divergent plate boundary
... • Neural networks are configured for a specific application, such as pattern recognition or data classification, through a learning process • In a biological system, learning involves adjustments to the synaptic connections between neurons same for artificial neural networks (ANNs) ...
... • Neural networks are configured for a specific application, such as pattern recognition or data classification, through a learning process • In a biological system, learning involves adjustments to the synaptic connections between neurons same for artificial neural networks (ANNs) ...
OLD_s1a_alg_analysis..
... • multiply two matrices together the total number of elements in the two matrices And sometimes the input order as well (e.g., sorting algorithms). ...
... • multiply two matrices together the total number of elements in the two matrices And sometimes the input order as well (e.g., sorting algorithms). ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... III.3 PCA networks Principal component analysis networks (PCAs) combine unsupervised and supervised learning in the same topology. PCA is a very well-known statistical procedure in which input data of very large dimensionality (D dimensions) is projected onto a smaller-dimensionality space M (M < D) ...
... III.3 PCA networks Principal component analysis networks (PCAs) combine unsupervised and supervised learning in the same topology. PCA is a very well-known statistical procedure in which input data of very large dimensionality (D dimensions) is projected onto a smaller-dimensionality space M (M < D) ...
Video recording
... Individuals are concerned about confidentiality Companies are concerned about confidentiality Video-based Interaction Analysis is time consuming and expensive Video-based data is difficult to work with Incorporating screen-capture ups the ante on time, expertise and complexity Camera effects may ari ...
... Individuals are concerned about confidentiality Companies are concerned about confidentiality Video-based Interaction Analysis is time consuming and expensive Video-based data is difficult to work with Incorporating screen-capture ups the ante on time, expertise and complexity Camera effects may ari ...
Deep Machine Learning—A New Frontier in Artificial Intelligence
... added to the network improves the logprobability of the training data, which we can think of as increasing true representational power. This meaningful expansion, in conjunction with the utilization of unlabeled data, is a critical component in any deep learning application. At the top two layers, t ...
... added to the network improves the logprobability of the training data, which we can think of as increasing true representational power. This meaningful expansion, in conjunction with the utilization of unlabeled data, is a critical component in any deep learning application. At the top two layers, t ...
Computational intelligence meets the NetFlix prize IEEE
... basic FA architecture consists of two-layer nodes or neurons, the feature representation field F1, and the category representation field F2, as shown in Fig. 1. The neurons in layer F1 are activated by the input pattern, while the prototypes of the formed clusters are stored in layer F2. The neurons ...
... basic FA architecture consists of two-layer nodes or neurons, the feature representation field F1, and the category representation field F2, as shown in Fig. 1. The neurons in layer F1 are activated by the input pattern, while the prototypes of the formed clusters are stored in layer F2. The neurons ...
SueMerchant
... •develop new types of models •interpret statistics •see the wood for the trees •understand dimension and significance •pick out important relationships from data •Know the most effective way of displaying data •appreciate the stochastic nature of some problems ...
... •develop new types of models •interpret statistics •see the wood for the trees •understand dimension and significance •pick out important relationships from data •Know the most effective way of displaying data •appreciate the stochastic nature of some problems ...
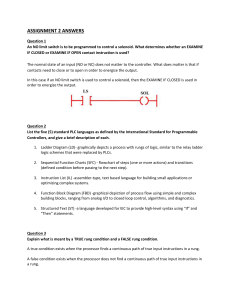
assignment 2 answers
... IF CLOSED or EXAMINE IF OPEN contact instruction is used? The normal state of an input (NO or NC) does not matter to the controller. What does matter is that if contacts need to close or to open in order to energize the output. In this case if an NO limit switch is used to control a solenoid, then t ...
... IF CLOSED or EXAMINE IF OPEN contact instruction is used? The normal state of an input (NO or NC) does not matter to the controller. What does matter is that if contacts need to close or to open in order to energize the output. In this case if an NO limit switch is used to control a solenoid, then t ...
International Journal on Advanced Computer Theory and
... Neural Networks etc. Most of these techniques are based on finding the distances or uses statistical methods. Classification Using Distance (K-Nearest Neighbors algorithm (KNN), this approach, places items in the class to which they are “closest” to their neighbor. It must determine distance between ...
... Neural Networks etc. Most of these techniques are based on finding the distances or uses statistical methods. Classification Using Distance (K-Nearest Neighbors algorithm (KNN), this approach, places items in the class to which they are “closest” to their neighbor. It must determine distance between ...
Machine Learning
... Outline of topics • Groundwork: probability and slopes • Classification overview: Training, testing, and overfitting • Basic classifiers: Naïve Bayes and Logistic Regression • Advanced classifiers: Neural networks and support vector machines ...
... Outline of topics • Groundwork: probability and slopes • Classification overview: Training, testing, and overfitting • Basic classifiers: Naïve Bayes and Logistic Regression • Advanced classifiers: Neural networks and support vector machines ...
Applications for Gaming in AI
... Please don’t ask me questions about this game… student is currently researching ...
... Please don’t ask me questions about this game… student is currently researching ...
Improving the Design and Discovery of Dynamic in Sequential Decision-Making
... In recent years, we have investigated algorithmic methods for automatically discovering and optimizing sequential treatments for chronic and life-threatening diseases. In this talk I will discuss two aspects of this work, first the problem of efficiently collecting data to learn good sequential trea ...
... In recent years, we have investigated algorithmic methods for automatically discovering and optimizing sequential treatments for chronic and life-threatening diseases. In this talk I will discuss two aspects of this work, first the problem of efficiently collecting data to learn good sequential trea ...
Diapositiva 1
... Remarks on k-NN classification •The distance weighted kNN is robust to noisy training data and is quite effective when it is provided a sufficiently large set of training examples. •One drawbak of kNN method is that, it defers all computation till a new querry point is presented. Various methods ha ...
... Remarks on k-NN classification •The distance weighted kNN is robust to noisy training data and is quite effective when it is provided a sufficiently large set of training examples. •One drawbak of kNN method is that, it defers all computation till a new querry point is presented. Various methods ha ...
Machine Learning - Dipartimento di Informatica
... Studied as computing paradigms since the 40 ‘ Neurobiological inspiration Nowadays: set of powerful computing models for function approximation and with predictive capabilities supported by a rigorous theoretical ground (learning theory) Models for Deep Learning ...
... Studied as computing paradigms since the 40 ‘ Neurobiological inspiration Nowadays: set of powerful computing models for function approximation and with predictive capabilities supported by a rigorous theoretical ground (learning theory) Models for Deep Learning ...