Study Guide for Ch
... Who was Sargon? How did he control and maintain his empire? What strategies did he use to conquer the independent city-states of Sumer? Did the Akkadians adopt Sumerian writing and language? Explain. BABYLONIA: Who was Hammurabi? What was the significance of his code of laws? What else d ...
... Who was Sargon? How did he control and maintain his empire? What strategies did he use to conquer the independent city-states of Sumer? Did the Akkadians adopt Sumerian writing and language? Explain. BABYLONIA: Who was Hammurabi? What was the significance of his code of laws? What else d ...
mesopotamia british museum
... 6. Each city had its own god or goddess. What did the god/goddess do for the city? _____________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Where did the gods/goddesses live? ____________________________________ ...
... 6. Each city had its own god or goddess. What did the god/goddess do for the city? _____________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Where did the gods/goddesses live? ____________________________________ ...
mesopotamia and beginning of civilization
... it parted and became four riverheads. 11 The name of the first is Pishon; it is the one which skirts the whole land of Havilah, where there is gold. 12 And the gold of that land is good. Bdellium and the onyx stone are there. 13 The name of the second river is Gihon; it is the one which goes around ...
... it parted and became four riverheads. 11 The name of the first is Pishon; it is the one which skirts the whole land of Havilah, where there is gold. 12 And the gold of that land is good. Bdellium and the onyx stone are there. 13 The name of the second river is Gihon; it is the one which goes around ...
In Mesopotamia, floods deposited silt which made the soil? Fertile
... Ziggurat A system of writing developed be the Sumerians that used wedge-shaped marks made in soft clay is called. cuneiform A person who copies or writes out documents; often a record keeper is called? scribe A long poem that records the deeds of a legendary or real hero is called? epic An Amount th ...
... Ziggurat A system of writing developed be the Sumerians that used wedge-shaped marks made in soft clay is called. cuneiform A person who copies or writes out documents; often a record keeper is called? scribe A long poem that records the deeds of a legendary or real hero is called? epic An Amount th ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Study Guide
... 10. Explain how levees and irrigations systems solved this problem near the Tigris and the Euphrates? ...
... 10. Explain how levees and irrigations systems solved this problem near the Tigris and the Euphrates? ...
Euphrates Rivers
... Sumerians were the first to make important contributions to Mesopotamia Sumer had no central government but was made up of independent city-states Sumerians were polytheistic – believed in many gods Sumerians built ziggurats – temples to honor their gods and goddesses Sumerians developed a system of ...
... Sumerians were the first to make important contributions to Mesopotamia Sumer had no central government but was made up of independent city-states Sumerians were polytheistic – believed in many gods Sumerians built ziggurats – temples to honor their gods and goddesses Sumerians developed a system of ...
Mesopotamia Vocabulary Review
... system in Mesopotamia Know the sequence of events that lead a king to gain power (government flow chart…in order) Know what each king is remembered for Understand Hammurabi’s law (“Eye for and Eye” and how social class impacted punishment) Know your vocabulary terms!! ...
... system in Mesopotamia Know the sequence of events that lead a king to gain power (government flow chart…in order) Know what each king is remembered for Understand Hammurabi’s law (“Eye for and Eye” and how social class impacted punishment) Know your vocabulary terms!! ...
Later Peoples of the Fertile Crescent
... trade, loans, and theft to injury, marriage, and murder. Some of its ideas are still found in laws today. The code was important not only for how thorough it was but also because it was written down for all to see. ...
... trade, loans, and theft to injury, marriage, and murder. Some of its ideas are still found in laws today. The code was important not only for how thorough it was but also because it was written down for all to see. ...
Blank Jeopardy - Troy City Schools
... What was the relationship between trade and the spread of the Phoenician alphabet? ...
... What was the relationship between trade and the spread of the Phoenician alphabet? ...
Mesopotamia – The Sumerians
... the Tigris and Euphrates. This society was built by the ________________________. They lived just north of Sumer, but they were not Sumerians. • In spite of their differences, the Akkadians and the Sumerians lived in peace for many years. •That peace was broken in the 2300s BC when ______________ so ...
... the Tigris and Euphrates. This society was built by the ________________________. They lived just north of Sumer, but they were not Sumerians. • In spite of their differences, the Akkadians and the Sumerians lived in peace for many years. •That peace was broken in the 2300s BC when ______________ so ...
ANCIENT CIVILIZATION UNIT TEST
... A. Ishtar B. Baal C. Marduk D. Nanna 6. Which god was thought to own the city of Ur? A. Namu B. Nanna C. Ishtar D. Baal 7. Which people irrigated their land with canals and is credited with developing the ...
... A. Ishtar B. Baal C. Marduk D. Nanna 6. Which god was thought to own the city of Ur? A. Namu B. Nanna C. Ishtar D. Baal 7. Which people irrigated their land with canals and is credited with developing the ...
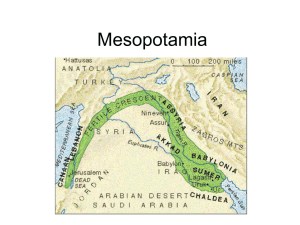
History of Mesopotamia
The history of Mesopotamia describes the history of the area known as Mesopotamia, roughly coinciding with the Tigris–Euphrates basin, from the earliest human occupation in the Lower Palaeolithic period up to the Muslim conquests in the 7th century AD. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often dubbed the cradle of civilization. The rise of the first cities in southern Mesopotamia dates to the Chalcolithic (Uruk period), from c. 5300 BC; its regional independence ended with the Achaemenid conquest in 539 BC, although a few native neo-Assyrian kingdoms existed at different times, namely Adiabene, Osroene and Hatra.