Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Enzymes are proteins that • catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body • increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation The enzyme carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction of CO2 and H2O. Chemistry: An Introduct ...
... Enzymes are proteins that • catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body • increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation The enzyme carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction of CO2 and H2O. Chemistry: An Introduct ...
Doc
... Benzanilide/Phenyl benzoate/Acetanilide from Aniline/ Phenol /Aniline by acylation reaction. 2,4,6-Tribromo aniline/Para bromo acetanilide from Aniline/ Acetanilide by halogenation (Bromination) reaction. 5-Nitro salicylic acid/Meta di nitro benzene from Salicylic acid / Nitro benzene by nitration r ...
... Benzanilide/Phenyl benzoate/Acetanilide from Aniline/ Phenol /Aniline by acylation reaction. 2,4,6-Tribromo aniline/Para bromo acetanilide from Aniline/ Acetanilide by halogenation (Bromination) reaction. 5-Nitro salicylic acid/Meta di nitro benzene from Salicylic acid / Nitro benzene by nitration r ...
CH_16_5_16_6_Enzymes_Enzyme_Action
... Enzymes are proteins that • catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body • increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation The enzyme carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction of CO2 and H2O. Chemistry: An Introduct ...
... Enzymes are proteins that • catalyze nearly all the chemical reactions taking place in the cells of the body • increase the rate of reaction by lowering the energy of activation The enzyme carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy needed for the reaction of CO2 and H2O. Chemistry: An Introduct ...
Document
... • The double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids form ‘kinks’ so the molecules cannot pack together to form solids. • saturated fatty acids can pack together closely and can form solids. ...
... • The double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids form ‘kinks’ so the molecules cannot pack together to form solids. • saturated fatty acids can pack together closely and can form solids. ...
CH 4: Chemical Reactions
... 3. An atom in a polyatomic ion or in a molecular compound usually has the same oxidation number it would have if it were a monatomic ion. A. Hydrogen can be either +1 or –1. B. Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of –2. In peroxides, oxygen is –1. C. Halogens usually have an oxidation number of – ...
... 3. An atom in a polyatomic ion or in a molecular compound usually has the same oxidation number it would have if it were a monatomic ion. A. Hydrogen can be either +1 or –1. B. Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of –2. In peroxides, oxygen is –1. C. Halogens usually have an oxidation number of – ...
Document
... – We can make twelve of the twenty amino acids. – The rest we must consume in our food. If we don’t get it the body uses one that we do have to make what’s missing. This results in certain proteins not being made. ...
... – We can make twelve of the twenty amino acids. – The rest we must consume in our food. If we don’t get it the body uses one that we do have to make what’s missing. This results in certain proteins not being made. ...
Area 4: Molecular recognition in biomolecules Computational
... There is a wide interest in designing peptides able to bind to a specific region of a protein with the aim of interfering with a known interaction or as starting point for the design of inhibitors. We plan to develop and implement a tool for the computational design of peptides binding to a protein ...
... There is a wide interest in designing peptides able to bind to a specific region of a protein with the aim of interfering with a known interaction or as starting point for the design of inhibitors. We plan to develop and implement a tool for the computational design of peptides binding to a protein ...
Pseudoatom-driven solvent accessibility refinement (PaDSAR) Method
... This suite of NAMD input files is to support the application of the PaDSAR method for membrane protein refinement based on EPR data. This method is used for incorporating solvent accessibility data from electron paramagnetic resonance experiments in the structural refinement of membrane proteins thr ...
... This suite of NAMD input files is to support the application of the PaDSAR method for membrane protein refinement based on EPR data. This method is used for incorporating solvent accessibility data from electron paramagnetic resonance experiments in the structural refinement of membrane proteins thr ...
Fundamental Knowledge for Analysis of Chemical Reactor
... equivolumetric mixture of P.O. and methanol 2.5 times volume of 0.1%H2SO4 water solution uniform concentration and temperature inside whole reactor products is continuously discharged from reactor with the same concentration and temperature as inside reactor what we want to know: production ability, ...
... equivolumetric mixture of P.O. and methanol 2.5 times volume of 0.1%H2SO4 water solution uniform concentration and temperature inside whole reactor products is continuously discharged from reactor with the same concentration and temperature as inside reactor what we want to know: production ability, ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... Pyruvate freely diffuses through the outer membrane of mitochondria through the channels formed by transmembrane proteins porins. ...
... Pyruvate freely diffuses through the outer membrane of mitochondria through the channels formed by transmembrane proteins porins. ...
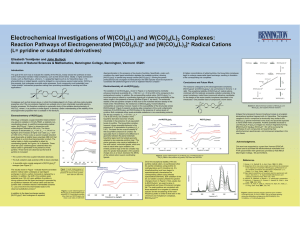
Electrochemical Investigations of W(CO) (L) and W(CO) (L) Complexes:
... moeity, such as Re(CO)3(LL), where LL = a polypyridyl ligand such as 2,2’-bipyridine (bpy), 1,10phenanthroline or related ligands, would be bridged to a non-emissive second metal center, W(CO)5 in this example, that undergoes reversible redox processes. Such compounds could potentially have “redox-t ...
