Nuclear Chemistry
... So here energy a good amount of the chemical potential is retained as chemical energy for use in other biosynthetic or energy requiring reactions. Examples of the use of this “stored energy” Strenuous exercise causes pyruvate to change to lactate. And NADH helps out in this rxn! pyruvate + NADH + H+ ...
... So here energy a good amount of the chemical potential is retained as chemical energy for use in other biosynthetic or energy requiring reactions. Examples of the use of this “stored energy” Strenuous exercise causes pyruvate to change to lactate. And NADH helps out in this rxn! pyruvate + NADH + H+ ...
Energy Transfer and Glycolysis Cellular Respiration • Remember
... Remember that there are four stages that occur in three different places within the cell 1. Glycolysis: occurs in the cytoplasm 2. Pyruvate Oxidation: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 3. Kreb Cycle: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 4. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis: occur on ...
... Remember that there are four stages that occur in three different places within the cell 1. Glycolysis: occurs in the cytoplasm 2. Pyruvate Oxidation: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 3. Kreb Cycle: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 4. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis: occur on ...
Fermentation/ Citric Acid Cycle
... The Electron Transport Chain: - Occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane - NADH and FADH2 contain high energy electrons that are passed along a transport chain (similar to the chain in the light reactions of photosynthesis) - The energy they released is used to PUMP PROTONS out of the MATRIX - CH ...
... The Electron Transport Chain: - Occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane - NADH and FADH2 contain high energy electrons that are passed along a transport chain (similar to the chain in the light reactions of photosynthesis) - The energy they released is used to PUMP PROTONS out of the MATRIX - CH ...
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm
... 27. [2] Transamination from alanine to α-ketoglutarate requires the coenzyme: A) B) C) D) E) ...
... 27. [2] Transamination from alanine to α-ketoglutarate requires the coenzyme: A) B) C) D) E) ...
Document
... Acetyl CoA Cannot Fill Up CAC • A key branch point of human metabolism • Glucogenic vs. ketogenic • No net glucose from acetyl CoA ...
... Acetyl CoA Cannot Fill Up CAC • A key branch point of human metabolism • Glucogenic vs. ketogenic • No net glucose from acetyl CoA ...
C383 Study Guide for the Final Exam Spring 2017 Basic Information
... overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule through the intermediates it becomes on the way to being glucose. Draw the structure of glutamate a ...
... overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule through the intermediates it becomes on the way to being glucose. Draw the structure of glutamate a ...
Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) - LSU School of Medicine
... The Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle; The TCA Cycle • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism ...
... The Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle; The TCA Cycle • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism ...
Lecture 14: Alternative Pathways in Cell respiration
... convert NAD+ to NADH, which is used in the ETC to make ATP ...
... convert NAD+ to NADH, which is used in the ETC to make ATP ...
chap16
... o A protein kinase inactivates E1 through phosphorylation (in response to high levels of ATP) o A phosphatase reactivates E1 by cleaving the phosphate off the enzyme ...
... o A protein kinase inactivates E1 through phosphorylation (in response to high levels of ATP) o A phosphatase reactivates E1 by cleaving the phosphate off the enzyme ...
L24_Krebs
... which carboxylic group comes from acetyl CoA & oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy ...
... which carboxylic group comes from acetyl CoA & oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy ...
C383 Study Guide for the Final Exam Spring 2016 Basic Information
... overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule through the intermediates it becomes on the way to being glucose. Draw the structure of glutamate a ...
... overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule through the intermediates it becomes on the way to being glucose. Draw the structure of glutamate a ...
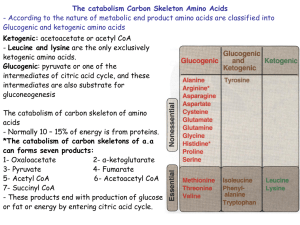
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Review of Glucose Metabolism File
... Review of Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _ ...
... Review of Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain _ ...
Review over Glucose Metabolism
... Review over Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain ...
... Review over Glucose Metabolism Match each of the following occurrences to the correct part of the glucose metabolism process. If more than one answer is correct, write all letters in the blank. A. Glycolysis B. Fermentation C. Cellular Respiration (aerobic) D. Krebs Cycle E. Electron Transport Chain ...
