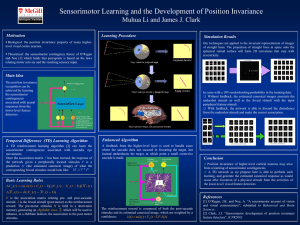
Artificial Intelligence, Lecture 7.1, Page 1
... The tendency to prefer one hypothesis over another is called a bias. Saying a hypothesis is better than N’s or P’s hypothesis isn’t something that’s obtained from the data. To have any inductive process make predictions on unseen data, you need a bias. What constitutes a good bias is an empirical qu ...
... The tendency to prefer one hypothesis over another is called a bias. Saying a hypothesis is better than N’s or P’s hypothesis isn’t something that’s obtained from the data. To have any inductive process make predictions on unseen data, you need a bias. What constitutes a good bias is an empirical qu ...
Lecture 1 2015 INF3490/INF4490: Biologically Inspired Computing
... • Increase intelligence in both single node and multiple node systems ...
... • Increase intelligence in both single node and multiple node systems ...
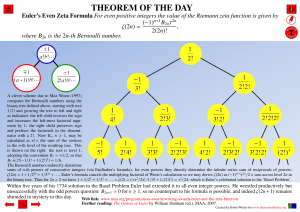
0.8 x 0.8 x 0.2 x 0.2 = 0.0256.
... Throughout the course ( in Chapters 2, 3 and 4) we have focussed on data which we can assume comes from the Normal distribution. ...
... Throughout the course ( in Chapters 2, 3 and 4) we have focussed on data which we can assume comes from the Normal distribution. ...
Part 7.2 Neural Networks
... Learning algorithm Target Value, T : When we are training a network we not only present it with the input but also with a value that we require the network to produce. For example, if we present the network with [1,1] for the AND function the target value will be 1 Output , O : The output value fro ...
... Learning algorithm Target Value, T : When we are training a network we not only present it with the input but also with a value that we require the network to produce. For example, if we present the network with [1,1] for the AND function the target value will be 1 Output , O : The output value fro ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... • Planning (get the robot to find the bananas in the other room). • Machine Learning (adapt to new circumstances). • Natural language understanding. • Machine vision, speech recognition, finding data on the web, robotics, and much more. ...
... • Planning (get the robot to find the bananas in the other room). • Machine Learning (adapt to new circumstances). • Natural language understanding. • Machine vision, speech recognition, finding data on the web, robotics, and much more. ...
Lec13-BayesNet
... conditional probabilities and priors. • If max k inputs to a node, and n RVs, then need at most n*2^k table entries. • Data and computation reduced. ...
... conditional probabilities and priors. • If max k inputs to a node, and n RVs, then need at most n*2^k table entries. • Data and computation reduced. ...
Algebra 2 Name: Date: What is the science of statistics? The science
... 1. What is the science of statistics? The science of statistics deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. 2. Describe descriptive statistics? Organizing and summarizing data is called descriptive data. 3. What are the two ways to summarize data? Two ways to summa ...
... 1. What is the science of statistics? The science of statistics deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. 2. Describe descriptive statistics? Organizing and summarizing data is called descriptive data. 3. What are the two ways to summarize data? Two ways to summa ...
Review Hybrid Statistics Exam 1 – Chapters 1,2 and 9 Identify
... 2. If the solution is an integer, say 32, then the pth percentile value is the 32nd data point from the sample in ascending order. If the solution is not an integer then you find the average value be the two surrounding points. For example, say the solution is 23.7 for the index of the pth percentil ...
... 2. If the solution is an integer, say 32, then the pth percentile value is the 32nd data point from the sample in ascending order. If the solution is not an integer then you find the average value be the two surrounding points. For example, say the solution is 23.7 for the index of the pth percentil ...
The Elements of Statistical Learning
... Step 2: Similarly, generate 10 means from the from the bivariate Gaussian distribution N((0,1)T,I) and label this class RED Step 3: For each class, generate 100 observations as follows: l ...
... Step 2: Similarly, generate 10 means from the from the bivariate Gaussian distribution N((0,1)T,I) and label this class RED Step 3: For each class, generate 100 observations as follows: l ...
Preface
... Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers continue to face large challenges in their quest to develop truly intelligent systems. e recent developments in the area of neural-symbolic integration bring an opportunity to combine symbolic AI with robust neural computation to tackle some of these challen ...
... Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers continue to face large challenges in their quest to develop truly intelligent systems. e recent developments in the area of neural-symbolic integration bring an opportunity to combine symbolic AI with robust neural computation to tackle some of these challen ...
Anomaly Detection via Online Over-Sampling Principal Component
... data instances. However, most anomaly detection methods are typically implemented in batch mode, and thus cannot be easily extended to large-scale problems without sacrificing computation and memory requirements. In this paper, we propose an online over-sampling principal component analysis (osPCA) ...
... data instances. However, most anomaly detection methods are typically implemented in batch mode, and thus cannot be easily extended to large-scale problems without sacrificing computation and memory requirements. In this paper, we propose an online over-sampling principal component analysis (osPCA) ...