Globalisation: Definitions and Perspectives
... relations have been recast to resemble not a pyramid but a three tier structure of concentric circles. All three circles cut across national and regional boundaries. In the core circle we find the elites of all continents and nations, albeit in different proportions in relation to their respective g ...
... relations have been recast to resemble not a pyramid but a three tier structure of concentric circles. All three circles cut across national and regional boundaries. In the core circle we find the elites of all continents and nations, albeit in different proportions in relation to their respective g ...
Study Guide 15 Part I Emergence of Complex Societies in India and
... 7. What are examples of Indian literature that influenced artistic developments in neighboring regions and in later time periods? 8. What would be an example of India’s influence on architectural styles in surrounding regions? ...
... 7. What are examples of Indian literature that influenced artistic developments in neighboring regions and in later time periods? 8. What would be an example of India’s influence on architectural styles in surrounding regions? ...
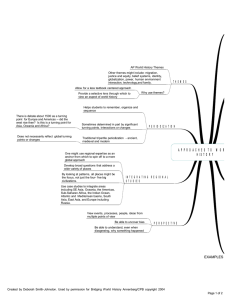
approaches to world history
... AP World History Themes Other themes might include: migration, justice and equity, belief systems, identity, globalization, power, human environment interaction, technology,and family. ...
... AP World History Themes Other themes might include: migration, justice and equity, belief systems, identity, globalization, power, human environment interaction, technology,and family. ...
SC/NATS 1840 – Lecture 8 - Colonial Expansion and Resource
... Competition for Empire in the 19th Century - Naylor argues that the Nineteenth century saw a competition, primarily between the English and the French, for control of global trade and resources - Importantly, countries began to realize that disrupting trade was as important as military victory, as m ...
... Competition for Empire in the 19th Century - Naylor argues that the Nineteenth century saw a competition, primarily between the English and the French, for control of global trade and resources - Importantly, countries began to realize that disrupting trade was as important as military victory, as m ...
Unit One – Seeds of Culture The Earliest Americans
... as spices, sugar and fabrics Spices – such as cinnamon and pepper were very valuable during the Middle Ages. They were used to preserve and flavor foods. These spices came from India, SE Asia and the Middle East. Italian city states – Merchants from Venice, Florence and Genoa dominated this trade. G ...
... as spices, sugar and fabrics Spices – such as cinnamon and pepper were very valuable during the Middle Ages. They were used to preserve and flavor foods. These spices came from India, SE Asia and the Middle East. Italian city states – Merchants from Venice, Florence and Genoa dominated this trade. G ...
Mongol - BTHS.edu
... 1. New banking houses in Italy and central Europe became more prominent. 2. Commercial alliances were formed between Europeans and the Seljuk Turks. 3. The Swahili city-states of eastern Africa ended the competing Indian Ocean trade. 4. Catholicism spread throughout western Europe. 5. The downfall o ...
... 1. New banking houses in Italy and central Europe became more prominent. 2. Commercial alliances were formed between Europeans and the Seljuk Turks. 3. The Swahili city-states of eastern Africa ended the competing Indian Ocean trade. 4. Catholicism spread throughout western Europe. 5. The downfall o ...
The Renaissance - Woodland Hills School District
... • Spread foods, animals, and ideas from one continent to another. • Known as the Columbian Exchange. • Also introduced European disease to the New World. Wiped large populations of native americans. ...
... • Spread foods, animals, and ideas from one continent to another. • Known as the Columbian Exchange. • Also introduced European disease to the New World. Wiped large populations of native americans. ...
A. Paleolithic Persistence: Australia and North America
... I. The Shapes of Human Communities A. Paleolithic Persistence: Australia and North America 1. Gatherers and hunters have a history, too: While non-literate and non-urban, these societies did change over time; we just don’t have written records of it. 2. Manipulation of the environment and trade: In ...
... I. The Shapes of Human Communities A. Paleolithic Persistence: Australia and North America 1. Gatherers and hunters have a history, too: While non-literate and non-urban, these societies did change over time; we just don’t have written records of it. 2. Manipulation of the environment and trade: In ...
Perspective!
... to grow food was therefore the foundation of wealth of nations, since the greater the food surplus the larger the potential base for non-agricultural activities. Since China and India were mostly relying on rice cultivation (the most productive form of agriculture) supported by extensive irrigation ...
... to grow food was therefore the foundation of wealth of nations, since the greater the food surplus the larger the potential base for non-agricultural activities. Since China and India were mostly relying on rice cultivation (the most productive form of agriculture) supported by extensive irrigation ...
Forms of Economic Globalization - sugarhoover ¨¨ rit´s portfolio
... financial market. While in 1978 the daily volume of operations of the exchange dealing was $15 billion, and $880 billion in 1992, presently it amounts to $1.5 trillion. Pension and mutual funds, insurance companies and trusts, transnational banks are the main subjects of international financial mark ...
... financial market. While in 1978 the daily volume of operations of the exchange dealing was $15 billion, and $880 billion in 1992, presently it amounts to $1.5 trillion. Pension and mutual funds, insurance companies and trusts, transnational banks are the main subjects of international financial mark ...
Foundationrev
... Theme 5: Cultural, intellectual, and religious developments Theme 6: Changes in functions and structures of states. ...
... Theme 5: Cultural, intellectual, and religious developments Theme 6: Changes in functions and structures of states. ...
Foundation
... Theme 5: Cultural, intellectual, and religious developments Theme 6: Changes in functions and structures of states. ...
... Theme 5: Cultural, intellectual, and religious developments Theme 6: Changes in functions and structures of states. ...
