full text pdf
... Lignocellulose substrate grinding alone as a physical treatment technique is usually not regarded effective enough, and subsequent combination with other techniques has been suggested [5]. Our studies have shown that during the initial phase of hydrolysis, sugar formation occurred with the same tren ...
... Lignocellulose substrate grinding alone as a physical treatment technique is usually not regarded effective enough, and subsequent combination with other techniques has been suggested [5]. Our studies have shown that during the initial phase of hydrolysis, sugar formation occurred with the same tren ...
lec27_2013 - Andrew.cmu.edu
... Introduction to Metabolism Required reading in Horton: 10.1-10.5. Nelson: 13.1 Bioenergetics and Thermodynamics. ...
... Introduction to Metabolism Required reading in Horton: 10.1-10.5. Nelson: 13.1 Bioenergetics and Thermodynamics. ...
What is a Protein?
... “R” represents the “Radical” side chain that is different for each amino acid. The “R” group can either be one atom (H) or a group of atoms. ...
... “R” represents the “Radical” side chain that is different for each amino acid. The “R” group can either be one atom (H) or a group of atoms. ...
Modes of Macromolecular Classification
... But how are we to understand tertiary structure? We might abstract away from the peptide bonds (the links between individual amino acids) and think of a protein’s three-dimensional structure as simply the relative location of individual amino acids (in the manner we think of a crystalline structure ...
... But how are we to understand tertiary structure? We might abstract away from the peptide bonds (the links between individual amino acids) and think of a protein’s three-dimensional structure as simply the relative location of individual amino acids (in the manner we think of a crystalline structure ...
Lecture #9
... • Membrane bound carriers transfer electrons (redox reactions) • Proton motive force (PMF) • Chemiosmosis ...
... • Membrane bound carriers transfer electrons (redox reactions) • Proton motive force (PMF) • Chemiosmosis ...
Chapter 3 Objectives
... A covalent bonding capacity of four makes it have the ability to form diverse molecules. Carbon atoms can bond with other carbon atoms, forming the carbon skeleton of organic compounds. Figure 0402 Figure 0403 -Describe how carbon skeletons may vary, and explain how this variation contributes to the ...
... A covalent bonding capacity of four makes it have the ability to form diverse molecules. Carbon atoms can bond with other carbon atoms, forming the carbon skeleton of organic compounds. Figure 0402 Figure 0403 -Describe how carbon skeletons may vary, and explain how this variation contributes to the ...
Chemistry
... a. definition - in ionic bonds electrons are transferred to other atoms to completely fill outer shells; atoms are electrically neutral, but when they gain or lose electrons in combining with other atoms, they are called ions (charged atoms) & they take on a positive or negative charge; in other wor ...
... a. definition - in ionic bonds electrons are transferred to other atoms to completely fill outer shells; atoms are electrically neutral, but when they gain or lose electrons in combining with other atoms, they are called ions (charged atoms) & they take on a positive or negative charge; in other wor ...
bio ch3 powerpoint outline
... SOLUTIONS: How does the presence of substances dissolved in water affect the properties of water? In solutions, some substances change the balance of hydronium ions and hydroxide ions. A solution is a mixture in which ions or molecules of one or more substances are evenly distributed in another subs ...
... SOLUTIONS: How does the presence of substances dissolved in water affect the properties of water? In solutions, some substances change the balance of hydronium ions and hydroxide ions. A solution is a mixture in which ions or molecules of one or more substances are evenly distributed in another subs ...
Introductory Microbiology Chap. 5 Chapter Outlines/Notes I
... 1. Example of Competitive Inhibition and its use in Medicine: Sulfa Drugs All cells require folic acid for growth. Folic acid (vitamin B9) in food diffuses or is transported into human cells. However, folic acid cannot cross bacterial cell walls by diffusion or active transport. For this reason bact ...
... 1. Example of Competitive Inhibition and its use in Medicine: Sulfa Drugs All cells require folic acid for growth. Folic acid (vitamin B9) in food diffuses or is transported into human cells. However, folic acid cannot cross bacterial cell walls by diffusion or active transport. For this reason bact ...
Glycolysis
... • 6 carbon sugar (fructose) is split into two 3-carbon molecules • Each molecule gets one of the phosphate groups • The molecules are not identical • One molecule is isomerized (rearranged) so the two 3-carbon molecules become identical: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ...
... • 6 carbon sugar (fructose) is split into two 3-carbon molecules • Each molecule gets one of the phosphate groups • The molecules are not identical • One molecule is isomerized (rearranged) so the two 3-carbon molecules become identical: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ...
Model Description Sheet
... issues. Inspired by nature, artificial photosynthesis through water splitting by solar energy conversion is the most attractive approach for the development. The overall water splitting includes two half-catalytic reactions, i. e. hydrogen (HER) and oxygen (OER) evolution reactions. An efficient cat ...
