each other, meaning they _____________________________________. ...
analyze #17: building a concept map
... f. The highway department is creating new stop signs (octagons). How many degrees should they make each angle in the stop sign? g. On a visit to Washington DC, you go to the Pentagon, which is the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense. You notice that the building is ...
... f. The highway department is creating new stop signs (octagons). How many degrees should they make each angle in the stop sign? g. On a visit to Washington DC, you go to the Pentagon, which is the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense. You notice that the building is ...
Section 9.4 - Geometry in Three Dimensions
... • A polyhedron is a convex polyhedron if and only if the segment connecting any two points in the interior of the polyhedron is itself in the interior. • A concave polyhedron is a polyhedron that is not convex. • A regular polyhedron is a convex polyhedron whose faces are congruent regular polygonal ...
... • A polyhedron is a convex polyhedron if and only if the segment connecting any two points in the interior of the polyhedron is itself in the interior. • A concave polyhedron is a polyhedron that is not convex. • A regular polyhedron is a convex polyhedron whose faces are congruent regular polygonal ...
Click here
... Hi kids, here is the review for your upcoming exam. Enjoy! (1) Section 5.4: The Fundamental Theorem of Inversive Geometry. We discussed the manner in which there exists a unique Möbius Transformation that takes any 3 points in Ĉ to any other 3 points in Ĉ, and how such a Möbius transformation is ...
... Hi kids, here is the review for your upcoming exam. Enjoy! (1) Section 5.4: The Fundamental Theorem of Inversive Geometry. We discussed the manner in which there exists a unique Möbius Transformation that takes any 3 points in Ĉ to any other 3 points in Ĉ, and how such a Möbius transformation is ...
Investigate Angle Sums in Polygons
... 1. Look for a pattern in the last column of the table. What is the sum of the ...
... 1. Look for a pattern in the last column of the table. What is the sum of the ...
Mid-Term Review Part II
... State the postulate or theorem (SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS or HL) you can use to prove each pair of triangles congruent. If the triangles cannot be proven congruent, write not enough information. ...
... State the postulate or theorem (SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS or HL) you can use to prove each pair of triangles congruent. If the triangles cannot be proven congruent, write not enough information. ...
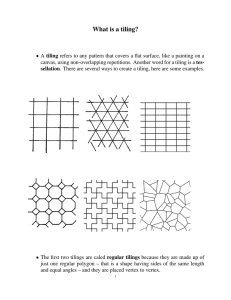
What is a tiling?
... So, the answer for the triangular wrinkle is yes, while the answer for the hexagonal what is going on: If we break the regular tiling (b) in Figure 2 along all or some of the wrinkle is no. What happens with other regular polygons? A moment’s reflection will horizontal lines, or along all or some of ...
... So, the answer for the triangular wrinkle is yes, while the answer for the hexagonal what is going on: If we break the regular tiling (b) in Figure 2 along all or some of the wrinkle is no. What happens with other regular polygons? A moment’s reflection will horizontal lines, or along all or some of ...
Polygons - NEHSTechShowcase
... A polygon is a closed figure formed by a finite number of coplanar segments such that… 1. The sides that have a common endpoint are noncollinear,and 2. Each side intersects exactly two other sides, but only at their endpoints A regular polygon is a convex polygon with all sides congruent and all an ...
... A polygon is a closed figure formed by a finite number of coplanar segments such that… 1. The sides that have a common endpoint are noncollinear,and 2. Each side intersects exactly two other sides, but only at their endpoints A regular polygon is a convex polygon with all sides congruent and all an ...
8.4
... Circular cylinder: formed by two parallel planes intersecting a sphere and the line segments connecting the circular regions by their edges such that every perpendicular planar cross section of the cylinder would be a circular region; the bases of the cylinder are circles, while the lateral face of ...
... Circular cylinder: formed by two parallel planes intersecting a sphere and the line segments connecting the circular regions by their edges such that every perpendicular planar cross section of the cylinder would be a circular region; the bases of the cylinder are circles, while the lateral face of ...
2.3-2.4 Polygons!.
... Polygon - A closed plane figure whose sides are segments that intersect only at their endpoints. Put the terms that you don’t know (by heart!!) in your notes. Key terms on the left! # of sides ...
... Polygon - A closed plane figure whose sides are segments that intersect only at their endpoints. Put the terms that you don’t know (by heart!!) in your notes. Key terms on the left! # of sides ...
CP Geometry Name: Lesson 6-1: Properties and Attributes of
... Recall, a ___________________ is a plane figure that meets the following conditions: 1. It is a closed figure formed by three or more coplanar segments called ______________. 2. Sides that have a common endpoint are ________________________________. 3. Each side intersects exactly two other sides, o ...
... Recall, a ___________________ is a plane figure that meets the following conditions: 1. It is a closed figure formed by three or more coplanar segments called ______________. 2. Sides that have a common endpoint are ________________________________. 3. Each side intersects exactly two other sides, o ...
List of regular polytopes and compounds
This page lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces.The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an n-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an n-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of a (n-1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example the cube has Schläfli symbol {4,3}, and with its octahedral symmetry, [4,3] or File:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png, is represented by Coxeter diagram File:CDel node 1.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png.The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconvex and infinite forms. Nonconvex forms use the same vertices as the convex forms, but have intersecting facets. Infinite forms tessellate a one-lower-dimensional Euclidean space.Infinite forms can be extended to tessellate a hyperbolic space. Hyperbolic space is like normal space at a small scale, but parallel lines diverge at a distance. This allows vertex figures to have negative angle defects, like making a vertex with seven equilateral triangles and allowing it to lie flat. It cannot be done in a regular plane, but can be at the right scale of a hyperbolic plane.A more general definition of regular polytopes which do not have simple Schläfli symbols includes regular skew polytopes and regular skew apeirotopes with nonplanar facets or vertex figures.