Math Notes-chap 1
... The line of reflection ___________ (cuts in half) the line segment connecting each image point with its corresponding point on the original figure. Based on the picture, AP=_____. ...
... The line of reflection ___________ (cuts in half) the line segment connecting each image point with its corresponding point on the original figure. Based on the picture, AP=_____. ...
4.11 Curriculum Framework
... A vertex is the point at which two or more lines, line segments, or rays meet to form an angle. In solid figures, a vertex is the point at which three or more faces meet. A cube is a solid figure with six congruent, square faces. All edges are the same length. A cube has eight vertices and 12 edges. ...
... A vertex is the point at which two or more lines, line segments, or rays meet to form an angle. In solid figures, a vertex is the point at which three or more faces meet. A cube is a solid figure with six congruent, square faces. All edges are the same length. A cube has eight vertices and 12 edges. ...
practice problems
... (f) Do there exist hyperbolic lines l and m with the property that the distance from a point of m to l is the same for any choice of a point on m? (g) Show that the angle sum of the two interior angles of an omega triangle is less than 180◦ . (h) Show that limiting parallels cannot have a common per ...
... (f) Do there exist hyperbolic lines l and m with the property that the distance from a point of m to l is the same for any choice of a point on m? (g) Show that the angle sum of the two interior angles of an omega triangle is less than 180◦ . (h) Show that limiting parallels cannot have a common per ...
Strange Geometries
... Euclid set out a list of five postulates on which he thought geometry should be built. One of them, the fifth, was equivalent to a statement we are all familiar with: that the angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees. However, this postulate did not seem as obvious as the other four on Euclid’s li ...
... Euclid set out a list of five postulates on which he thought geometry should be built. One of them, the fifth, was equivalent to a statement we are all familiar with: that the angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees. However, this postulate did not seem as obvious as the other four on Euclid’s li ...
4-6-int-ext-angles
... using our formula. *Now, we are already given 7 angles...what can we do to find the last one? ...
... using our formula. *Now, we are already given 7 angles...what can we do to find the last one? ...
MA.8.G.2.3 Demonstrate that the sum of the angles in a triangle is
... MA.8.G.2.3 Demonstrate that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180-degrees and apply this fact to find unknown measure of angles, and the sum of angles in polygons. ...
... MA.8.G.2.3 Demonstrate that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180-degrees and apply this fact to find unknown measure of angles, and the sum of angles in polygons. ...
Chapter 11 – Area of Polygons and Circles Section 11.1
... Theorems about Exterior Angles Thm 11.2 - Polygon Exterior Angles Thm The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a convex polygon, one angle at each vertex, is 360°. Corollary to Thm 11.2 The measure of each exterior angle of a regular n-gon is: ...
... Theorems about Exterior Angles Thm 11.2 - Polygon Exterior Angles Thm The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a convex polygon, one angle at each vertex, is 360°. Corollary to Thm 11.2 The measure of each exterior angle of a regular n-gon is: ...
Solutions 13-14 - Durham University
... some intermediate size of PEucl such that the corresponding hyperbolic regular pentagon has right angles. 14.9. (*) An ideal triangle is a hyperbolic triangle with all three vertices an the absolute. (a) Show that all ideal triangles are congruent. (b) Show that the altitudes of an ideal triangle ar ...
... some intermediate size of PEucl such that the corresponding hyperbolic regular pentagon has right angles. 14.9. (*) An ideal triangle is a hyperbolic triangle with all three vertices an the absolute. (a) Show that all ideal triangles are congruent. (b) Show that the altitudes of an ideal triangle ar ...
6th Grade Geometry Vocabulary
... A 3-D shape with a top and bottom (base) that are congruent polygons and lateral faces that are parallelograms. A 3-D shape with one polygonal base and lateral sides that are all triangles that meet at a vertex opposite the base. ...
... A 3-D shape with a top and bottom (base) that are congruent polygons and lateral faces that are parallelograms. A 3-D shape with one polygonal base and lateral sides that are all triangles that meet at a vertex opposite the base. ...
Chapter 8 Notes - Kenston Local Schools
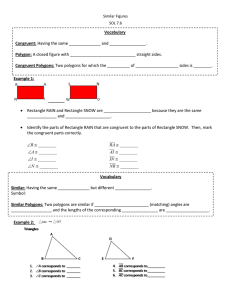
... A polygon is a closed figure made up of straight line segments connected end-to-end. These segments may not cross (intersect) at any other points. A regular polygon is equilateral and equiangular (all sides have the same length the interior angles have equal measure). The example is a regular hexago ...
... A polygon is a closed figure made up of straight line segments connected end-to-end. These segments may not cross (intersect) at any other points. A regular polygon is equilateral and equiangular (all sides have the same length the interior angles have equal measure). The example is a regular hexago ...
Solutions #6
... III. Let ∠P QA be a right angle, and let ε be any positive number. Show that there exists a point R on the ray QA such that ∠P RQ < ε◦ . (Refer to Figure 6.10 on page 125 of Baragar’s book.) Begin by choosing a point R 1 on the ray QA such that |QR1 | = |QP |. By pons asinorum, we know that ∠QR1 P = ...
... III. Let ∠P QA be a right angle, and let ε be any positive number. Show that there exists a point R on the ray QA such that ∠P RQ < ε◦ . (Refer to Figure 6.10 on page 125 of Baragar’s book.) Begin by choosing a point R 1 on the ray QA such that |QR1 | = |QP |. By pons asinorum, we know that ∠QR1 P = ...
List of regular polytopes and compounds
This page lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces.The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an n-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an n-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of a (n-1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example the cube has Schläfli symbol {4,3}, and with its octahedral symmetry, [4,3] or File:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png, is represented by Coxeter diagram File:CDel node 1.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png.The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconvex and infinite forms. Nonconvex forms use the same vertices as the convex forms, but have intersecting facets. Infinite forms tessellate a one-lower-dimensional Euclidean space.Infinite forms can be extended to tessellate a hyperbolic space. Hyperbolic space is like normal space at a small scale, but parallel lines diverge at a distance. This allows vertex figures to have negative angle defects, like making a vertex with seven equilateral triangles and allowing it to lie flat. It cannot be done in a regular plane, but can be at the right scale of a hyperbolic plane.A more general definition of regular polytopes which do not have simple Schläfli symbols includes regular skew polytopes and regular skew apeirotopes with nonplanar facets or vertex figures.

![Math 2A: [10-6] Polygons](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008401966_1-100b9dc0ad4de55e40f3e764aa8c850d-300x300.png)