ORIGIN OF ELECTRONICS
... between the fields has become less sharp with technical progress. For example, in the high voltage transmission of electric power, large arrays of electronic devices are used to convert transmissionline current at power levels in the tens of megawatts. Moreover, in the regulation and control of inte ...
... between the fields has become less sharp with technical progress. For example, in the high voltage transmission of electric power, large arrays of electronic devices are used to convert transmissionline current at power levels in the tens of megawatts. Moreover, in the regulation and control of inte ...
No Slide Title
... ES demo 7-3. Transformer operation using two AC voltmeters and an oscilloscope. BE demo 1-4 ...
... ES demo 7-3. Transformer operation using two AC voltmeters and an oscilloscope. BE demo 1-4 ...
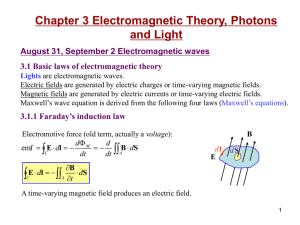
Electromagnetic Induction
... Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating electric current with a magnetic field. It occurs whenever a magnetic field and an electric conductor, such as a coil of wire, move relative to one another. As long as the conductor is part of a closed circuit, current will flow through it whene ...
... Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating electric current with a magnetic field. It occurs whenever a magnetic field and an electric conductor, such as a coil of wire, move relative to one another. As long as the conductor is part of a closed circuit, current will flow through it whene ...
Active course file - College of DuPage
... Course description to appear in catalog: Algebra-based study of electrostatics, electric fields, Gauss' law, capacitance, current, resistance, magnetic forces and fields, electromagnetic induction, DC and AC circuits, electromagnetic waves, mirrors, lenses, optics, and modern physics. Repeatable for ...
... Course description to appear in catalog: Algebra-based study of electrostatics, electric fields, Gauss' law, capacitance, current, resistance, magnetic forces and fields, electromagnetic induction, DC and AC circuits, electromagnetic waves, mirrors, lenses, optics, and modern physics. Repeatable for ...
- IEEE Projects IN MADURAI
... introducing diode-assisted capacitor network. With parallel capacitive charging and series capacitive discharging, the new topology extends voltage regulation range and avoids extreme duty ratio of switching devices in the front boost circuit. As for the unique structure, various novel pulse-width m ...
... introducing diode-assisted capacitor network. With parallel capacitive charging and series capacitive discharging, the new topology extends voltage regulation range and avoids extreme duty ratio of switching devices in the front boost circuit. As for the unique structure, various novel pulse-width m ...
CE Mark #8002 - Cooper Bussmann
... machinery operators and non-operators in the surrounding area. A machine is defined as an assembly of linked parts or components, at least one of which moves, with the appropriate machine actuator, control, and power circuits, etc., joined together for a specific application, in particular for the p ...
... machinery operators and non-operators in the surrounding area. A machine is defined as an assembly of linked parts or components, at least one of which moves, with the appropriate machine actuator, control, and power circuits, etc., joined together for a specific application, in particular for the p ...
Emagnetism - WordPress.com
... deflected by an electric current in a nearby wire. In 1831, MICHAEL FARADAY showed that a changing magnetic field can induce a current in a circuit. In 1860, JAMES CLERK MAXWELL predicted that a changing electric field has an associated magnetic field and wrote the mathematical equations that descri ...
... deflected by an electric current in a nearby wire. In 1831, MICHAEL FARADAY showed that a changing magnetic field can induce a current in a circuit. In 1860, JAMES CLERK MAXWELL predicted that a changing electric field has an associated magnetic field and wrote the mathematical equations that descri ...
Lesson 7
... Never lose awareness of the overhead hazard and location of the machine/machine parts. If work is conducted near an electrical transmission line, a person should be assigned by the employer to signal and warn the machine operator if any machine part comes within 3 meters (10 feet) of the power lin ...
... Never lose awareness of the overhead hazard and location of the machine/machine parts. If work is conducted near an electrical transmission line, a person should be assigned by the employer to signal and warn the machine operator if any machine part comes within 3 meters (10 feet) of the power lin ...
KGA – AC Interference
... Placed below the pipeline Depending on soil resistance Place in the lowest resistance area Minimum Two feet away from the pipeline Make connection to the pipeline in a junction box or test station Commonly used, a minimum of a no. 4 gauge wire connected to the pipeline and zinc ribbon May ne ...
... Placed below the pipeline Depending on soil resistance Place in the lowest resistance area Minimum Two feet away from the pipeline Make connection to the pipeline in a junction box or test station Commonly used, a minimum of a no. 4 gauge wire connected to the pipeline and zinc ribbon May ne ...
AVR040: EMC Design Considerations
... one shown in the figure ESD Test Generator, a few pulse-shaping components are added, but the basic principle is the same. See IEC 1000-4-5 for details of this test setup. The surge test is performed only on power supply lines, so this is typically a power supply design issue. However, note that if ...
... one shown in the figure ESD Test Generator, a few pulse-shaping components are added, but the basic principle is the same. See IEC 1000-4-5 for details of this test setup. The surge test is performed only on power supply lines, so this is typically a power supply design issue. However, note that if ...
Syllabus for Physics
... infinitely long current carrying straight wire and circular coil – Tangent galvanometer – Construction and working – Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid – magnetic field lines. Ampere’s circuital law and its application. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic field and electric field – cyclot ...
... infinitely long current carrying straight wire and circular coil – Tangent galvanometer – Construction and working – Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid – magnetic field lines. Ampere’s circuital law and its application. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic field and electric field – cyclot ...
A Simple Computational Electromagnetic Analysis Example
... battery power is disabled through software means which de-activatesseveral solid state powering switches (some of which are shown in Figure 1). Lacking battery power (or the means to activate such power) there is only one more source that could provide the needed Vgs=4V ---electromagnetic field coup ...
... battery power is disabled through software means which de-activatesseveral solid state powering switches (some of which are shown in Figure 1). Lacking battery power (or the means to activate such power) there is only one more source that could provide the needed Vgs=4V ---electromagnetic field coup ...
Electromagnetic compatibility

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical sciences which studies the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy with reference to the unwanted effects (electromagnetic interference, or EMI) that such energy may induce. The goal of EMC is the correct operation, in the same electromagnetic environment, of different equipment which use electromagnetic phenomena, and the avoidance of any interference effects.In order to achieve this, EMC pursues two different kinds of issues. Emission issues are related to the unwanted generation of electromagnetic energy by some source, and to the countermeasures which should be taken in order to reduce such generation and to avoid the escape of any remaining energies into the external environment. Susceptibility or immunity issues, in contrast, refer to the correct operation of electrical equipment, referred to as the victim, in the presence of unplanned electromagnetic disturbances.Interference mitigation and hence electromagnetic compatibility is achieved by addressing both emission and susceptibility issues, i.e., quieting the sources of interference and hardening the potential victims. The coupling path between source and victim may also be separately addressed to increase its attenuation.