Resilience in Youth with type 1 diabetes following an earthquake
... setting where a disaster is less anticipated. Another limitation was the low questionnaire response rate, of 23 percent. Responses are likely to have been subject to individual biases, although it is difficult to know in which direction such biases were operating, towards over-reporting or under-rep ...
... setting where a disaster is less anticipated. Another limitation was the low questionnaire response rate, of 23 percent. Responses are likely to have been subject to individual biases, although it is difficult to know in which direction such biases were operating, towards over-reporting or under-rep ...
Neotectonics guide - San Francisco State University
... 3. How do various factors affect the depth to the BPT and strength envelopes in general? At about what depth is the BPT in CA and NV, and how do we know? Qtz and feldspar rich rocks in continental crust at depth of 13–18 km. CA & NV: western plate boundary, high geothermal gradient, basement of seis ...
... 3. How do various factors affect the depth to the BPT and strength envelopes in general? At about what depth is the BPT in CA and NV, and how do we know? Qtz and feldspar rich rocks in continental crust at depth of 13–18 km. CA & NV: western plate boundary, high geothermal gradient, basement of seis ...
attachment 7: discussion of mce and obe - Susitna
... FERC guidelines only establish the requirements for a seismic hazard analysis for a project, but do not give guidance as to the selected ground motions. Until recently, FERC guidelines are based on a deterministic approach in which the maximum magnitude is estimated for each known seismic source. Th ...
... FERC guidelines only establish the requirements for a seismic hazard analysis for a project, but do not give guidance as to the selected ground motions. Until recently, FERC guidelines are based on a deterministic approach in which the maximum magnitude is estimated for each known seismic source. Th ...
On the earthquake predictability of fault interaction models
... Since early 1990s, the space-time earthquake clustering has been mostly explained by fault interaction [Stein et al., 1992; King et al., 1994]. When an earthquake occurs, the state of stress in the Earth is altered as a consequence of the seismic dislocation. The change in the stress field can be pre ...
... Since early 1990s, the space-time earthquake clustering has been mostly explained by fault interaction [Stein et al., 1992; King et al., 1994]. When an earthquake occurs, the state of stress in the Earth is altered as a consequence of the seismic dislocation. The change in the stress field can be pre ...
the el salvador earthquakes of 2001: implication for seismic risk from
... the zonation map simply divides El Salvador into a southern and a northern zone, the former containing the volcanic chain and the coast and being of greater hazard [12]. It is interesting to note that the first seismic code was introduced after the 1965 San Salvador earthquake and was essentially a ...
... the zonation map simply divides El Salvador into a southern and a northern zone, the former containing the volcanic chain and the coast and being of greater hazard [12]. It is interesting to note that the first seismic code was introduced after the 1965 San Salvador earthquake and was essentially a ...
Seismological evidence of simultaneous mountain-building and crust-thickening 7.6)
... of the Chi-Chi earthquake. The fault plane for the main shock was gently dipping to the east (Chang, 2000; Chen et al., 2001b; Wang et al., 2002; Johnson et al., 2001; Ma et al., 2001). In contrast, a clear seismic zone in the lower crust dipping to the west was shown at Fig. 2(b). Although the foca ...
... of the Chi-Chi earthquake. The fault plane for the main shock was gently dipping to the east (Chang, 2000; Chen et al., 2001b; Wang et al., 2002; Johnson et al., 2001; Ma et al., 2001). In contrast, a clear seismic zone in the lower crust dipping to the west was shown at Fig. 2(b). Although the foca ...
UGRC 144_Session 3
... • The science of earthquakes is seismology, "study of shaking" in scientific Greek. Earthquake energy comes from the stresses of plate tectonics. • As plates move, the rocks on their edges deform and take up strain until the weakest point, a fault, ruptures and releases the strain. • The occurrence ...
... • The science of earthquakes is seismology, "study of shaking" in scientific Greek. Earthquake energy comes from the stresses of plate tectonics. • As plates move, the rocks on their edges deform and take up strain until the weakest point, a fault, ruptures and releases the strain. • The occurrence ...
Concurrent density dependence and independence in
... high (Fig. 3a). At the time of the shallow intrusion, the rift opened about 2 m (refs 11, 15, 21), an eruptive ®ssure formed (Fig. 1), and seismicity within this region of the south ¯ank immediately increased by more than a factor of ten (Fig. 2a). The intrusion also resulted in changes in the patte ...
... high (Fig. 3a). At the time of the shallow intrusion, the rift opened about 2 m (refs 11, 15, 21), an eruptive ®ssure formed (Fig. 1), and seismicity within this region of the south ¯ank immediately increased by more than a factor of ten (Fig. 2a). The intrusion also resulted in changes in the patte ...
Nature of Earthquakes - Elements of Seismology and Earthquake
... • Unpredictable natural phenomenon of vibration of the ground • It becomes one of the most devastating natural hazard only if it’s ...