Chapter 16
... b. The Europeans began to slowly work their way into being stronger than the Muslims on the seas – the Spanish defeated the Ottoman Empire in the Battle of Lepanto in 1571. c. The Europeans began to set up ports on the coast of Africa and other countries as well, serving as trading posts and contact ...
... b. The Europeans began to slowly work their way into being stronger than the Muslims on the seas – the Spanish defeated the Ottoman Empire in the Battle of Lepanto in 1571. c. The Europeans began to set up ports on the coast of Africa and other countries as well, serving as trading posts and contact ...
the globalization of markets
... institutions were created by voluntary agreement between individual nation-states, and their functions are enshrined in international treaties. The World Trade Organization(like the GATT before it) is primarily responsible for policing the world trading system and making sure nationstates adhere to ...
... institutions were created by voluntary agreement between individual nation-states, and their functions are enshrined in international treaties. The World Trade Organization(like the GATT before it) is primarily responsible for policing the world trading system and making sure nationstates adhere to ...
Review
... the Rest. How did this transformation take place? Findlay and O’Rourke offer an answer to this question towards the end of the book, to which we will return. Chapter three to chapter ten analyze the world trade in successive periods: from the year 1000 to 1500 (the economic consequences of Genghis K ...
... the Rest. How did this transformation take place? Findlay and O’Rourke offer an answer to this question towards the end of the book, to which we will return. Chapter three to chapter ten analyze the world trade in successive periods: from the year 1000 to 1500 (the economic consequences of Genghis K ...
Slide 1
... Globalization and the North The pre-1945 divisions of labor have changed radically in the last few decades. While the richer countries of Europe and North America along with Japan still largely export industrial products, among the poorer nations, six groups have ...
... Globalization and the North The pre-1945 divisions of labor have changed radically in the last few decades. While the richer countries of Europe and North America along with Japan still largely export industrial products, among the poorer nations, six groups have ...
crusades
... – Banks issue a letter of credit to merchant who then exchanges once he arrives at destination. ...
... – Banks issue a letter of credit to merchant who then exchanges once he arrives at destination. ...
Period IV Review Questions
... Both made extensive use of indenture servitude to provide a labor force. ...
... Both made extensive use of indenture servitude to provide a labor force. ...
Chapter 15 PP
... The elite, upper classes of western Europe had become obsessed with the more refined products of Asia like spices, silks, perfumes, and jewels. The cruder European goods such as wool, copper, tin, honey, and salt could not make up the discrepancy in value. The balance had to be made up in gold shi ...
... The elite, upper classes of western Europe had become obsessed with the more refined products of Asia like spices, silks, perfumes, and jewels. The cruder European goods such as wool, copper, tin, honey, and salt could not make up the discrepancy in value. The balance had to be made up in gold shi ...
Making of the Modern World 13 New Ideas and Cultural Contacts
... Cities located along major land and sea routes (Europe, West Asia, Indian Ocean regions and China) ...
... Cities located along major land and sea routes (Europe, West Asia, Indian Ocean regions and China) ...
resurgence long paper - Brooklyn Technical High School
... 12. What was the basis for the feudal economy during the Middle Ages in Western Europe? 1. local trade between the different manors 2. trade contacts with Arab merchants from north Africa and the Iberian peninsula 3. agricultural labor of the peasant classes 4. exports of raw materials to the Byzant ...
... 12. What was the basis for the feudal economy during the Middle Ages in Western Europe? 1. local trade between the different manors 2. trade contacts with Arab merchants from north Africa and the Iberian peninsula 3. agricultural labor of the peasant classes 4. exports of raw materials to the Byzant ...
Post-Classical Trade Routes, 500 - 1500 CE
... What I find interesting about this lesson: 1. Trade has had an enormous impact on world history. 2. The movement of pastoral peoples greatly affected history. 3. A wind, a camel, or a strait had the power to increase trade. Provide a general overview of the Silk Road trading networks. ____________ ...
... What I find interesting about this lesson: 1. Trade has had an enormous impact on world history. 2. The movement of pastoral peoples greatly affected history. 3. A wind, a camel, or a strait had the power to increase trade. Provide a general overview of the Silk Road trading networks. ____________ ...
Archaic globalization
Archaic globalization is a phase in the history of globalization, and conventionally refers to globalizing events and developments from the time of the earliest civilizations until roughly 1600 (the following period is known as early modern globalization). This term is used to describe the relationships between communities and states and how they were created by the geographical spread of ideas and social norms at both local and regional levels.States began to interact and trade with others within close proximity as a way to acquire coveted goods that were considered a luxury. This trade led to the spread of ideas such as religion, economic structure and political ideals. Merchants became connected and aware of others in ways that had not been apparent. Archaic globalization is comparable to present day globalization on a much smaller scale. It not only allowed the spread of goods and commodities to other regions, but it also allowed people to experience other cultures. Cities that partook in trading were bound together by sea lanes, rivers, and great overland routes, some of which had been in use since antiquity. Trading was broken up according to geographic location, with centers between flanking places serving as ""break-in-bulk"" and exchange points for goods destined for more distant markets. During this time period the subsystems were more self-sufficient than they are today and therefore less vitally dependent upon one another for everyday survival. While long distance trading came with many trials and tribulations, still so much of it went on during this early time period. Linking the trade together involved eight interlinked subsystems that were grouped into three large circuits, which encompassed the western European, the Middle Eastern, and the Far Eastern. This interaction during trading was early civilization's way to communicate and spread many ideas which caused modern globalization to emerge and allow a new aspect to present day society.