Atoms
... Meats - contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms and break down into amino acids which are important for regulating chemical reactions that occur in living things. These are building materials of all cell parts. ...
... Meats - contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms and break down into amino acids which are important for regulating chemical reactions that occur in living things. These are building materials of all cell parts. ...
Alpha-Lipoic Acid The Universal Antioxidant
... into the cell. This may be explained by its functions in the glucose-metabolizing enzymes, PDH and alphaKGDH, but some researchers suspect a more direct role in cellular glucose uptake at the cell membrane. As early as 1959, alpha-lipoic acid was suggested to be an antioxidant, since it could extend ...
... into the cell. This may be explained by its functions in the glucose-metabolizing enzymes, PDH and alphaKGDH, but some researchers suspect a more direct role in cellular glucose uptake at the cell membrane. As early as 1959, alpha-lipoic acid was suggested to be an antioxidant, since it could extend ...
1 Chapter 2 Section 1- Nature of matter Atom: smallest unit of
... All atoms “want” to be stable, like the noble gases in column 8. They try to fill up their valence shell (with up to 2 or 8 electrons). Elements in columns 4-‐7 will gain electrons to have ...
... All atoms “want” to be stable, like the noble gases in column 8. They try to fill up their valence shell (with up to 2 or 8 electrons). Elements in columns 4-‐7 will gain electrons to have ...
Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 2
... • Polysaccharides: examples are starch, glycogen (animal starch), and cellulose. These are made of many rings of carbon (many simple sugars joined together). ...
... • Polysaccharides: examples are starch, glycogen (animal starch), and cellulose. These are made of many rings of carbon (many simple sugars joined together). ...
bioshield - CelVitali International
... cell membranes, proteins and lipids of healthy cells. Bioshield provides a micronutrient formulation that is robust in antioxidants. Antioxidants have been shown to reduce oxidative damage and disease states. The release of free radicals and oxidative damage are associated with tissue and DNA damage ...
... cell membranes, proteins and lipids of healthy cells. Bioshield provides a micronutrient formulation that is robust in antioxidants. Antioxidants have been shown to reduce oxidative damage and disease states. The release of free radicals and oxidative damage are associated with tissue and DNA damage ...
Free Radical Tissue Damage and - University of Missouri Animal
... and from the activity of certain oxidases, cyclooxygenases, lipoxygenases, dehydrogenases, and peroxidases. Oxidases and electron trans port systems are prime, continuous sources of intracellular, reactive oxygenated free radicals. Electron transfer from transitionmetals such as iron to oxygen-conta ...
... and from the activity of certain oxidases, cyclooxygenases, lipoxygenases, dehydrogenases, and peroxidases. Oxidases and electron trans port systems are prime, continuous sources of intracellular, reactive oxygenated free radicals. Electron transfer from transitionmetals such as iron to oxygen-conta ...
Chemical Basis of Life – Biochemistry - Har
... located in the nucleus of the atom Electrons are in an electron cloud outside of the nucleus ...
... located in the nucleus of the atom Electrons are in an electron cloud outside of the nucleus ...
AP Respiration Test Review
... 1. Organic fuel molecules cannot directly drive metabolic activity. What molecule can? 2. What is the sum total of all chemical reactions within an organism? 3. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? 4. What is the term for the meta ...
... 1. Organic fuel molecules cannot directly drive metabolic activity. What molecule can? 2. What is the sum total of all chemical reactions within an organism? 3. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? 4. What is the term for the meta ...
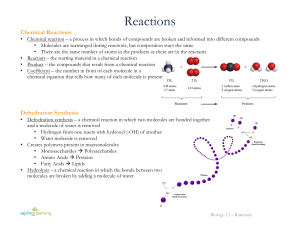
Reactions
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
CHAPTER 2 OBJECTIVE EXERCISE
... Compare and contrast the major divisions (types of chemical reactions) of metabolism, in terms of a general descriptive sentence, additional descriptive terms, how energy is involved, whether bonds are formed or broken, and how water is involved. Also write a chemical reaction for each and give an e ...
... Compare and contrast the major divisions (types of chemical reactions) of metabolism, in terms of a general descriptive sentence, additional descriptive terms, how energy is involved, whether bonds are formed or broken, and how water is involved. Also write a chemical reaction for each and give an e ...
Section 2-1: Nature of Matter
... that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the p ...
... that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the p ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... A species that seeks out areas of high electron density and accepts an electron pair to form a covalent bond when it reacts. eg, H+, Br+, SO3, NO2+. Nucleophile: A species that has a lone pair of electrons and is able to attack positive regions in other molecules and form covalent (dative) bonds. eg ...
... A species that seeks out areas of high electron density and accepts an electron pair to form a covalent bond when it reacts. eg, H+, Br+, SO3, NO2+. Nucleophile: A species that has a lone pair of electrons and is able to attack positive regions in other molecules and form covalent (dative) bonds. eg ...
Chemistry Review
... A water molecule has this distribution because the Oxygen has a stronger attraction for electrons than the 2 Hydrogens. This uneven distribution causes one end of a molecule to have a slightly positive charge and one end to have a slightly negative charge. ...
