Metabolism & Enzymes
... allosteric inhibitor binds to allosteric site causes enzyme to change shape conformational change ...
... allosteric inhibitor binds to allosteric site causes enzyme to change shape conformational change ...
Similarities: Differences Differences
... been discovered in the ocean - dominant form of life below 300 meters in the oceans! ...
... been discovered in the ocean - dominant form of life below 300 meters in the oceans! ...
Zhan-3-Enzyme
... Enzyme are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction by lowering the energy of the transition state. Enzymes are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. Enzyme molecules contain a special pocket or cleft called the active site. The active site contains amino acid si ...
... Enzyme are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction by lowering the energy of the transition state. Enzymes are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. Enzyme molecules contain a special pocket or cleft called the active site. The active site contains amino acid si ...
Biochemical fossils of the ancient transition from geoenergetics to
... protein methyltransferase Corrinoid iron–sulfur protein (CFeSP) ...
... protein methyltransferase Corrinoid iron–sulfur protein (CFeSP) ...
Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis 1 2 3 4
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
Metabolism of exercise
... METABOLISM DURING EXERCISE During exercise, metabolic events within the liver, which are regulated by hormone levels and substrate supply, integrate pathways of carbohydrate, fat, and amino acid metabolism. These processes function to provide substrates for muscular energy. The increased fuel demand ...
... METABOLISM DURING EXERCISE During exercise, metabolic events within the liver, which are regulated by hormone levels and substrate supply, integrate pathways of carbohydrate, fat, and amino acid metabolism. These processes function to provide substrates for muscular energy. The increased fuel demand ...
Biosketch - NC State University
... to examine the impact of local adipocytes on mitochondrial function and insulin action in neighboring myocytes. We also seek to understand how exercise combats age-related metabolic decline. To this end, we are collaborating with Dr. William Kraus to perform metabolic and transcriptional profiling a ...
... to examine the impact of local adipocytes on mitochondrial function and insulin action in neighboring myocytes. We also seek to understand how exercise combats age-related metabolic decline. To this end, we are collaborating with Dr. William Kraus to perform metabolic and transcriptional profiling a ...
eprint_1_29837_493
... body such as digestion , breathing , synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates m fats and proteins are catalysed and controlled by specific enzymes . Most chemical reactions of the living cells would have occurred very slowly had it not catalysed by enzymes . The substance upon which an enzymes acts ...
... body such as digestion , breathing , synthesis and breakdown of carbohydrates m fats and proteins are catalysed and controlled by specific enzymes . Most chemical reactions of the living cells would have occurred very slowly had it not catalysed by enzymes . The substance upon which an enzymes acts ...
Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
Predicting functional linkages from gene fusions with
... Such benchmarks have previously utilised the keywords associated with proteins in sequence databases such as SwissProt (Bairoch and Apweiler 2000) or the hierarchical functional categorisations of proteins, such as the KEGG database (Kanehisa and Goto 2000) or MIPS database (Mewes et al 2002), in wh ...
... Such benchmarks have previously utilised the keywords associated with proteins in sequence databases such as SwissProt (Bairoch and Apweiler 2000) or the hierarchical functional categorisations of proteins, such as the KEGG database (Kanehisa and Goto 2000) or MIPS database (Mewes et al 2002), in wh ...
Metabolomics of a Single Vacuole Reveals
... method, because perfusion must be conducted carefully to prevent metabolite movement across the vacuolar membrane during isolation, which would result in misleading metabolomic results. On the other hand, vacuolar solution can be isolated in approximately 10 s after loss of turgor pressure by our me ...
... method, because perfusion must be conducted carefully to prevent metabolite movement across the vacuolar membrane during isolation, which would result in misleading metabolomic results. On the other hand, vacuolar solution can be isolated in approximately 10 s after loss of turgor pressure by our me ...
Chapter 15 Enzymes
... multiple forms; each catalyzes the same reaction. • Example: lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the oxidation of lactate to pyruvate. • The enzyme is a tetramer of H and M chains. • H4 is present predominately in heart muscle. • M4 is present predominantly in the liver and in ...
... multiple forms; each catalyzes the same reaction. • Example: lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the oxidation of lactate to pyruvate. • The enzyme is a tetramer of H and M chains. • H4 is present predominately in heart muscle. • M4 is present predominantly in the liver and in ...