... issues. Inspired by nature, artificial photosynthesis through water splitting by solar energy conversion is the most attractive approach for the development. The overall water splitting includes two half-catalytic reactions, i. e. hydrogen (HER) and oxygen (OER) evolution reactions. An efficient cat ...
Document
... Thioredoxin and Peroxyredoxin are very important regulators of the p38 and JNK S-T pathways in addition to being important antioxidant proteins… In a sense, they are cellular redox sensors that help to quench ROS when there are elevated levels of them and they also enhance the p38 and ERK S-T pathw ...
... Thioredoxin and Peroxyredoxin are very important regulators of the p38 and JNK S-T pathways in addition to being important antioxidant proteins… In a sense, they are cellular redox sensors that help to quench ROS when there are elevated levels of them and they also enhance the p38 and ERK S-T pathw ...
Chapter 8 - Plant Biology
... The results of some plant enzyme activities are easy to detect. The darkening of an apple fruit after it has been cut or bitten results from the action of the enzyme polyphenol oxidase on chemicals released from the cells. The softening of a tomato fruit as it ripens is caused by the action of seve ...
... The results of some plant enzyme activities are easy to detect. The darkening of an apple fruit after it has been cut or bitten results from the action of the enzyme polyphenol oxidase on chemicals released from the cells. The softening of a tomato fruit as it ripens is caused by the action of seve ...
Exam 2 Practice - Nicholls State University
... b. the inhibition is reversible by adding more substrate c. the degree of inhibition does not change with change in substrate concentration d. the inhibitor can be saturated 10. Which substance is most likely to be a cofactor? a. NAD+ b. ATP c. AMP d. Ca++ 11. In theory, how many ATP can be produced ...
... b. the inhibition is reversible by adding more substrate c. the degree of inhibition does not change with change in substrate concentration d. the inhibitor can be saturated 10. Which substance is most likely to be a cofactor? a. NAD+ b. ATP c. AMP d. Ca++ 11. In theory, how many ATP can be produced ...
Name
... cellulose, and glycogen. Starch and glycogen are easily broken down into sugars for energy. Cellulose, on the other hand, which is made in plants, can be broken down only by a few organisms in the world (primarily the bacteria in the guts of termites). What happens to the cellulose (fiber) you eat? ...
... cellulose, and glycogen. Starch and glycogen are easily broken down into sugars for energy. Cellulose, on the other hand, which is made in plants, can be broken down only by a few organisms in the world (primarily the bacteria in the guts of termites). What happens to the cellulose (fiber) you eat? ...
Answers to end of chapter questions
... 22. An allosteric site is the part of an enzyme that does what? (A) Binds an inhibitor or other effector molecule 23. What is the name given to the first step in a metabolic pathway that produces an intermediate that is unique to that pathway? (B) Commitment step 24. The concerted and sequent ...
... 22. An allosteric site is the part of an enzyme that does what? (A) Binds an inhibitor or other effector molecule 23. What is the name given to the first step in a metabolic pathway that produces an intermediate that is unique to that pathway? (B) Commitment step 24. The concerted and sequent ...
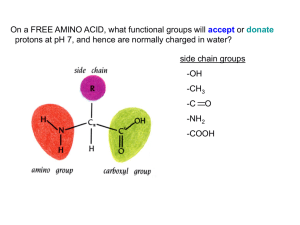
Lab 1 activity, AMINO ACIDS - Cal State LA
... Which amino acid side chains are positively charged at pH 7? ...
... Which amino acid side chains are positively charged at pH 7? ...
Metabolic Pathway Flux Enhancement by Synthetic
... to observe biochemically in vitro. For example, purine biosynthesis in eukaryotes involves six enzymes. Despite early anticipation of potential interactions between these enzymes, only recently was it understood, by fluorescently tagging these enzymes in vivo, that all six proteins coassemble (An et ...
... to observe biochemically in vitro. For example, purine biosynthesis in eukaryotes involves six enzymes. Despite early anticipation of potential interactions between these enzymes, only recently was it understood, by fluorescently tagging these enzymes in vivo, that all six proteins coassemble (An et ...
Unit 2 Student Guided Notes Introduction Carbon is the basic
... acid and an Oxygen further down the chain. An alpha helix contains 3.6 amino acids per spiral. There are other secondary structures, but the alpha helix is the most common and the one you will need to know for this course. Protein Structure - Tertiary and Quaternary Structures The third level is des ...
... acid and an Oxygen further down the chain. An alpha helix contains 3.6 amino acids per spiral. There are other secondary structures, but the alpha helix is the most common and the one you will need to know for this course. Protein Structure - Tertiary and Quaternary Structures The third level is des ...
Document
... 1. Arginine is biosynthesized from this precursor: A) Pyruvate B) Oxaloacetate C) a-ketoglutarate D) 3-phosphoglycerate 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competit ...
... 1. Arginine is biosynthesized from this precursor: A) Pyruvate B) Oxaloacetate C) a-ketoglutarate D) 3-phosphoglycerate 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competit ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.