... moeity, such as Re(CO)3(LL), where LL = a polypyridyl ligand such as 2,2’-bipyridine (bpy), 1,10phenanthroline or related ligands, would be bridged to a non-emissive second metal center, W(CO)5 in this example, that undergoes reversible redox processes. Such compounds could potentially have “redox-t ...
Supplementary Text 2: Extensions to the prototype model
... Kobayashi and Nagiec6 showed the importance of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) in regulating the flow of de novo sphingolipid synthesis towards ceramide, complex sphingolipids, and free sphingoid bases and their phosphates. Modeling this observation requires the inclusion of C26-CoA as a dynami ...
... Kobayashi and Nagiec6 showed the importance of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) in regulating the flow of de novo sphingolipid synthesis towards ceramide, complex sphingolipids, and free sphingoid bases and their phosphates. Modeling this observation requires the inclusion of C26-CoA as a dynami ...
chemical reaction
... Factors Affecting Rates of Reactions, continued • Concentration In general, a high concentration of reactants causes a fast rate of reaction. Concentration is a measure of the amount of one substance when it is dissolved in another substance. • When concentration is high, there are many reactant par ...
... Factors Affecting Rates of Reactions, continued • Concentration In general, a high concentration of reactants causes a fast rate of reaction. Concentration is a measure of the amount of one substance when it is dissolved in another substance. • When concentration is high, there are many reactant par ...
02b Basic equations two substrates
... The thermodynamic cycles L. Thermodynamic cycles Thermodynamic functions such as Gibbs free energy G, enthalpy H, and entropy S, are functions of state. This means that they depend only on the state of the system being considered and not on how that system came into being. Changes in functions of s ...
... The thermodynamic cycles L. Thermodynamic cycles Thermodynamic functions such as Gibbs free energy G, enthalpy H, and entropy S, are functions of state. This means that they depend only on the state of the system being considered and not on how that system came into being. Changes in functions of s ...
Enzymes: Principles of Catalysis
... • Kinetic mechanism: the order of binding of substrates and release of products • When two or more reactants are involved, enzyme kinetics allows to distinguish between different kinetic mechanisms ...
... • Kinetic mechanism: the order of binding of substrates and release of products • When two or more reactants are involved, enzyme kinetics allows to distinguish between different kinetic mechanisms ...
2.4 Chemical equilibria
... Conc. soln. of Potassium dichromate 2M HCl 2M NaOH 250ml conical flask ...
... Conc. soln. of Potassium dichromate 2M HCl 2M NaOH 250ml conical flask ...
Full Text - Journal of The Royal Society Interface
... interact with any other cytoplasmic protein, catalyse reactions with any of the several hundreds of metabolites or otherwise interact with any important physiological process. In other words, it is rather difficult to predict the effect of expanding the cellular genome, in any case quantitatively, bu ...
... interact with any other cytoplasmic protein, catalyse reactions with any of the several hundreds of metabolites or otherwise interact with any important physiological process. In other words, it is rather difficult to predict the effect of expanding the cellular genome, in any case quantitatively, bu ...
Lect 6 - BIDD - National University of Singapore
... is not fully understood. • The primary sequence may not fully specify the tertiary structure. – chaperones ...
... is not fully understood. • The primary sequence may not fully specify the tertiary structure. – chaperones ...
Answer Key for the Supplemental Problem Set #1
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
Starter S-30
... A. Balance the following reactions H2SO4 + KOH K2SO4 + H2O B. What is the molar mass of the sulfuric acid. C. If 20.0g of sulfuric acid is used, how many moles is that? D. How many moles of water would be produced? ...
... A. Balance the following reactions H2SO4 + KOH K2SO4 + H2O B. What is the molar mass of the sulfuric acid. C. If 20.0g of sulfuric acid is used, how many moles is that? D. How many moles of water would be produced? ...
The activity reaction core and plasticity of metabolic networks
... tetrahydrofolte biosynthesis. Both pathways are present in H. pylori and E. coli. ...
... tetrahydrofolte biosynthesis. Both pathways are present in H. pylori and E. coli. ...
KREBS CYCLE Definition Krebs cycle (aka tricarboxylic acid cycle
... 2. Before the oxidation reactions can begin, the hydroxyl group of citrate must be repositioned. This is done by removing a water molecule from one carbon and the water is added to different carbon. The product is an isomer of citrate called isocitrate. ...
... 2. Before the oxidation reactions can begin, the hydroxyl group of citrate must be repositioned. This is done by removing a water molecule from one carbon and the water is added to different carbon. The product is an isomer of citrate called isocitrate. ...
*1496/Chap 06.quark
... How do chemists determine whether a proposed mechanism supports the experimentally determined rate law? They must consider how the rates of the elementary reactions relate to the rate of the overall reaction. Elementary reactions in mechanisms all have different rates. Usually one elementary reactio ...
... How do chemists determine whether a proposed mechanism supports the experimentally determined rate law? They must consider how the rates of the elementary reactions relate to the rate of the overall reaction. Elementary reactions in mechanisms all have different rates. Usually one elementary reactio ...
Unit 2 Summary - A
... (iii) E/Z isomerism as an example of stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, (iv) cis-trans isomerism as a special case of EIZ isomerism in which two of the substituent grou ...
... (iii) E/Z isomerism as an example of stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, (iv) cis-trans isomerism as a special case of EIZ isomerism in which two of the substituent grou ...