... • Unpredictable natural phenomenon of vibration of the ground • It becomes one of the most devastating natural hazard only if it’s ...
Plate-wide deformation before the Sumatra
... SWS time-delays in Band-1 directions within the shear-wave window are sensitive to aspectratios (CRAMPIN 1999). Band-1 directions are the solid angle subtending 15º-to-45º to the vertical crack plane. Time-delays in Band-2 directions, ±(0º-to-15º) to the crack plane, are sensitive to crack density b ...
... SWS time-delays in Band-1 directions within the shear-wave window are sensitive to aspectratios (CRAMPIN 1999). Band-1 directions are the solid angle subtending 15º-to-45º to the vertical crack plane. Time-delays in Band-2 directions, ±(0º-to-15º) to the crack plane, are sensitive to crack density b ...
Earthquake Prone Building Policy
... severe damage to buildings caused by a rupture of the Alpine Fault or several other potentially active faults throughout Otago such as the Dunstan Fault. An estimated magnitude of 8 on the Modified Mercalli scale could result from a rupture of the Alpine Fault. The recurrence interval for earthquake ...
... severe damage to buildings caused by a rupture of the Alpine Fault or several other potentially active faults throughout Otago such as the Dunstan Fault. An estimated magnitude of 8 on the Modified Mercalli scale could result from a rupture of the Alpine Fault. The recurrence interval for earthquake ...
Advances in Natural and Applied Sciences
... volcanic eruptions, landslides and avalanches. (Solano and Scaruzzo, 2013). The earthquake is known as the most common natural disaster, because many earthquakes are registered with different dimensions during decades which caused many damages. Due to the earthquakes registered, the rate of mortalit ...
... volcanic eruptions, landslides and avalanches. (Solano and Scaruzzo, 2013). The earthquake is known as the most common natural disaster, because many earthquakes are registered with different dimensions during decades which caused many damages. Due to the earthquakes registered, the rate of mortalit ...
Introduction to Earthquakes
... Earthquake Intensity and Magnitude The severity of an earthquake is expressed in terms of the intensity and magnitude. The intensity is based on the observed effects of the earthquake — it is an assessment of the damage caused by an earthquake at a specific location. Thus the intensity of an earthq ...
... Earthquake Intensity and Magnitude The severity of an earthquake is expressed in terms of the intensity and magnitude. The intensity is based on the observed effects of the earthquake — it is an assessment of the damage caused by an earthquake at a specific location. Thus the intensity of an earthq ...
Earthquake-induced thermal anomalies at active volcanoes
... earthquake (Indonesia, MW = 9.3) earthquake, a megathrust event that involved an ~1000-km-long fault segment. Following this event, the heat flux generated by global volcanic activity, which was already at relatively high level since April 2004, underwent a 300% increase (Fig. 1B). The response pers ...
... earthquake (Indonesia, MW = 9.3) earthquake, a megathrust event that involved an ~1000-km-long fault segment. Following this event, the heat flux generated by global volcanic activity, which was already at relatively high level since April 2004, underwent a 300% increase (Fig. 1B). The response pers ...
Earthquakes, Plate Boundaries, and Depth Indiana Standard
... tool, the “Jules Verne Voyager, Jr.” to correlate and assess the location of earthquakes and plate boundaries, the age of the ocean and continental crust and the depth of earthquakes, and types of plate boundaries where earthquakes occur. Description of activity: Students will use downloaded data se ...
... tool, the “Jules Verne Voyager, Jr.” to correlate and assess the location of earthquakes and plate boundaries, the age of the ocean and continental crust and the depth of earthquakes, and types of plate boundaries where earthquakes occur. Description of activity: Students will use downloaded data se ...
Chapter 5 Earthquakes - Sandpoint Middle
... – Liquefaction factors: occurs when the violent shaking turns loose, soft soil into a thick mud, causing buildings to sink and underground tanks to float to the surface. Triggers landslides. – Aftershocks: smaller earthquakes that follow the first one (hours, days, or even months later) – Tsunamis: ...
... – Liquefaction factors: occurs when the violent shaking turns loose, soft soil into a thick mud, causing buildings to sink and underground tanks to float to the surface. Triggers landslides. – Aftershocks: smaller earthquakes that follow the first one (hours, days, or even months later) – Tsunamis: ...
Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin 31
... of similar magnitude located within a small area. The magnitude of the largest earthquakes in a swarm is typically less than 4 (Ma & Eaton 2009). Swarm activity is distinctly different from the more common mainshock–aftershock activity, which is characterised by one large earthquake (mainshock) foll ...
... of similar magnitude located within a small area. The magnitude of the largest earthquakes in a swarm is typically less than 4 (Ma & Eaton 2009). Swarm activity is distinctly different from the more common mainshock–aftershock activity, which is characterised by one large earthquake (mainshock) foll ...