8.1 Glycolysis Know the overall reaction: the materials that go in
... Be able to recognize relative oxidation states, which carbons are more oxidized or reduced 9.2 Citric Acid Cycle Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA Mechanism: If I give you the bonds, you draw the arrows. If I give you the arrows, you draw the bonds. Reactions of the Citric Acid Cycle Mechanisms: ...
... Be able to recognize relative oxidation states, which carbons are more oxidized or reduced 9.2 Citric Acid Cycle Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA Mechanism: If I give you the bonds, you draw the arrows. If I give you the arrows, you draw the bonds. Reactions of the Citric Acid Cycle Mechanisms: ...
Metabolism - California Science Teacher
... Learn the whole diagram of the control of cellular respiration , with glucose that is stimulated by AMP regulates into Fructose-6-phosphate which inhibits into pyruvate. ATP occurs which combines with Acetyl CoA , which goes in the citric acid cycle, later is the function of Oxidation phophorilation ...
... Learn the whole diagram of the control of cellular respiration , with glucose that is stimulated by AMP regulates into Fructose-6-phosphate which inhibits into pyruvate. ATP occurs which combines with Acetyl CoA , which goes in the citric acid cycle, later is the function of Oxidation phophorilation ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... ☻OAA, the first substrate to bind to the enzyme, induce a large conformational change, creating a binding site for the second substrate, acetyl-CoA. When citroyl-CoA forms on the enzyme surface, another conformational change brings the side of a crucial Asp residue into position to cleavage the ...
... ☻OAA, the first substrate to bind to the enzyme, induce a large conformational change, creating a binding site for the second substrate, acetyl-CoA. When citroyl-CoA forms on the enzyme surface, another conformational change brings the side of a crucial Asp residue into position to cleavage the ...
Chapter 16
... 14. Succinate dehydrogenase is the only membrane-bound citric acid enzyme since the covalently bound FADH2 is only oxidized by the electron transport chain reaction. 15. Although the oxaloacetate formation form L-malate is relatively high endergonic reaction, this reaction occurs, because: 1. The [o ...
... 14. Succinate dehydrogenase is the only membrane-bound citric acid enzyme since the covalently bound FADH2 is only oxidized by the electron transport chain reaction. 15. Although the oxaloacetate formation form L-malate is relatively high endergonic reaction, this reaction occurs, because: 1. The [o ...
Glycolysis Animation
... • Aerobic requires O2 as final electron acceptor (happens in ETC) • Location --inside mitochondria “One-Two Punch” • Carbonyl group released as CO2 • NAD+ reduced to NADH • Leaves Acetyl--picked up by CoA & becomes Acetyl CoA ...
... • Aerobic requires O2 as final electron acceptor (happens in ETC) • Location --inside mitochondria “One-Two Punch” • Carbonyl group released as CO2 • NAD+ reduced to NADH • Leaves Acetyl--picked up by CoA & becomes Acetyl CoA ...
Microbial Metabolism (Part 2) I. Objectives II. What does a
... IV. Step 2: What to do next with energy extracted from glucose A. ...
... IV. Step 2: What to do next with energy extracted from glucose A. ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... transport pathway in the inner mitochondrial membrane • The electrons transferred from succinate to FAD (to form FADH2) are passed directly to ubiquinone (UQ) in the electron transport pathway • Enzyme inhibited by malonate ...
... transport pathway in the inner mitochondrial membrane • The electrons transferred from succinate to FAD (to form FADH2) are passed directly to ubiquinone (UQ) in the electron transport pathway • Enzyme inhibited by malonate ...
BCHM 463 Supplemental Problems for Friday, April 9, 2004 1. a
... of 3 enzymes. a) Name these enzymes and give all species that inhibit (negatively modulate) the enzymes’ activities. Citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and ∝-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase are the control points for the citric acid cycle. See figure 16-14 for the intermediates and products whi ...
... of 3 enzymes. a) Name these enzymes and give all species that inhibit (negatively modulate) the enzymes’ activities. Citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and ∝-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase are the control points for the citric acid cycle. See figure 16-14 for the intermediates and products whi ...
Citric acid cycle
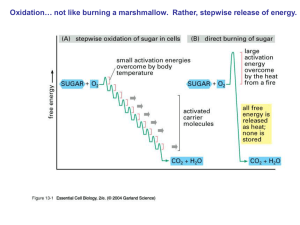
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.