Thermodynamics - myersparkphysics
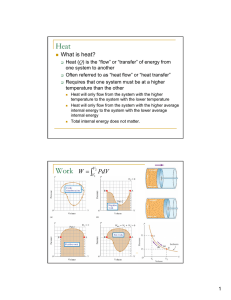
... INCREASES. Both are measured in joules. But when you add heat, there is usually an increase in temperature associated with the change. ...
... INCREASES. Both are measured in joules. But when you add heat, there is usually an increase in temperature associated with the change. ...
Thermodynamics
... INCREASES. Both are measured in joules. But when you add heat, there is usually an increase in temperature associated with the change. ...
... INCREASES. Both are measured in joules. But when you add heat, there is usually an increase in temperature associated with the change. ...
2nd law - WordPress.com
... heat engine E acting together constitute a heat engine operating in cycles and producing net work while exchanging heat only with one body at a single fixed temperature. This violates the Kelvin-Planck statement. ...
... heat engine E acting together constitute a heat engine operating in cycles and producing net work while exchanging heat only with one body at a single fixed temperature. This violates the Kelvin-Planck statement. ...
PHY2216: Tutorial Questions 5 TEMPERATURE 5.1 Temperature
... A piece of copper of mass 120g is heated in an enclosure to a temperature of 1250C. It is then taken out of the enclosure and held in the air for half a minute and dropped carefully into a copper calorimeter of mass 105g containing 200g of water at 200C. The temperature of the water rises to 250C. C ...
... A piece of copper of mass 120g is heated in an enclosure to a temperature of 1250C. It is then taken out of the enclosure and held in the air for half a minute and dropped carefully into a copper calorimeter of mass 105g containing 200g of water at 200C. The temperature of the water rises to 250C. C ...
Heat Work
... cyclic engine that converts thermal energy from a body into an equivalent amount of mechanical work without a further change in its surroundings. ...
... cyclic engine that converts thermal energy from a body into an equivalent amount of mechanical work without a further change in its surroundings. ...
Thermodynamic Characteristics of Solid
... (thermodynamic agent). In reference to a solid this non-determined (or ignored) state limit is determined by the temperature T1 , corresponding with the moment of the occurrence of the specific volume increment. That temperature may be read out of the dilatometric curve (accurately done), on which t ...
... (thermodynamic agent). In reference to a solid this non-determined (or ignored) state limit is determined by the temperature T1 , corresponding with the moment of the occurrence of the specific volume increment. That temperature may be read out of the dilatometric curve (accurately done), on which t ...
Calorimetry Lab
... B. Do you think all the ice melted? Explain. ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ C. Look at the GRAPH. The graph shows two separate stages: the heating of the ice and then the melting of the ice. How much did the water’s temperature ...
... B. Do you think all the ice melted? Explain. ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ C. Look at the GRAPH. The graph shows two separate stages: the heating of the ice and then the melting of the ice. How much did the water’s temperature ...
the latent heat of fusion of ice
... e) Calculate the water equivalent of the calorimeter from equation (4) using the data collected in steps (a) through (d). If the value of the water equivalent is negative, then carefully repeat steps (a) through (d) until a positive value is obtained. f) Empty the calorimeter and fill it until it is ...
... e) Calculate the water equivalent of the calorimeter from equation (4) using the data collected in steps (a) through (d). If the value of the water equivalent is negative, then carefully repeat steps (a) through (d) until a positive value is obtained. f) Empty the calorimeter and fill it until it is ...
INTRODUCTION - WordPress.com
... In the macroscopic approach, as followed in classical thermodynamics, one is concerned with the timeaveraged influence of many molecules that can be perceived by the senses and measured by the instruments. In this approach, the structure of matter is not considered and no attention is focused on t ...
... In the macroscopic approach, as followed in classical thermodynamics, one is concerned with the timeaveraged influence of many molecules that can be perceived by the senses and measured by the instruments. In this approach, the structure of matter is not considered and no attention is focused on t ...
Optimal boiling temperature for ORC installation
... ORC turbine inlet. In this paper presented will be calculations with heating the ORC using the bleed steam. The evaporation temperature of working fluid is optimizing. The condensation temperature has been assumed at the level of 30 o C. In Tab. 1 presented is a short characteristics of considered wo ...
... ORC turbine inlet. In this paper presented will be calculations with heating the ORC using the bleed steam. The evaporation temperature of working fluid is optimizing. The condensation temperature has been assumed at the level of 30 o C. In Tab. 1 presented is a short characteristics of considered wo ...
Energy / Thermodynamics (Heat)
... if movement is unrestricted. 2. Air is not a good conductor, but it is ideal for convection. Hot air rises by convection. 3. Convection currents-streams of hot air (ideal for gliding) or streams of warm water (in the ocean). ...
... if movement is unrestricted. 2. Air is not a good conductor, but it is ideal for convection. Hot air rises by convection. 3. Convection currents-streams of hot air (ideal for gliding) or streams of warm water (in the ocean). ...