ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES
... this and cuts off the power before he/she can get injured. GFCIs are generally installed where electrical circuits may accidentally come into contact with water. They are most often found in kitchens, bath and laundry rooms, or even out-of-doors or in the garage where electric power tools might be u ...
... this and cuts off the power before he/she can get injured. GFCIs are generally installed where electrical circuits may accidentally come into contact with water. They are most often found in kitchens, bath and laundry rooms, or even out-of-doors or in the garage where electric power tools might be u ...
14PE1 Maximum power transfer tracking for Ultralow
... This paper describes the design and operation of power conditioning system with maximum power transfer tracking (MPTT) for low-power electromagnetic energy harvesters. The system is fully autonomous, starts up from zero stored energy, and actively rectifies and boosts the harvester voltage. The powe ...
... This paper describes the design and operation of power conditioning system with maximum power transfer tracking (MPTT) for low-power electromagnetic energy harvesters. The system is fully autonomous, starts up from zero stored energy, and actively rectifies and boosts the harvester voltage. The powe ...
Guass`s Law for magnetism
... An electric field is produced by: • Charged particle (moving or stationary) • Changing magnetic field A magnetic field is produced by: • A curent (moving charge) • Changing electric field ...
... An electric field is produced by: • Charged particle (moving or stationary) • Changing magnetic field A magnetic field is produced by: • A curent (moving charge) • Changing electric field ...
Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic (EM) Waves James Clerk
... • An electric field exerts a force on any charged particle • A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charged particle ...
... • An electric field exerts a force on any charged particle • A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charged particle ...
ENERGY, WAVES, and ELECTRICITY UNIT REVIEW
... 3. Why does acquiring excess static charge (electrons) cause you to “shock” someone if you touch them? 4. How is electricity produced in power plants (give three examples)? 5. What is the difference between voltage, resistance and current in an electric system? How do they relate to each other and t ...
... 3. Why does acquiring excess static charge (electrons) cause you to “shock” someone if you touch them? 4. How is electricity produced in power plants (give three examples)? 5. What is the difference between voltage, resistance and current in an electric system? How do they relate to each other and t ...
An antenna is a transducer designed to transmit or receive radio
... and negligible energy radiated in other directions. An antenna array is two or more antennas coupled to a common source or load to produce a specific directional radiation pattern. The spatial relationship between individual antennas contributes to the directivity of the antenna. The term active ele ...
... and negligible energy radiated in other directions. An antenna array is two or more antennas coupled to a common source or load to produce a specific directional radiation pattern. The spatial relationship between individual antennas contributes to the directivity of the antenna. The term active ele ...
electricity and magnet vocab
... circuit– path along which electric current flows; it has 4 parts: power source (battery), connectors (wires), a switch and the load (lamp, computer, etc..) closed circuit – a complete, unbroken circuit (this enables the light to turn on) open circuit - a circuit that has a break or opening; electric ...
... circuit– path along which electric current flows; it has 4 parts: power source (battery), connectors (wires), a switch and the load (lamp, computer, etc..) closed circuit – a complete, unbroken circuit (this enables the light to turn on) open circuit - a circuit that has a break or opening; electric ...
Reduction of crosstalk on printed circuit board using genetic
... This fitness function can be calculated very quickly and provides quick online iteration with different chromosomes. The best solution can be obtained with maximum fitness and lowest coupling index. New chromosomes can be spawned by many reproduction methods [14]. The tournament method of selection ...
... This fitness function can be calculated very quickly and provides quick online iteration with different chromosomes. The best solution can be obtained with maximum fitness and lowest coupling index. New chromosomes can be spawned by many reproduction methods [14]. The tournament method of selection ...
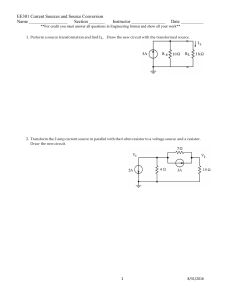
EE301 Current Sources and Source Conversion Name
... 3. Transform the voltage source to a current source. Draw the new circuit. Simplify the circuit to a minimum number of components and find the total current. ...
... 3. Transform the voltage source to a current source. Draw the new circuit. Simplify the circuit to a minimum number of components and find the total current. ...
PHYSICS - KEE 2016 Electrostatics
... Ohm’s law – Electrical resistance – V-I chraracteristics – Electrical resistivity and conductivity – Classification of materials in terms of conductivity – Superconductivity – Elementary ideas – Carbon resistors – Colour code for carbon resistors – Combination of resistors – Series and parallel – Te ...
... Ohm’s law – Electrical resistance – V-I chraracteristics – Electrical resistivity and conductivity – Classification of materials in terms of conductivity – Superconductivity – Elementary ideas – Carbon resistors – Colour code for carbon resistors – Combination of resistors – Series and parallel – Te ...
Electromagnetic compatibility

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical sciences which studies the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy with reference to the unwanted effects (electromagnetic interference, or EMI) that such energy may induce. The goal of EMC is the correct operation, in the same electromagnetic environment, of different equipment which use electromagnetic phenomena, and the avoidance of any interference effects.In order to achieve this, EMC pursues two different kinds of issues. Emission issues are related to the unwanted generation of electromagnetic energy by some source, and to the countermeasures which should be taken in order to reduce such generation and to avoid the escape of any remaining energies into the external environment. Susceptibility or immunity issues, in contrast, refer to the correct operation of electrical equipment, referred to as the victim, in the presence of unplanned electromagnetic disturbances.Interference mitigation and hence electromagnetic compatibility is achieved by addressing both emission and susceptibility issues, i.e., quieting the sources of interference and hardening the potential victims. The coupling path between source and victim may also be separately addressed to increase its attenuation.