MS Earthquakes Worksheets
... The earliest earthquake scale was the Mercalli scale. This scale measures earthquake intensity. There are several problems with the Mercalli scale. The damage from an earthquake is affected by many things in addition to the energy released during the quake. Also, different people may experience an e ...
... The earliest earthquake scale was the Mercalli scale. This scale measures earthquake intensity. There are several problems with the Mercalli scale. The damage from an earthquake is affected by many things in addition to the energy released during the quake. Also, different people may experience an e ...
A SITE AMPLIFICATION STUDY USING OBSERVED RECORDS AT
... Nakamura method is that Hb/Vb is unity or two and Vs/Vb is unity. Hb/Vb of microtremor becomes roughly unity perhaps because of surface waves’ dominance, whereas that of earthquake motions becomes a little bit larger and complicated perhaps because of mixture of body waves. Vertical transfer functio ...
... Nakamura method is that Hb/Vb is unity or two and Vs/Vb is unity. Hb/Vb of microtremor becomes roughly unity perhaps because of surface waves’ dominance, whereas that of earthquake motions becomes a little bit larger and complicated perhaps because of mixture of body waves. Vertical transfer functio ...
4 - Earthquakes
... motion and a side-‐to-‐side vibration. ! During an earthquake, Earth’s surface rolls like ocean waves and writhes from side to side like a snake ...
... motion and a side-‐to-‐side vibration. ! During an earthquake, Earth’s surface rolls like ocean waves and writhes from side to side like a snake ...
Literature review of health impact post-earthquakes
... were described in China from 1906 to 2007. Earthquakes regularly rattle the vast Tibetan plateau, including Tibet and the far west region of Xinjiang and Qinghai provinces. They are also common in southwest Yunnan province. Earthquakes are relatively rare in central China and along the eastern seabo ...
... were described in China from 1906 to 2007. Earthquakes regularly rattle the vast Tibetan plateau, including Tibet and the far west region of Xinjiang and Qinghai provinces. They are also common in southwest Yunnan province. Earthquakes are relatively rare in central China and along the eastern seabo ...
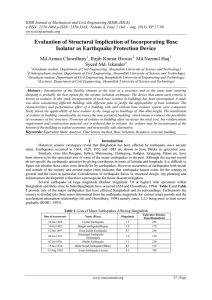
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X,
... do not specify the earthquake epicenter by giving coordinates in terms of latitude and longitude. It is difficult to figure out whether these cities were directly hit by earthquakes. However occurrence of earthquakes both inside and outside of the country and around major cities indicates that earth ...
... do not specify the earthquake epicenter by giving coordinates in terms of latitude and longitude. It is difficult to figure out whether these cities were directly hit by earthquakes. However occurrence of earthquakes both inside and outside of the country and around major cities indicates that earth ...
Earthquake Disaster Simulation in Immersive 3D Environment
... dimensions. This selection depends upon immersive 3D system capabilities. A system which has projection system all around can very effectively produce the room effect. On the other hand if system is not fully immersive and is to be viewed by many people at the same time, it is more useful to show ou ...
... dimensions. This selection depends upon immersive 3D system capabilities. A system which has projection system all around can very effectively produce the room effect. On the other hand if system is not fully immersive and is to be viewed by many people at the same time, it is more useful to show ou ...
April 2015 Nepal earthquake

The April 2015 Nepal earthquake (also known as the Gorkha earthquake) killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000. It occurred at 11:56 NST on 25 April, with a magnitude of 7.8Mw or 8.1Ms and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of IX (Violent). Its epicenter was east of the district of Lamjung, and its hypocenter was at a depth of approximately 8.2 km (5.1 mi). It was the worst natural disaster to strike Nepal since the 1934 Nepal–Bihar earthquake.The earthquake triggered an avalanche on Mount Everest, killing at least 19, making April 25, 2015 the deadliest day on the mountain in history. The earthquake triggered another huge avalanche in the Langtang valley, where 250 people were reported missing.Hundreds of thousands of people were made homeless with entire villages flattened, across many districts of the country. Centuries-old buildings were destroyed at UNESCO World Heritage sites in the Kathmandu Valley, including some at the Kathmandu Durbar Square, the Patan Durbar Square, the Bhaktapur Durbar Square, the Changu Narayan Temple and the Swayambhunath Stupa. Geophysicists and other experts had warned for decades that Nepal was vulnerable to a deadly earthquake, particularly because of its geology, urbanization, and architecture.Continued aftershocks occurred throughout Nepal at the intervals of 15–20 minutes, with one shock reaching a magnitude of 6.7 on 26 April at 12:54:08 NST. The country also had a continued risk of landslides.A major aftershock occurred on 12 May 2015 at 12:51 NST with a moment magnitude (Mw) of 7.3. The epicenter was near the Chinese border between the capital of Kathmandu and Mt. Everest. More than 200 people were killed and more than 2,500 were injured by this aftershock.