GLBRC Highlight Deng 2016
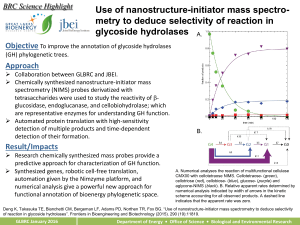
... A. Numerical analyses the reaction of multifunctional cellulase CMX00 with cellotetraose NIMS. Cellotetraose- (green), cellotriose (red), cellobiose- (blue), glucose- (purple) and aglycone-NIMS (black). B. Relative apparent rates determined by numerical analysis indicated by width of arrows in the k ...
... A. Numerical analyses the reaction of multifunctional cellulase CMX00 with cellotetraose NIMS. Cellotetraose- (green), cellotriose (red), cellobiose- (blue), glucose- (purple) and aglycone-NIMS (black). B. Relative apparent rates determined by numerical analysis indicated by width of arrows in the k ...
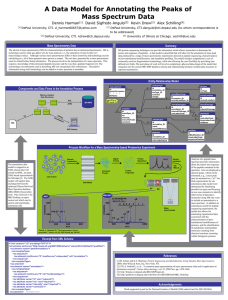
A Data Model for Annotating the Peaks of Mass
... spectrum. Ions are displayed as spectral peaks, which can be annotated, e.g., a mass peak may be annotated as a “y3” ion. Data requirements for our annotations data model were determined by identifying possible ion types and focusing on use case scenarios to identify other forms of data that a resea ...
... spectrum. Ions are displayed as spectral peaks, which can be annotated, e.g., a mass peak may be annotated as a “y3” ion. Data requirements for our annotations data model were determined by identifying possible ion types and focusing on use case scenarios to identify other forms of data that a resea ...
Mass spectrometry - Justin Benesch
... • Ions are accelerated into a cell containing neutral, chemically inert gas (e.g. Ar) • Upon collision some of the ions’ kinetic energy is converted into internal modes • The excited ion can decay into fragments, detectable on timescale of measurement ...
... • Ions are accelerated into a cell containing neutral, chemically inert gas (e.g. Ar) • Upon collision some of the ions’ kinetic energy is converted into internal modes • The excited ion can decay into fragments, detectable on timescale of measurement ...
Mass Spectrometry
... • Analysis of nucleic acids by mass spectrometry lags behind proteins because negatively charged nucleic acid have a high affinity for sodium ion greatly reducing ionisation efficiency. • Additionally, the generation of intact molecular ions from oligomers of more than two nucleotides proved to be d ...
... • Analysis of nucleic acids by mass spectrometry lags behind proteins because negatively charged nucleic acid have a high affinity for sodium ion greatly reducing ionisation efficiency. • Additionally, the generation of intact molecular ions from oligomers of more than two nucleotides proved to be d ...
Field Analyzer
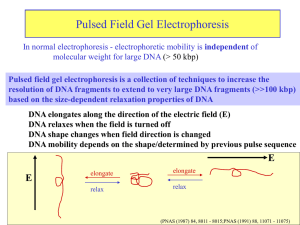
... Pulsed field gel electrophoresis is a collection of techniques to increase the resolution of DNA fragments to extend to very large DNA fragments (>>100 kbp) based on the size-dependent relaxation properties of DNA DNA elongates along the direction of the electric field (E) DNA relaxes when the field ...
... Pulsed field gel electrophoresis is a collection of techniques to increase the resolution of DNA fragments to extend to very large DNA fragments (>>100 kbp) based on the size-dependent relaxation properties of DNA DNA elongates along the direction of the electric field (E) DNA relaxes when the field ...
Document
... •They are accelerated by high voltage and separated based on the time it takes them to travel to the detector •All ions gain same kinetic energy •A spectrum of ion intensity as a function of travel time is recorded •The ion’s passage through the drift tube can be described as: ...
... •They are accelerated by high voltage and separated based on the time it takes them to travel to the detector •All ions gain same kinetic energy •A spectrum of ion intensity as a function of travel time is recorded •The ion’s passage through the drift tube can be described as: ...
mass
... • Newly charged molecules are introduced into an electric and/or magnetic field in gas phase, • Their path through the field is a function of the mass to charge ratio m/z, • m/z of the ionized species can be used to deduce the mass of the analyte with high precision. ...
... • Newly charged molecules are introduced into an electric and/or magnetic field in gas phase, • Their path through the field is a function of the mass to charge ratio m/z, • m/z of the ionized species can be used to deduce the mass of the analyte with high precision. ...
כימיה כללית ופיסיקלית למדעי החיים
... (4) It has four times as many H atoms as O atoms, but four times the mass of O as of H. 47. Indigo, the dye for blue jeans, has a percent composition, by mass of 73.27% C, 3.84% H, 10.68% N, and the remainder as oxygen. Its molecular mass is 262.3 u. what is the molecular formula for indigo? 49. The ...
... (4) It has four times as many H atoms as O atoms, but four times the mass of O as of H. 47. Indigo, the dye for blue jeans, has a percent composition, by mass of 73.27% C, 3.84% H, 10.68% N, and the remainder as oxygen. Its molecular mass is 262.3 u. what is the molecular formula for indigo? 49. The ...
ENVE3503 – Environmental Engineering Expectations for Chapter 2
... b. Mercury levels in Lake Erie walleye averaged 0.3 ppm in 1977. Express this in an appropriate mass/mass format. 4. Understand how mass/volume and mole/volume concentration units are applied in expressing contaminant levels in water. 5. Be able to perform mass/volume and mole/volume calculations, e ...
... b. Mercury levels in Lake Erie walleye averaged 0.3 ppm in 1977. Express this in an appropriate mass/mass format. 4. Understand how mass/volume and mole/volume concentration units are applied in expressing contaminant levels in water. 5. Be able to perform mass/volume and mole/volume calculations, e ...
Taícia P. Fill1, Edson Rodrigues Filho1
... Brasiliamides (Figure 1) are interesting secondary metabolites produced by the endophytic fungus Penicillium brasilianum which present important antiparasitic and antibacteriological activities[1]. In the present work, the biosynthesis of these compounds was evaluated through the addition of labeled ...
... Brasiliamides (Figure 1) are interesting secondary metabolites produced by the endophytic fungus Penicillium brasilianum which present important antiparasitic and antibacteriological activities[1]. In the present work, the biosynthesis of these compounds was evaluated through the addition of labeled ...
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that helps identify the amount and type of chemicals present in a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions.A mass spectrum (plural spectra) is a plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. The spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and other chemical compounds. Mass spectrometry works by ionizing chemical compounds to generate charged molecules or molecule fragments and measuring their mass-to-charge ratios.In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gas, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break into charged fragments. These ions are then separated according to their mass-to-charge ratio, typically by accelerating them and subjecting them to an electric or magnetic field: ions of the same mass-to-charge ratio will undergo the same amount of deflection. The ions are detected by a mechanism capable of detecting charged particles, such as an electron multiplier. Results are displayed as spectra of the relative abundance of detected ions as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. The atoms or molecules in the sample can be identified by correlating known masses to the identified masses or through a characteristic fragmentation pattern.