ASA Guidelines for Undergraduate Programs in Statistical Science
... Simple linear regression Multiple regression Generalized linear models Model selection Diagnostics Statistical Cross-validation Models Mixed models Time Series Survival analysis Generalized additive models Regression trees Statistical and machine learning techniques Spatial analysis Multivariate met ...
... Simple linear regression Multiple regression Generalized linear models Model selection Diagnostics Statistical Cross-validation Models Mixed models Time Series Survival analysis Generalized additive models Regression trees Statistical and machine learning techniques Spatial analysis Multivariate met ...
SUPPLEMENTARY information
... : Model Derivation and Validation Development of Prediction Model In order to generate the probability of hepatic injury for each patient with HCC, expression data from patients who had undergone partial hepatectomy or liver transplantation (training set, Fig 1) were used to build a classifier based ...
... : Model Derivation and Validation Development of Prediction Model In order to generate the probability of hepatic injury for each patient with HCC, expression data from patients who had undergone partial hepatectomy or liver transplantation (training set, Fig 1) were used to build a classifier based ...
P(x | i )
... P(x | D ) ~ N(n , 2 n2 ) (Desired class-conditional density P(x | Dj, j)) Therefore: P(x | Dj, j) together with P(j) and using Bayes formula, we obtain the Bayesian classification rule: ...
... P(x | D ) ~ N(n , 2 n2 ) (Desired class-conditional density P(x | Dj, j)) Therefore: P(x | Dj, j) together with P(j) and using Bayes formula, we obtain the Bayesian classification rule: ...
WritingToDatabases
... The data is presented for modification The data is updated using the key value from the first step. ...
... The data is presented for modification The data is updated using the key value from the first step. ...
word - Andrew L. Diamond
... Machine Learning– Classifier design and analysis for multiple projects, mainly, using own implementation of Boosted Stochastic Gradient Trees providing a robust classification and automatic quantification of feature importance. Implementation includes a module that translates trained classifier into ...
... Machine Learning– Classifier design and analysis for multiple projects, mainly, using own implementation of Boosted Stochastic Gradient Trees providing a robust classification and automatic quantification of feature importance. Implementation includes a module that translates trained classifier into ...
view presentation - The National Academies of Sciences
... 140 miles of dirt tracks in California and Nevada ...
... 140 miles of dirt tracks in California and Nevada ...
Bug Localization with Association Rule Mining
... frequent patterns than building classification models Difficulties: ...
... frequent patterns than building classification models Difficulties: ...
Introduction
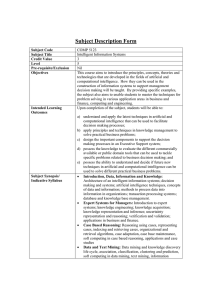
... instead generate solutions and then determine their value • This is the idea of enumeration: generate all possible solutions, and either • Return the first “correct” solution • Return the “best” solution ...
... instead generate solutions and then determine their value • This is the idea of enumeration: generate all possible solutions, and either • Return the first “correct” solution • Return the “best” solution ...
Why Probability?
... belonging to 2 clusters must belong to all clusters along path connecting them – Becomes part of the knowledge representation – Changes only if the graph changes ...
... belonging to 2 clusters must belong to all clusters along path connecting them – Becomes part of the knowledge representation – Changes only if the graph changes ...
Intro to Computer Algorithms Lecture 6
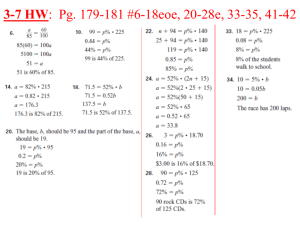
... More on Recurrences Exhaustive Search Divide and Conquer ...
... More on Recurrences Exhaustive Search Divide and Conquer ...
an overview of extensions of bayesian networks towards first
... having to ‘flatten’ the data (i.e. not considering the information stored in the structure). See [4]. D. Relational Bayesian networks The original BN models can be used to model first-order predicates as well. In this case the result of a query in the presence of some evidence is the probability of ...
... having to ‘flatten’ the data (i.e. not considering the information stored in the structure). See [4]. D. Relational Bayesian networks The original BN models can be used to model first-order predicates as well. In this case the result of a query in the presence of some evidence is the probability of ...