... A water molecule has this distribution because the Oxygen has a stronger attraction for electrons than the 2 Hydrogens. This uneven distribution causes one end of a molecule to have a slightly positive charge and one end to have a slightly negative charge. ...
ppt - Castle High School
... – All salts are electrolytes (substances that conduct an electrical current in solvent) • Release ions when dissolved in water ...
... – All salts are electrolytes (substances that conduct an electrical current in solvent) • Release ions when dissolved in water ...
Biochemistry Vocab Key
... The positive charge from the hydrogen atom of one water molecule can attract a negative charge from another molecule. Two atoms form a molecule using a covalent bond. having partial positive and partial negative charges Molecule which has no separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are ...
... The positive charge from the hydrogen atom of one water molecule can attract a negative charge from another molecule. Two atoms form a molecule using a covalent bond. having partial positive and partial negative charges Molecule which has no separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are ...
Reactive Oxygen Species and Cellular Defense System
... deterioration has become an area of intense interest. The free radicals have a special affinity for lipids, proteins, and DNA [1]. A free radical is an atom, molecule, or compound that is highly unstable because of its atomic or molecular structure (i.e., the distribution of electrons within the mol ...
... deterioration has become an area of intense interest. The free radicals have a special affinity for lipids, proteins, and DNA [1]. A free radical is an atom, molecule, or compound that is highly unstable because of its atomic or molecular structure (i.e., the distribution of electrons within the mol ...
A.P. Chemistry Complexation Reactions
... (B) in a compound A single element must be more reactive to replace another element. ...
... (B) in a compound A single element must be more reactive to replace another element. ...
Oxygen Metabolism and Oxygen Toxicity
... prevent carbon based organisms such as our selves from spontaneously igniting in our oxygen atmosphere. The parallel electron spins prevent oxidation by 2 electron transfers. Oxidation by molecular oxygen can only occur by the transfer of single electrons. Organic molecules that serve as substrates ...
... prevent carbon based organisms such as our selves from spontaneously igniting in our oxygen atmosphere. The parallel electron spins prevent oxidation by 2 electron transfers. Oxidation by molecular oxygen can only occur by the transfer of single electrons. Organic molecules that serve as substrates ...
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Nature`s Che
... The systematic name for isoprene is 2-methylbuta-1,3-diene. The term terpene is used to include compounds containing different functional groups. Oxidation of terpenes in plants is responsible for the aroma of many spices. ...
... The systematic name for isoprene is 2-methylbuta-1,3-diene. The term terpene is used to include compounds containing different functional groups. Oxidation of terpenes in plants is responsible for the aroma of many spices. ...
Acetaldehyde2
... Hydrogen can make one covalent bonds-One unpaired electron Oxygen can make two covalent bonds-Two unpaired electrons ...
... Hydrogen can make one covalent bonds-One unpaired electron Oxygen can make two covalent bonds-Two unpaired electrons ...
Methane - ARZELORIVAS IS
... This reaction has the following characteristic properties. It doesn't take place in the dark or at low temperatures. It occurs in the presence of ultraviolet light or at temperatures above 250oC. Once the reaction gets started, it continues after the light is turned off. The products of the ...
... This reaction has the following characteristic properties. It doesn't take place in the dark or at low temperatures. It occurs in the presence of ultraviolet light or at temperatures above 250oC. Once the reaction gets started, it continues after the light is turned off. The products of the ...
Radical (chemistry)

In chemistry, a radical (more precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valency electrons.With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make free radicals highly chemically reactive towards other substances, or even towards themselves: their molecules will often spontaneously dimerize or polymerize if they come in contact with each other. Most radicals are reasonably stable only at very low concentrations in inert media or in a vacuum.A notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO•), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (:CH2) which have two unpaired electrons. In contrast, the hydroxyl anion (HO−) is not a radical, since the unpaired electron is resolved by the addition of an electron; singlet oxygen and singlet carbene are not radicals as the two electrons are paired.Free radicals may be created in a number of ways, including synthesis with very dilute or rarefied reagents, reactions at very low temperatures, or breakup of larger molecules. The latter can be affected by any process that puts enough energy into the parent molecule, such as ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, electrolysis, and chemical reactions. Indeed, radicals are intermediate stages in many chemical reactions.Free radicals play an important role in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. In living organisms, the free radicals superoxide and nitric oxide and their reaction products regulate many processes, such as control of vascular tone and thus blood pressure. They also play a key role in the intermediary metabolism of various biological compounds. Such radicals can even be messengers in a process dubbed redox signaling. A radical may be trapped within a solvent cage or be otherwise bound.Until late in the 20th century the word ""radical"" was used in chemistry to indicate any connected group of atoms, such as a methyl group or a carboxyl, whether it was part of a larger molecule or a molecule on its own. The qualifier ""free"" was then needed to specify the unbound case. Following recent nomenclature revisions, a part of a larger molecule is now called a functional group or substituent, and ""radical"" now implies ""free"". However, the old nomenclature may still occur in the literature.