Mendelian Traits
... The fragile X syndrome (FXS) was first described by Martin and Bell (1943) although it took several decades to fully characterize the disorder. Initially called the Martin-Bell syndrome, its current name comes from karyotypes in which it appeared that a section of the X chromosome was close to break ...
... The fragile X syndrome (FXS) was first described by Martin and Bell (1943) although it took several decades to fully characterize the disorder. Initially called the Martin-Bell syndrome, its current name comes from karyotypes in which it appeared that a section of the X chromosome was close to break ...
Organic Acids The basics
... Further delineation of the primary defect is more difficult. Methylmalonyl CoA mutase can be assayed directly although these account for only a small proportion of cases. Since direct enzyme assays for the enzymes of adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin biosynthesis are difficult, the usual approac ...
... Further delineation of the primary defect is more difficult. Methylmalonyl CoA mutase can be assayed directly although these account for only a small proportion of cases. Since direct enzyme assays for the enzymes of adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin biosynthesis are difficult, the usual approac ...
Towards the storage metabolome: profiling the barley vacuole
... and vacuoles were performed as described previously (Endler et al., 2009). In order to get rid of the isolation solution an additional centrifugation step as described in materials and methods was included. Protoplast samples were prepared as three replicates (P1~P3), vacuole samples were prepared a ...
... and vacuoles were performed as described previously (Endler et al., 2009). In order to get rid of the isolation solution an additional centrifugation step as described in materials and methods was included. Protoplast samples were prepared as three replicates (P1~P3), vacuole samples were prepared a ...
Hexokinase
... – Then oxidized to DHAP by the action of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase – NAD+ as the required coenzyme ...
... – Then oxidized to DHAP by the action of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase – NAD+ as the required coenzyme ...
Enzymes - HKEdCity
... Ø As substrate concentration is increased, more and more sites come into use. Ø When over the saturation point, a point where all active sites are being occupied by substrates, increasing the substrate concentration cannot increase the rate of reaction. This is because any extra substrate has to wai ...
... Ø As substrate concentration is increased, more and more sites come into use. Ø When over the saturation point, a point where all active sites are being occupied by substrates, increasing the substrate concentration cannot increase the rate of reaction. This is because any extra substrate has to wai ...
ENZYME WEBQUEST Name
... Induced Fit 17. Observe the INDUCED FIT ANIMATION and describe what happens below: ...
... Induced Fit 17. Observe the INDUCED FIT ANIMATION and describe what happens below: ...
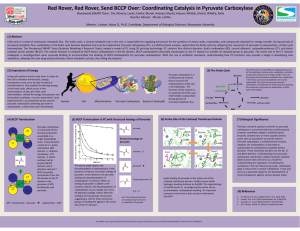
Poster
... (7) Biological Significance The basic research question centered on pyruvate carboxylase is concerned with how multifunctional enzymes coordinate catalysis. Multifunctional enzymes combine two or more spatially distinct active sites to accomplish an overall reaction. Pyruvate carboxylase, a multifun ...
... (7) Biological Significance The basic research question centered on pyruvate carboxylase is concerned with how multifunctional enzymes coordinate catalysis. Multifunctional enzymes combine two or more spatially distinct active sites to accomplish an overall reaction. Pyruvate carboxylase, a multifun ...
Jane M. Carlton, , 207 (2007); DOI: 10.1126/science.1132894
... We describe the genome sequence of the protist Trichomonas vaginalis, a sexually transmitted human pathogen. Repeats and transposable elements comprise about two-thirds of the ~160-megabase genome, reflecting a recent massive expansion of genetic material. This expansion, in conjunction with the sha ...
... We describe the genome sequence of the protist Trichomonas vaginalis, a sexually transmitted human pathogen. Repeats and transposable elements comprise about two-thirds of the ~160-megabase genome, reflecting a recent massive expansion of genetic material. This expansion, in conjunction with the sha ...
Gluconeogenesis
... The synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors is called gluconeogenesis. This metabolic pathway is very important because glucose is the primary energy source for the brain. Erythrocytes do not have mitochondria and derive all of their energy by glycolysis converting glucose into two mole ...
... The synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors is called gluconeogenesis. This metabolic pathway is very important because glucose is the primary energy source for the brain. Erythrocytes do not have mitochondria and derive all of their energy by glycolysis converting glucose into two mole ...
Metabolic network modelling

Metabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle) into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.In general, the process to build a reconstruction is as follows: Draft a reconstruction Refine the model Convert model into a mathematical/computational representation Evaluate and debug model through experimentation↑