relativistically intense plane electromagnetic waves in cold
... unmagnetized locally non-neutral electron-positron plasmas. One of these regimes is that of the nonlinear self-modulation – it occurs when the plasma longitudinal field potential magnitude is below the critical level, which corresponds exactly to the relativistic field strength. The other one is the ...
... unmagnetized locally non-neutral electron-positron plasmas. One of these regimes is that of the nonlinear self-modulation – it occurs when the plasma longitudinal field potential magnitude is below the critical level, which corresponds exactly to the relativistic field strength. The other one is the ...
Super low loss transformers
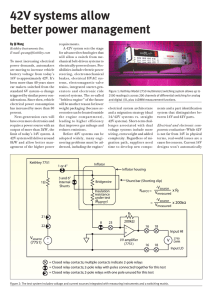
... Most electrical equipment is designed to operate within a voltage range of 220V - 240V. As the average voltage in the UK is around 242V, this means that many items of electrical equipment are operated at a higher voltage than is ...
... Most electrical equipment is designed to operate within a voltage range of 220V - 240V. As the average voltage in the UK is around 242V, this means that many items of electrical equipment are operated at a higher voltage than is ...
Exercises
... 6. Explain why producing voltage by pushing a magnet through a wire loop doesn’t violate the law of conservation of energy. ...
... 6. Explain why producing voltage by pushing a magnet through a wire loop doesn’t violate the law of conservation of energy. ...
1 Introduction
... power transmission. In these cases there is usually no signal modulation and the electromagnetic wave interacts directly with solid or liquid materials. Radio frequency (RF) is a term that refers to a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be easily generated using an alternating current ( ...
... power transmission. In these cases there is usually no signal modulation and the electromagnetic wave interacts directly with solid or liquid materials. Radio frequency (RF) is a term that refers to a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be easily generated using an alternating current ( ...
Read Me First: Safety and Radio
... measurements on hard-wired equipment such as equipment in fixed installations, distribution boards, and circuit breakers. Other examples are wiring, including cables, bus bars, junction boxes, switches, socket outlets in the fixed installation, and stationary motors with permanent connections to fix ...
... measurements on hard-wired equipment such as equipment in fixed installations, distribution boards, and circuit breakers. Other examples are wiring, including cables, bus bars, junction boxes, switches, socket outlets in the fixed installation, and stationary motors with permanent connections to fix ...
Coupling Fields - Iowa State University
... two conductors, #1 is on the stator; #2 is on the rotor. The magnetic system is assumed linear. So Wf is given by (with J=2): ...
... two conductors, #1 is on the stator; #2 is on the rotor. The magnetic system is assumed linear. So Wf is given by (with J=2): ...
• Maxwell`s equations and electromagnetic waves • sinusoidal
... ∴Ba = µ0ε 0 Eac Ba = µ0ε 0 (cB)ac ...
... ∴Ba = µ0ε 0 Eac Ba = µ0ε 0 (cB)ac ...
NON-INVASIVE RADIO-FREQUENCY FOR EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF
... ultrasound, 0.73, 0.69 and 0.48 respectively. Discussion: The results of this study confirm the possibility of electromagnetic exclusion of cancer. When the device response is negative it means that further invasive investigations are not necessary (NPV > 98%). On the contrary when the response is p ...
... ultrasound, 0.73, 0.69 and 0.48 respectively. Discussion: The results of this study confirm the possibility of electromagnetic exclusion of cancer. When the device response is negative it means that further invasive investigations are not necessary (NPV > 98%). On the contrary when the response is p ...
CHAPTER 2: Special Theory of Relativity
... approaches a receiver and a decreased frequency as the source recedes. Christian Andreas Doppler ...
... approaches a receiver and a decreased frequency as the source recedes. Christian Andreas Doppler ...
Chapter 4
... DC = flows in only ONE direction AC= flows both directions (positive and negative – NOT polarity) and posses magnetic properties Power = Measured in WATTS (W) P=IR V. Magnetism and why it’s important in electricity (AC current only!) - ANY charged particle in motion creates a magnetic field - The ma ...
... DC = flows in only ONE direction AC= flows both directions (positive and negative – NOT polarity) and posses magnetic properties Power = Measured in WATTS (W) P=IR V. Magnetism and why it’s important in electricity (AC current only!) - ANY charged particle in motion creates a magnetic field - The ma ...
EMI EMC Considerations for Energy Meters Application Note
... interference. These noise signals travel over air and no physical contact is made between the noise source and the victim, instead these noise signals behave as electromagnetic waves and couple with the signals on the system’s PCB. This noise signal is present in the frequency band of 30 MHz to 1000 ...
... interference. These noise signals travel over air and no physical contact is made between the noise source and the victim, instead these noise signals behave as electromagnetic waves and couple with the signals on the system’s PCB. This noise signal is present in the frequency band of 30 MHz to 1000 ...
Electric Potential
... generated by moving a conductor through a magnetic field or a magnetic field through a conductor. Electromotive Force: When a wire moves through a magnetic field, a force is exerted on these charges causing them to flow as current. Magnetic Flux: The strength of a magnetic field is determined by the ...
... generated by moving a conductor through a magnetic field or a magnetic field through a conductor. Electromotive Force: When a wire moves through a magnetic field, a force is exerted on these charges causing them to flow as current. Magnetic Flux: The strength of a magnetic field is determined by the ...
Faraday`s Law of Electromagnetic Induction - UTK-EECS
... Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction 1. If the flux linking a loop (or turn) varies as a function of time, a voltage is induced between its terminals. 2. The value of the induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux The “-” sign indicates that the inducted E has a tendency to ...
... Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction 1. If the flux linking a loop (or turn) varies as a function of time, a voltage is induced between its terminals. 2. The value of the induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux The “-” sign indicates that the inducted E has a tendency to ...
PSURGE 30.2 3OkV SURGE TEST SYSTEM ONE SOLUTION
... Energy surges are generated by atmospheric lightning discharge and switching in power circuits. A surge is characterised by high energy fast rise time impulses. Pulse durations are widely variable as are the coupling paths. ...
... Energy surges are generated by atmospheric lightning discharge and switching in power circuits. A surge is characterised by high energy fast rise time impulses. Pulse durations are widely variable as are the coupling paths. ...
SDC-2010 ANOTHER ENERGY CONSERVATION PRODUCT
... A high tech efficient car power adapter built to provide stable clean DC power for the voltage sensitive electronic digital equipment with minimal strain on the car's electrical power source. ...
... A high tech efficient car power adapter built to provide stable clean DC power for the voltage sensitive electronic digital equipment with minimal strain on the car's electrical power source. ...
Electromagnetic compatibility

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical sciences which studies the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy with reference to the unwanted effects (electromagnetic interference, or EMI) that such energy may induce. The goal of EMC is the correct operation, in the same electromagnetic environment, of different equipment which use electromagnetic phenomena, and the avoidance of any interference effects.In order to achieve this, EMC pursues two different kinds of issues. Emission issues are related to the unwanted generation of electromagnetic energy by some source, and to the countermeasures which should be taken in order to reduce such generation and to avoid the escape of any remaining energies into the external environment. Susceptibility or immunity issues, in contrast, refer to the correct operation of electrical equipment, referred to as the victim, in the presence of unplanned electromagnetic disturbances.Interference mitigation and hence electromagnetic compatibility is achieved by addressing both emission and susceptibility issues, i.e., quieting the sources of interference and hardening the potential victims. The coupling path between source and victim may also be separately addressed to increase its attenuation.